In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, efficient operations management is crucial for organizations to maintain a competitive edge. Enter Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) — a powerful technology that has revolutionized how companies handle their operational processes. If you are wondering what is ERP, it can be defined as an integrated system that brings together multiple business functions such as manufacturing, supply chain, finance, and human resources into a unified digital ecosystem.
This ERP definition highlights its role as a central nervous system for organizations, enabling seamless communication, data sharing, and streamlined workflows. The result is enhanced productivity, better decision-making, and improved overall efficiency.

What Is Erp in Operations Management?
ERP in Operations Management is an all-encompassing software solution to refine and maximize diverse organizational and operational procedures. Simply put, if someone asks what is ERP, the answer lies in its ability to integrate departments and functionalities into a single cohesive framework.
By combining areas such as manufacturing, supply chain, human resources, and finance, ERP enables seamless data exchange, heightened communication, and more informed decision-making. This ERP definition emphasizes its function as both a strategic and operational tool that drives efficiency, reduces costs, and improves overall organizational performance.
1. Centralized Database
A centralized database in ERP acts as a single repository for all organizational data. This means that information from various departments, such as sales, inventory, finance, and HR, is stored in one location. This centralization eliminates data duplication and ensures data consistency. For instance, when a customer’s contact information is updated in the CRM module, the same updated data is instantly reflected across all relevant modules, preventing discrepancies and confusion.
2. Integration
Integration within ERP goes beyond mere data sharing; it orchestrates processes across departments. When an order is placed, the ERP system initiates a sequence of events: it checks inventory levels, triggers procurement if needed, schedules production, and updates financial records. This end-to-end integration not only accelerates processes but also reduces errors that might occur when disparate systems communicate separately.
3. Real-time Reporting and Analytics
ERP’s reporting and analytics capabilities empower users with data-driven insights. Managers can generate real-time reports, charts, and graphs that provide a holistic view of business operations. For example, production managers can track production line efficiency in real time, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing workflows promptly. These insights enable quicker and more informed decision-making at all levels of the organization.
4.Supply Chain Management
In the supply chain management module of ERP, various processes are streamlined for optimal efficiency. Demand forecasting relies on historical data, market trends, and current orders, ensuring that inventory levels are maintained at just the right quantities to fulfill orders without excess stockpiles. If stock levels drop below a set threshold, the system automatically generates purchase orders, maintaining a seamless supply chain.
5.Financial Management
ERP’s financial management module handles intricate financial tasks. It automates processes such as invoicing, accounts payable, and receivable, minimizing human error and ensuring accurate financial records. Additionally, the module keeps track of tax regulations and accounting standards, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of financial discrepancies or legal issues.
6. Human Resource Management
ERP’s HR module encompasses the entire employee lifecycle. It manages recruitment, employee onboarding, training, performance evaluations, and payroll. This detailed tracking ensures that each employee’s journey is well-documented and aligns with organizational goals. For instance, performance evaluations can be linked to skill development programs, promoting a skilled and motivated workforce.
7. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM functionality in ERP focuses on nurturing and enhancing customer relationships. It tracks customer interactions, including inquiries, purchases, and service requests. This information aids sales teams in understanding customer preferences and behavior, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer interactions. The system also helps customer service teams resolve issues efficiently by providing a comprehensive view of customer history.
8. Mobile and Remote Access
ERP’s mobile and remote access feature extends its functionality beyond the office walls. Authorized users can access the ERP system from their mobile devices or remote locations. For instance, a sales representative visiting a client can use their tablet to check inventory levels, place orders, and update customer information in real time. This ensures that critical decisions and actions can be taken even when not in the office.
