In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficiency is the key to success. Whether you’re a small startup or a well-established organization, optimizing your assembly line processes can significantly impact your productivity and bottom line.
This blog aims to provide you with valuable insights, strategies, and practical tips to help you streamline your operations. We will explore various aspects of line assembly, including layout design, workflow management, automation technologies, Line assembly balancing and quality control. Join us as we delve into the world of efficient assembly lines and discover how you can enhance your business’s productivity and competitiveness.

What Is Line Assembly in Manufacturing?
Line assembly in manufacturing refers to a production process where a series of interconnected workstations are arranged linearly, enabling the sequential and efficient assembly of products. This method is commonly used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. For instance, many modern factories utilize a robot assembly line to achieve higher precision and efficiency. Here are the top six features of line assembly:
1. Sequential Flow:
Line assembly ensures that each workstation in the production line performs a specific task in a predetermined order. This allows for a streamlined and efficient flow of materials and components, minimizing unnecessary movements or delays.
2. Specialization:
Each workstation in the assembly line is dedicated to a specific task or set of tasks. This division of labor allows workers to specialize in their assigned tasks, leading to increased productivity and expertise.
3. Standardization:
Line assembly promotes standardization by implementing consistent procedures and work instructions at each workstation. This ensures uniformity in the assembly process, reduces errors, and improves overall quality control.
4. Interchangeability:
The use of standardized components and modular design facilitates the interchangeability of parts within the assembly line. This flexibility enables efficient reconfiguration or customization of products to meet varying customer demands or specific requirements.
5. High Production Volume:
Line assembly is particularly effective for high-volume production. By optimizing the assembly process and reducing idle time, manufacturers can achieve higher output rates and meet the demands of mass production.
6. Monitoring and Control:
Line assembly often incorporates automated systems and technologies for monitoring and controlling the production process. This includes quality control checks, error detection, and real-time data collection, allowing for prompt identification and resolution of issues, as well as continuous process improvement.
These features collectively contribute to the efficiency, productivity, and quality of the assembly process, making line assembly a widely adopted method in modern manufacturing.
Types of Assembly Lines in Manufacturing
A pcb assembly line is a common example, where electronic components are assembled with high precision and speed. Assembly lines are an integral part of modern manufacturing processes, designed to efficiently produce goods in large quantities. There are several types of assembly lines, each tailored to specific manufacturing needs and product requirements.
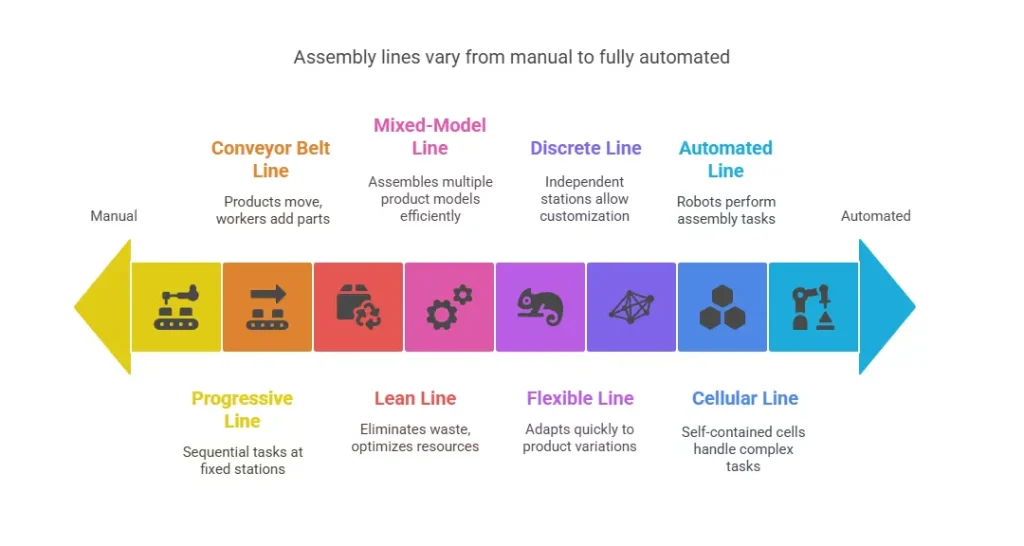
1. Progressive Assembly Line:
This type of line assembly is characterized by a linear flow, where a product moves from one station to the next in a sequential manner. Each station along the line contributes to the assembly process by adding components or performing specific tasks. The product gradually takes shape as it progresses along the line, with workers stationed at each station.
2. Discrete Assembly Line:
In contrast to the linear flow of a progressive assembly line, a discrete assembly line is composed of multiple workstations that function independently. Each workstation focuses on a specific assembly task, and products are moved between workstations as needed. This type of assembly line allows for greater flexibility and customization, as products can be routed to different workstations based on their specific requirements.
3. Cellular Assembly Line:
A cellular line assembly is organized into self-contained workstations, or cells, that are responsible for completing assembly tasks. Each cell operates as a small assembly line within the larger manufacturing process. This type of assembly line is particularly useful for complex products or processes that require specialized expertise or equipment.
4. Flexible Assembly Line:
A flexible assembly line is designed to accommodate a variety of product configurations. It allows for quick changeovers and adjustments to accommodate different product models or variations. This type of assembly line is commonly used in industries where customization or frequent product changes are required, such as automotive manufacturing.
5. Lean Assembly Line:
A lean assembly line focuses on efficiency and waste reduction. It is a line assembly that aims to eliminate non-value-added activities, streamline processes, and optimize resource utilization. Lean principles, such as just-in-time inventory management and continuous improvement, are applied to ensure the smooth flow of materials and minimize waste in the manufacturing process.
