Ever find yourself blindsided by customer requests or struggling to meet order demands? The uncertainty of product demand can be overwhelming, adding unnecessary stress and potentially harming your business if not managed effectively. Demand management offers a solution by leveraging historical data and current market trends to forecast, regulate, and prepare for customer demand. By anticipating and addressing customer needs before they arise, this enhances customer satisfaction.
This ensures that buyers receive what they desire without having to explicitly request it. In this guide, we’ll explore the significance of demand management and provide insights on implementing it within your business.
Let’s get right into it!
What is Demand Management?
Demand management encompasses processes aimed at analyzing and controlling consumption levels of goods or services. By conducting demand analysis, optimal consumption patterns can be determined to minimize total costs.
The outcomes of demand management, such as user options and competition, reflect the company’s policy and program interventions that influence demand. Effectively managing demand requires a “closed loop” system, where data from demand plans is continually fed back into the planning process to enhance predictability.
Today, demand variability poses a greater challenge than forecast variance. Demand management serves as a prerequisite for effective supply chain management (SCM). SCM involves a company’s procurement, development, manufacturing, and delivery activities, forming a complex, interconnected system.
Predicting demand becomes increasingly crucial as a company’s supply chain may depend on others. Companies across all departments, including sales, marketing, and logistics, must cultivate reciprocal relationships with suppliers and customers. Finance teams must optimize demand forecasts, while executives need to demonstrate support from the top.
Importance of Demand Management
Understanding customer preferences is vital because demand management not only reveals what products will sell but also aids in devising production plans. Whether you’re in services or manufacturing, it offers several benefits:
- Enhance Customer Satisfaction: Ensure customers receive what they truly desire, not just what you assume they want.
- Alleviate Potential Bottlenecks: Collaborate with procurement teams to ensure they can respond to projected demand effectively.
- Streamline Operations: Utilize strategies to align operations with meeting customer demand sustainably.
- Minimize Costs and Waste: With a clearer understanding of customer needs, adjust pricing and manufacturing processes accordingly to reduce waste and costs.
- Improve efficiency: By forecasting demand, identifying gaps and anticipating potential challenges, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
7 Steps in the Demand Management Process
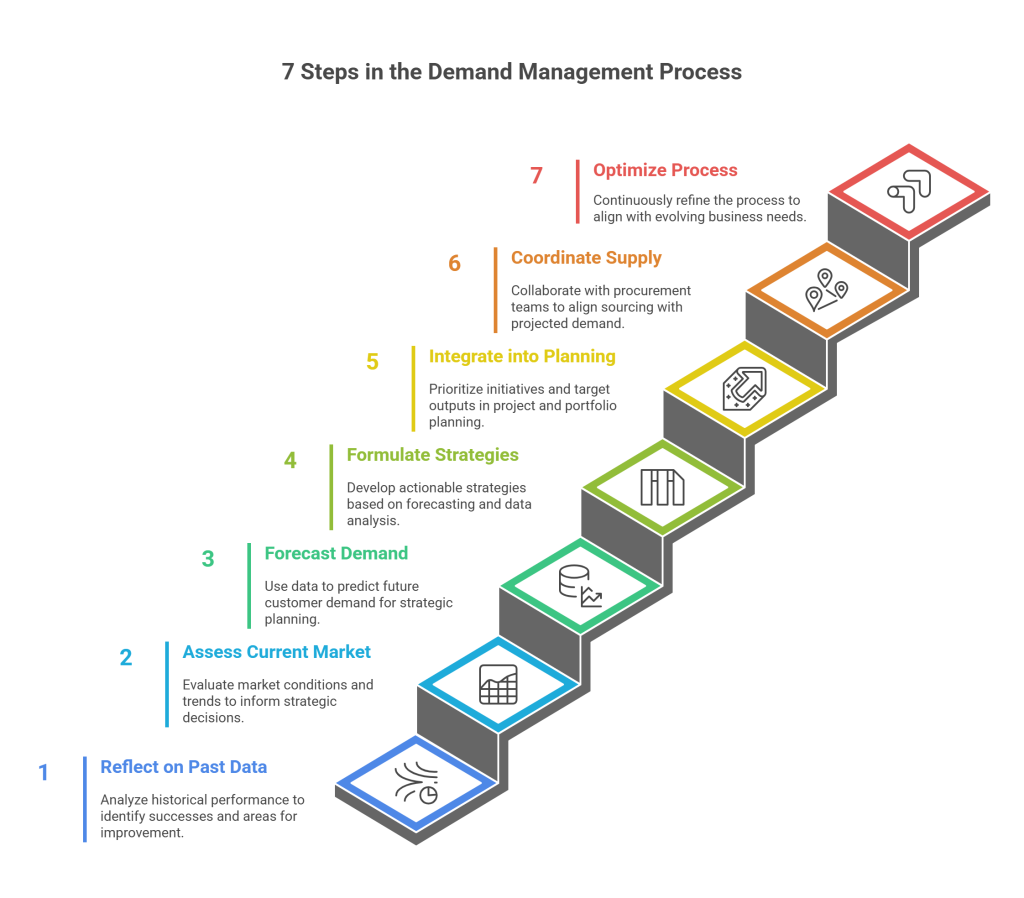
This process aims to grasp market dynamics and the demand chain, then devise an operational strategy tailored to the current market landscape. Once demand strategies are established, project portfolios are crafted, and portfolio management is utilized for execution.