In summary, ERP features work cohesively to create an integrated, efficient, and data-driven environment for organizations. By utilizing a centralized database, fostering integration, providing real-time insights, optimizing supply chains, managing finances, enhancing HR processes, nurturing customer relationships, and enabling mobile access, ERP systems empower businesses to operate smoothly and competitively in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
Benefits of ERP in Operations Management
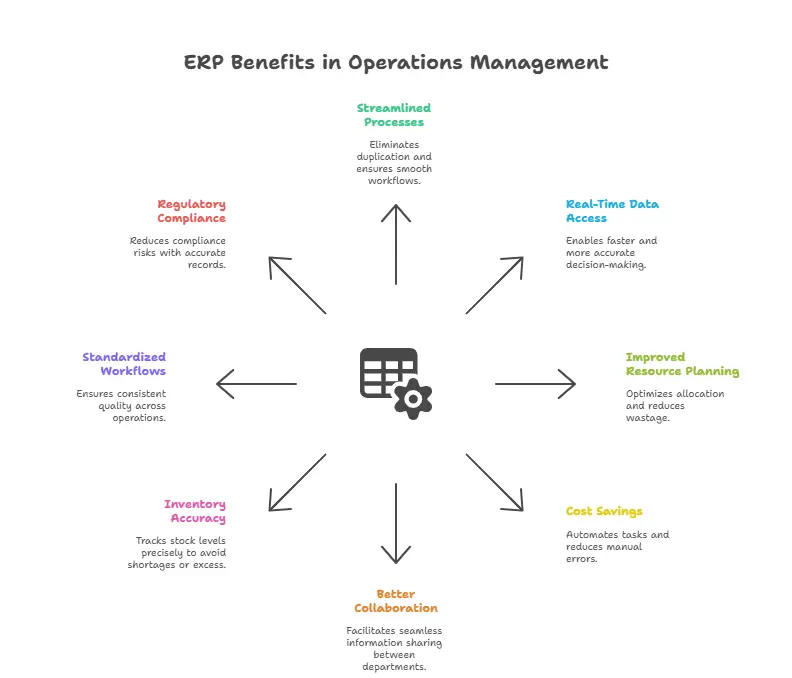
1. Streamlined Processes
ERP integrates all operational functions like production, inventory, procurement, and sales into one system, eliminating duplication and ensuring smooth workflows.
2. Real-Time Data Access
Provides managers and staff with up-to-date information, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.
3. Improved Resource Planning
Tracks manpower, materials, and machinery usage, helping optimize allocation and reduce wastage.
4. Cost Savings
By automating tasks, reducing manual errors, and controlling inventory, ERP significantly cuts operational costs.
5. Better Collaboration
Centralized data allows different departments to share information seamlessly, reducing communication gaps.
6. Inventory Accuracy
Tracks stock levels precisely, avoiding shortages that disrupt production or excess stock that increases holding costs.
7. Standardized Workflows
Ensures that all processes follow best practices and maintain consistent quality across operations.
8. Regulatory Compliance
Stores accurate records for audits, safety regulations, and industry standards, reducing compliance risks.
Role of Erp in Inventory Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are crucial in efficient business inventory management. By providing an integrated and centralized platform, ERP systems enable organizations to optimize inventory processes, enhance visibility, and streamline operations. Through real-time data synchronization and automation, ERP systems contribute to minimizing stock levels, reducing carrying costs, and improving overall supply chain management. Let us explore the role of ERP in inventory management in detail :
1. Real-time Visibility
ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of inventory levels, spanning various locations and departments. This real-time visibility helps businesses track inventory movement, assess stock availability, and anticipate potential shortages or excesses. With accurate and up-to-date information, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize inventory levels and meet customer demands efficiently.
2. Demand Forecasting
ERP systems leverage historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors to predict future demand. By analyzing patterns and seasonality, businesses can create more accurate demand forecasts. These forecasts assist in planning production schedules, optimizing inventory levels, and avoiding costly stock outs or overstock situations.
3. Inventory Optimization
ERP systems utilize sophisticated algorithms to balance supply and demand, considering factors such as lead times, order quantities, and reorder points. This optimization minimizes carrying costs while ensuring that the right amount of stock is available to meet customer demands. This approach prevents excess inventory and reduces the risk of stockouts.
