Businesses rely on technology to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and streamline operations. One such indispensable tool is the barcode scanner, a device that has revolutionised inventory management, retail checkout, and logistics. But what is a barcode scanner, and why is it so essential?
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore barcode scanners in detail, covering their types, how they work, key benefits, and industries that rely on them. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clear understanding of what a barcode scanner is and how it can transform your business operations.

Understanding Barcode Scanners
What is a barcode scanner? It captures and stores information in the form of barcodes and special patterns. These devices are commonly found in retail stores, warehouses, hospitals, and various other industries where tracking and managing inventory are essential.
How Does a Barcode Scanner Work?
Barcode scanners function using a combination of hardware and software. Here’s how they typically operate:
- Scanning the Barcode: The scanner emits a laser or LED light to illuminate the barcode.
- Reading the Pattern: The barcode reader detects the reflection of light from the barcode’s black and white patterns.
- Decoding the Data: The scanner converts the reflected light into electrical signals and interprets the barcode data.
- Transmitting the Information: The decoded data is sent to a connected system, such as a POS (Point of Sale) terminal or inventory management software.
Types of Barcode Scanners
There are various types of barcode scanner machines available, each designed for specific applications and environments. Choosing the right one depends on factors such as barcode type, scanning range, and industry requirements. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of barcode scanners:
1. Laser Barcode Technology
How They Work:
Laser scanners use laser beams to decode information. The scanner emits a laser light that reflects off the barcode, and a sensor detects the pattern of reflected light to decode the data.
Advantages:
- High-speed scanning makes them ideal for retail and high-volume environments.
- Can read barcodes from longer distances compared to CCD scanners.
- Works well in environments with adequate lighting.
Best Used For:
- Retail checkout counters (supermarkets, grocery stores, clothing stores).
- Warehouses where scanning barcodes from a moderate distance is required.
2. CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) Barcode Scanners
How They Work:
CCD scanners use an array of tiny LED lights to capture barcode data. Instead of scanning a single line like laser scanners, CCD scanners capture the entire barcode in one shot and analyse the pattern.
Advantages:
- Not prone to wear and tear.
- High accuracy, even for slightly damaged or smudged barcodes.
- Better suited for short-range scanning (within a few inches).
Best Used For:
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems in retail stores.
- Libraries and small-scale inventory management.
3. Imaging (2D) Barcode Scanners
How They Work:
Imaging scanners, also known as 2D barcode scanners, use a camera to capture an image of the barcode and decode it using advanced algorithms. Unlike traditional laser scanners, these can read both 1d and 2D barcodes.
Advantages:
- Can scan barcodes from any orientation (omnidirectional scanning).
- Capable of reading damaged, worn-out, or poorly printed barcodes.
- Can decode QR codes, Data Matrix, and other 2D barcodes.
Best Used For:
- Healthcare facilities (patient identification, medication tracking).
- Logistics and warehouse management.
- Ticketing systems (airports, concerts, public transport).
4. Pen-Type Barcode Scanners
How They Work: What is a Barcode Scanner?
Pen-type barcode scanners have a small light source and a photodiode at the tip. The user must swipe the pen across the barcode at a consistent speed to read the data. The photodiode measures the intensity of light reflected back and translates it into barcode information.
Advantages:
- Compact and lightweight, easy to carry.
- Lower cost compared to other barcode scanners.
- No external power source required (some models connect directly via USB).
Disadvantages:
- Requires a steady hand and precise movement for accurate scanning.
- Slower than lasers and imaging scanners.
Best Used For:
- Small-scale retail businesses.
- Office document tracking and asset management.
6. What is a Barcode Scanner? Fixed Mount
How They Work:
Fixed-mount scanners are installed at standalone POS systems and warehouse conveyor belts. They continuously scan barcodes as products pass through them.
Advantages:
- No manual operation required—perfect for high-speed scanning applications.
- Works well in automated production lines and assembly processes.
- Can be integrated with conveyor belts and robotic systems for seamless workflow.
Best Used For:
- Manufacturing plants and assembly lines.