Here’s the process:
1. Reflect on Past Data
Analyze historical performance data to identify successful products/services and understand the circumstances contributing to their success. Similarly, pinpoint areas for improvement or products/services that didn’t meet expectations to refine or discontinue them.
2. Assess the Current Market
Evaluate present market conditions and trends, including competitive advantages and industry benchmarks. Gather and analyze data on competitors and global trends to inform strategic decisions.
3. Forecast Demand
Utilize collected data to forecast upcoming and future customer demand, forming the basis of strategic planning.
4. Formulate Demand Strategies
Develop actionable strategies based on forecasting and data analysis to incorporate into day-to-day operations.
5. Integrate into Business Planning
Utilize insights to prioritize initiatives and target outputs in project and portfolio planning.
6. Coordinate with Supply Planning
Collaborate with procurement teams to ensure sourcing aligns with projected demand, preemptively addressing supply chain challenges.
7. Optimize the Process
Continuously refine this process to align with evolving business needs, ensuring its effectiveness and adaptability.
Types of Activities Within Demand Management
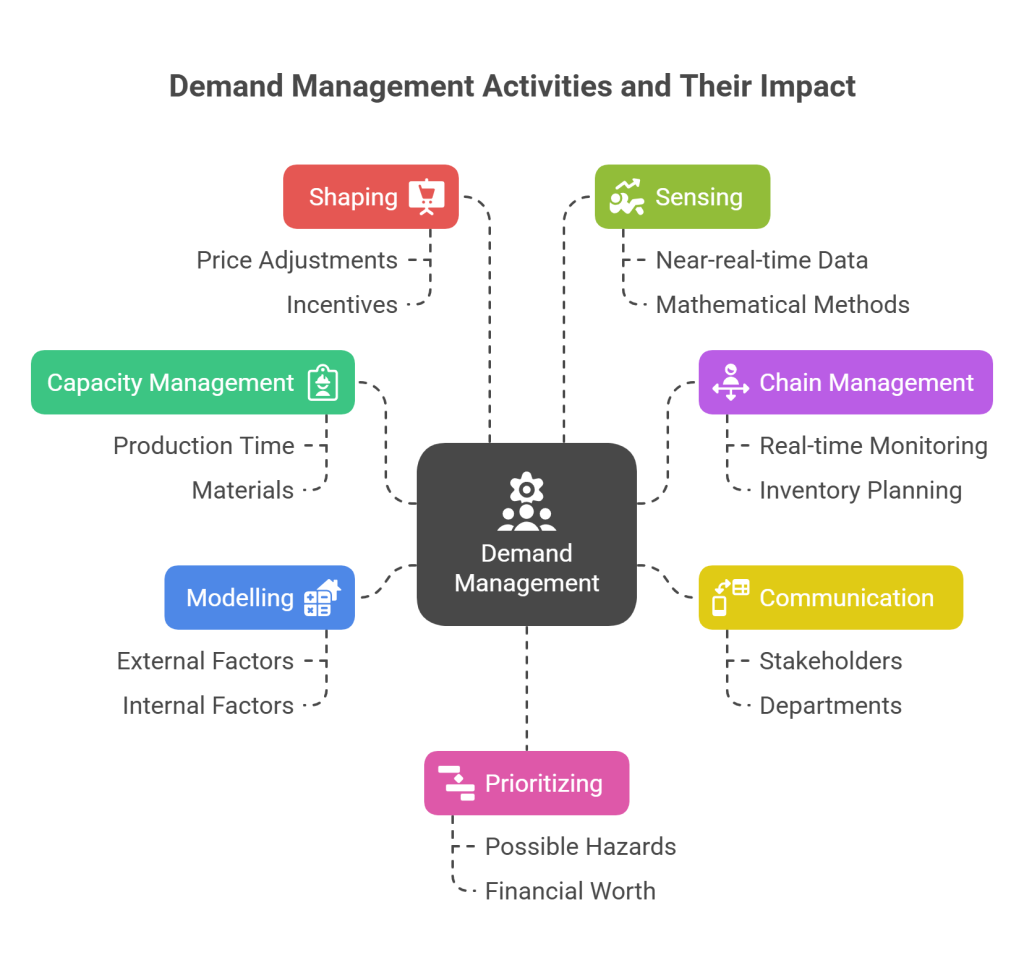
Demand management activities facilitate in-depth strategizing to support a more streamlined supply chain. These activities encompass various elements, including capacity management, chain management, communication, modelling, shaping, sensing, and prioritization.