6. Automated Assembly Line:
An automated assembly line incorporates advanced robotics and machinery to perform assembly tasks. It minimizes human intervention and relies on automated systems to handle the production process. This type of assembly line is commonly used in industries where precision, speed, and consistency are crucial, such as electronics manufacturing.
7. Conveyor Belt Assembly Line:
In a conveyor belt line assembly, products are transported along a continuous belt system that moves at a controlled speed. Workers stationed along the line perform specific assembly tasks as the products pass by them. This type of assembly line is efficient for high-volume production and is often used in industries like food processing, packaging, and material handling.
8. Mixed-Model Assembly Line:
A mixed-model assembly line is designed to produce multiple product models or variants on the same line. It allows for the efficient assembly of different products with minimal changeover time. The line is organized to accommodate the specific assembly requirements of each product model, ensuring a smooth flow of materials and components. This type of assembly line is commonly found in industries such as consumer electronics, appliances, and automotive manufacturing.
These are just a few examples of the various types of assembly lines in manufacturing. The choice of assembly line type depends on factors such as the product being manufactured, production volume, required flexibility, and efficiency goals of the manufacturing process.
How Can Line Assembly Streamline Manufacturing Processes?
Optimizing your assembly line production involves careful product design, streamlined workflow, and effective quality control. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how line assembly can streamline manufacturing business processes.
1. Product Design and Planning:
The manufacturing process begins with careful product design and planning. Engineers and designers create detailed specifications and identify the sequence of tasks required to assemble the product.
2. Workstation Setup:
The production line is set up by arranging workstations in a logical order to ensure a smooth flow of materials and components. Each workstation is equipped with the necessary tools and equipment to perform specific assembly tasks.
3. Division of Labor:
The tasks involved in assembling the product are divided among the workstations based on their expertise and capabilities. Each workstation focuses on a specific aspect of the assembly process, which allows workers to develop specialized skills and perform their tasks efficiently.
4. Continuous Flow:
The product moves along the assembly line in a continuous flow, guided by conveyors or other means of transportation. This eliminates the need for workers to manually transport the product between workstations, saving time and effort.
5. Standardized Work Processes:
Standardized work processes are established for each workstation, specifying the precise steps to be followed and the time allocated for each task. This ensures consistency and quality in the assembly process, reducing errors and rework.
6. Concurrent Operations:
Different workstations carry out their tasks simultaneously, ensuring that multiple components of the product are being assembled concurrently. This maximizes productivity and minimizes idle time, as each workstation can continue working on the next product while the previous one moves to the next station.
7. Quality Control:
Quality control measures are implemented at various points along the assembly line. Inspections and tests are conducted to identify any defects or issues early in the process, allowing for prompt corrective actions. This helps maintain high product quality and reduces the likelihood of faulty products reaching the end of the line.
8. Efficient Material Handling:
Line assembly incorporates efficient material handling techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) delivery of components and materials. This means that components arrive at the assembly line exactly when they are needed, minimizing inventory holding costs and optimizing production flow.
9. Continuous Improvement:
Line assembly encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Feedback from workers and supervisors is gathered, and regular evaluations are conducted to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for optimization. This iterative process helps streamline the manufacturing process further over time.
10. Increased Efficiency and Cost Reduction:
By implementing line assembly, manufacturing companies can achieve increased efficiency and cost reduction. The streamlined flow, division of labor, standardized processes, and optimized material handling contribute to higher production rates, reduced labor costs, minimized waste, improved product quality, and shorter lead times.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing your assembly line processes is crucial for enhancing efficiency and productivity. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can streamline your operations, reduce costs, and deliver higher-quality products. However, achieving these improvements may require expert guidance. That’s where Qodenext comes in.
Our experienced consultants specialize in process optimization and can tailor solutions to meet your specific needs. Contact us today for a consultation and take the first step towards maximizing your assembly line’s potential. Let’s revolutionize your manufacturing processes together.
FAQs
1. What is line assembly in manufacturing?
Line assembly is a production method where products are assembled step-by-step across a series of workstations. Each station performs a specific task in a defined order, allowing for faster and more efficient mass production.
2. How does line assembly improve manufacturing efficiency?
Line assembly boosts efficiency by minimizing idle time, reducing manual handling, standardizing tasks, and enabling continuous product flow. This leads to faster production rates, consistent quality, and cost savings.
3. What industries use line assembly processes?
Line assembly is widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, appliances, consumer goods, and food processing. Any business involved in large-scale production benefits from streamlined assembly lines.
4. What is the difference between progressive and discrete assembly lines?
A progressive assembly line follows a fixed sequence of tasks where each product passes through the same stations. In contrast, a discrete line consists of independent workstations where products can take different paths based on their specific requirements.
5. How does automation affect line assembly?
Automation reduces reliance on manual labor, enhances precision, speeds up production, and ensures consistency. Automated assembly lines are ideal for industries requiring high-volume and error-free production like electronics and automotive.
6. Can line assembly be used for customized products?
Yes, flexible and mixed-model assembly lines are designed to handle product variations. They allow quick changeovers and can adapt to different models or configurations without halting the entire production.
7. What role does quality control play in line assembly?
Quality control is critical in line assembly. It involves inspecting products at various stages to detect and fix defects early. This maintains product standards and reduces waste or rework.
8. How can Qodenext help with line assembly optimization?
Qodenext offers expert consulting and smart solutions tailored to improve assembly line performance. From layout planning to automation and real-time monitoring tools, Qodenext helps businesses streamline their manufacturing operations and boost productivity.