- Automated warehouse sorting systems.
- Airports for baggage handling and boarding pass scanning.
7. RFID Barcode Scanners
How They Work:
Unlike traditional barcode scanners that read visual barcodes, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) scanners use radio waves to read data stored in RFID tags. These tags can store more data and do not require direct line-of-sight scanning.
Advantages:
- Can scan multiple items at once, improving efficiency.
- Works even if the barcode or tag is hidden inside the packaging.
- Ideal for real-time asset tracking.
Best Used For:
- Large-scale inventory management.
- Tracking high-value assets in industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
- Supply chain and logistics for real-time shipment tracking.
Key Benefits of Barcode Scanners
Now that we understand what a barcode scanner is and how it works, let’s explore its benefits:
1. Increased Efficiency
Barcode scanners speed up data entry and eliminate the need for manual typing, reducing errors and improving operational efficiency.
2. Enhanced Accuracy
Manual data entry is prone to mistakes, whereas barcode scanning ensures nearly 100% accuracy in inventory management.
3. Cost Savings
Businesses save on labour costs and reduce losses from mismanaged inventory. A barcode scanner helps track items in real time, preventing discrepancies.
4. Faster Checkout Process
Retail stores benefit from barcode scanners at checkout counters, allowing cashiers to process sales quickly and improve customer experience.
5. Seamless Inventory Management
Warehouses and distribution centres rely on barcode scanners to track inventory movement, helping businesses maintain stock levels and avoid shortages.
What is a Barcode Scanner? Industries That Use It
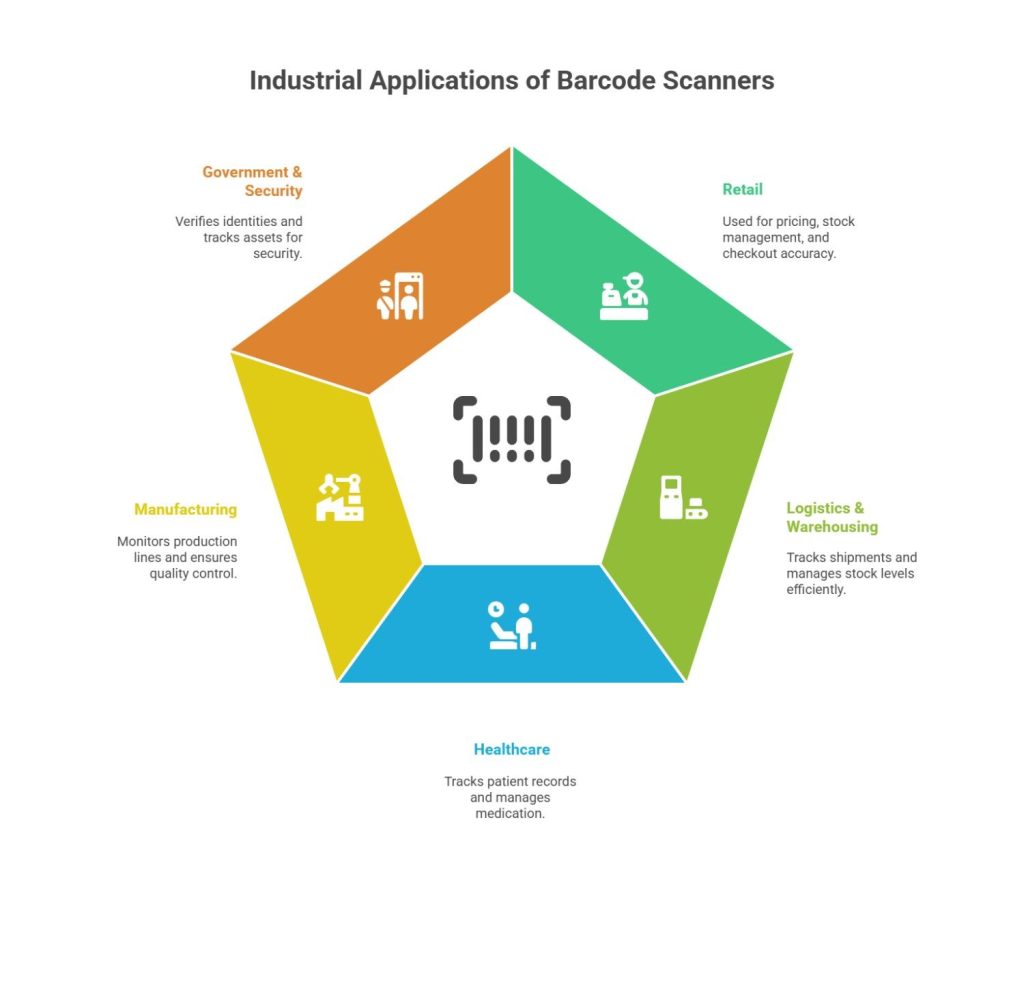
Barcode scanners are crucial in various industrial operations. Here are a few listed below:
1. Retail
Retailers use barcode scanners for pricing, stock management, and preventing checkout errors.