1. Capacity Management
Demand management assists in organizing capacity requirements, such as production time and materials. Effective capacity planning is crucial as it directly impacts cost centres. Maintaining alignment between demand and supply is essential to mitigate operating costs.
2. Chain Management
The demand chain focuses on acquiring products or services as needed, often referred to as pull. In the online economy, the demand chain-driven e-fulfilment approach accelerates timelines. It relies on real-time event monitoring, inventory planning, and information for forecasting and planning.
3. Communication
In a collaborative demand management system, forecast demand is shared transparently with all stakeholders, departments, and teams impacted. This fosters collaboration towards common objectives.
4. Modelling
Demand modelling entails forecasting demands from the ground up, separating external and internal factors and analyzing the demand stream to understand their influence on purchases.
5. Shaping
Demand shaping involves employing strategies such as price adjustments and incentives to stimulate customer purchases of specific products. It helps align demand for particular products with anticipated production volumes.
6. Sensing
Demand sensing, particularly valuable in high-demand e-commerce scenarios, relies on near-real-time data and mathematical methods to predict market demand fluctuations.
7. Prioritizing
The basis of this management is the identification and prioritization of projects. Critical elements, such as possible hazards, organizational capacity, financial worth, and consequences, can be taken into account while establishing policies.
Demand Forecasting in Operations Management
Demand forecasting involves predicting customer interest in existing products or services, as well as determining necessary adjustments and identifying potential new offerings to stimulate interest.
- Challenges include predicting consumer preferences, quantities, and timing, spanning from specific daily adjustments to broader timeframes.
- Forecasts may align with sales predictions for specific products or focus on generalized product categories.
- Various forecasting techniques are employed, with effectiveness depending on the case or scope.
- Success in demand forecasting requires understanding underlying principles and leveraging data, software, and analytics.
- Accurate forecasts are crucial for strategic decision-making for businesses and their customers.
- Effective forecasters transparently communicate the strengths, assumptions, and limitations of their predictions.
Moreover, effective forecasters not only deliver robust predictions but also transparently communicate the strengths, assumptions, and limitations associated with their forecasts.
Conclusion
Demand management is pivotal in navigating the complexities of today’s market landscape. By leveraging data-driven insights and proactive strategies, businesses can anticipate and fulfil customer demands effectively, enhancing customer satisfaction and optimizing operational efficiency.
Overcoming challenges in demand management requires a holistic approach, integrating advanced forecasting techniques, agile supply chain practices, and collaborative efforts across departments.
As businesses strive to adapt to evolving market dynamics, the role of a demand manager becomes increasingly crucial in orchestrating seamless operations. At Qodenext we offer a variety of solutions to empower businesses.
FAQs: What Is Demand Management? How To Forecast & Manage Demand in 2024
1. What is demand management and why is it important?
Demand management is the process of predicting, planning, and influencing customer demand to align supply chain activities accordingly. It helps businesses improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, avoid bottlenecks, and streamline operations.
2. What are the common challenges faced in demand management?
Challenges include forecast inaccuracies, managing unpredictable demand changes, aligning supply with fluctuating demand, and quickly responding to market dynamics and disruptions.
3. How can businesses overcome demand management challenges?
They can enhance forecasting using advanced analytics and machine learning, adopt agile supply chain strategies, foster collaboration between departments, and use real-time data to detect trends and respond swiftly.
4. What role does a demand manager play in an organization?
A demand manager forecasts customer demand, coordinates with sales, production, and supply teams, optimizes inventory levels, and implements strategies to balance supply and demand effectively.
5. What are the key steps in the demand management process?
The process includes analyzing past data, assessing the current market, forecasting demand, formulating demand strategies, integrating them into business planning, collaborating with supply planning, and continuously optimizing efforts.
6. What are some key activities within demand management?
These include capacity management (planning resources), demand chain management (pull-based replenishment), communication with stakeholders, demand modelling, demand shaping (influencing purchases), demand sensing (real-time prediction), and prioritization.
7. How does demand forecasting help operations management?
Demand forecasting predicts customer interest and purchase timing, aiding in production planning, inventory control, and strategic decision-making to meet market needs while minimizing waste and costs.
8. What is demand shaping and how is it used?
Demand shaping uses strategies like pricing adjustments and promotions to influence customer buying behavior, aligning demand with supply to optimize production and inventory levels.
9. Why is collaboration important in demand management?
Collaborative efforts between sales, marketing, procurement, production, and finance ensure that demand forecasts are accurate, supply plans are aligned, and the entire supply chain operates smoothly.
10. What are potential disadvantages of demand management?
Managing demand adds complexity and can increase costs related to inventory and planning. If not done correctly, it may lead to overproduction or missed opportunities to promptly respond to sudden market changes.