2. Logistics & Warehousing
Warehouses use scanners to track shipments, manage stock levels, and optimise supply chain operations.
3. Healthcare
Hospitals and pharmacies use barcode scanners for tracking patient records, medication management, and reducing human errors.
4. Manufacturing
Barcode scanners help track raw materials, monitor production lines, and ensure quality control in factories.
5. Government & Security
Governments use barcode scanners for identity verification, asset tracking, and maintaining security records.
Choosing the Right Barcode Scanner
When selecting a barcode scanner for your business, consider the following factors:
- Type of Barcode: Do you need to scan 1d barcodes (e.g., UPC codes) or 2D barcodes (e.g., QR codes)?
- Scanning Distance: Some scanners work best at close range, while others can scan barcodes from several feet away.
- Connectivity Options: Do you need a wired scanner, or would a wireless/Bluetooth scanner be more practical?
- Durability: For industrial environments, rugged barcode scanners are ideal to withstand tough conditions.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your POS or inventory management software.
Future Trends in Barcode Scanning
Barcode scanning is evolving to include newer technologies like hologram support, 2d scanning and more. Here’s what to expect.
- Mobile Barcode Scanning: Smartphones can now function as barcode scanners, making inventory management more accessible.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI-powered scanners can enhance barcode reading accuracy and automate tasks.
- RFID and Iot Integration: RFID technology is being combined with barcode scanning for improved asset tracking and real-time monitoring.
Conclusion
What is a barcode scanner, and how does it function? It’s clear why businesses across industries rely on them. Whether for inventory management, retail checkout, or healthcare applications, barcode scanners streamline operations, reduce human errors, and improve efficiency.
As technology advances, barcode scanning will continue to evolve, integrating AI, Iot, and mobile solutions to provide even greater accuracy and convenience. If you’re considering investing in a barcode scanner, get in touch with Qodenext today.
What is a barcode scanner? We hope you have understood this question. Now let’s explore the FAQ section.
FAQS – What is a Barcode Scanner?
1. What is a barcode scanner used for?
A barcode scanner is a device that reads and decodes barcode information, helping businesses improve efficiency, accuracy, and inventory management. It is used in warehouses, manufacturing hubs and storage facilities to track stock movement.
2. Which barcode scanner is the best?
2D imaging scanners are universal. They can scan detailed images from a distance, reducing manual labour to a large extent.
3. How do wireless barcode scanners work?
Wireless scanners depend on connectivity networks such as WIFI and Bluetooth to transfer data.
4. Are barcode scanners difficult to set up?
The installation process involves integrating the machine with an online application and software for optimal performance.
5. Can smartphones replace traditional barcode scanners?
Yes, with barcode scanning apps, smartphones can function as barcode readers. However, dedicated barcode scanners are faster and more accurate for high-volume scanning.
6. How to buy a barcode scanner?
First, understand the different scanners available in the market. Analyze your needs based on scanning volume, speed, and code compatibility. Explore top brands like Qodenext, Zebra Technologies, and Honeywell to find your desired product. Consider warranty, battery life, and ergonomic features.