4. Automated Reordering
ERP systems automate the reordering process by setting predefined stock thresholds. When inventory levels drop below a certain point, the system automatically generates purchase orders or production orders, streamlining the replenishment process. This automation reduces manual errors and eliminates the need for constant monitoring.
5. Supplier Collaboration
ERP systems facilitate efficient communication between businesses and suppliers. Electronic data interchange (EDI) capabilities and online portals enable seamless order placement, order confirmation, and delivery tracking. This collaboration ensures timely replenishment, reduces lead times, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
6. Batch and Serial Tracking
ERP systems enable tracking of items by batch or serial numbers throughout the supply chain. This capability is essential in industries with strict regulations, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics. It aids in managing recalls, tracing the origin of defective products, and ensuring compliance with quality standards.
7. Multi-location Management
ERP systems are equipped to manage inventory across multiple warehouses, stores, or distribution centers. They provide centralized control over stock levels, allowing businesses to allocate inventory efficiently based on demand patterns, location preferences, and supply constraints. This approach minimizes excess stock and optimizes resource utilization.
8. Data Analytics
ERP systems gather and analyze inventory-related data, offering valuable insights into inventory turnover rates, slow-moving items, and stock movement patterns. This data helps organizations identify opportunities to optimize their inventory management strategies, make informed decisions, and implement continuous improvement measures.
By addressing these roles comprehensively, ERP systems play a pivotal role in modernizing and enhancing inventory management practices, leading to cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and streamlined operations.
Examples of Erp in Inventory Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems play a pivotal role in optimizing inventory management by streamlining processes, enhancing visibility, and ensuring efficient resource allocation. These systems integrate various departments, data, and functions into a centralized platform, enabling businesses to manage their inventory effectively.
Here are some of the prominent examples of ERP in inventory management:
1. SAP ERP
SAP’s ERP software offers comprehensive inventory management tools that enable businesses to monitor stock levels, track movements, and optimize reorder points. It provides real-time insights into inventory positions across multiple locations, helping to reduce stockouts and overstocking.
2. Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite’s ERP solution incorporates advanced inventory management capabilities. It allows businesses to manage multiple warehouses, track inventory levels in real time, and automate reorder processes. The system also offers demand forecasting and order fulfillment features.
3. Microsoft Dynamics 365
This ERP system provides a robust inventory management module that offers visibility into stock levels, automates replenishment processes, and optimizes stock movement. It integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft tools, enhancing overall business operations.
4. Infor CloudSuite
Infor’s ERP solution includes powerful inventory management features that support multi-site inventory control, demand forecasting, and vendor management. Its advanced analytics capabilities enable data-driven decision-making for better inventory management strategies.
5. Epicor ERP
Epicor’s ERP system offers inventory optimization tools that aid in managing stock levels, reducing carrying costs, and improving demand forecasting accuracy. It also facilitates efficient tracking of inventory movements throughout the supply chain.
6. Acumatica Cloud ERP
Acumatica’s ERP solution empowers businesses with real-time insights into inventory positions, helping to minimize stockouts and streamline order fulfillment. It enables businesses to manage multiple warehouses, track lot and serial numbers, and automate inventory replenishment processes.
These ERP systems go beyond basic inventory tracking and management, offering advanced features like demand forecasting, integration with other business processes, and analytics-driven decision support. By employing these systems, enterprises can attain increased authority over their inventory, lower expenses, and improve the overall effectiveness of their supply chain.
Conclusion
In summary, it can be said that Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have significantly transformed Operations Management. This transformation is marked by optimizing procedures, heightened productivity, and providing up-to-the-minute insights. Integrating various business functions within a unified platform optimizes resource allocation, minimizes errors, and fosters informed decision-making. In this digital transformation era, Qodenext emerges as a catalyst for operational excellence.
With its state-of-the-art ERP solutions, Qodenext empowers businesses to seamlessly manage their operations, adapt to market dynamics, and achieve sustainable growth. To embark on a journey of operational efficiency, explore Qodenext’s offerings today and witness the transformation firsthand. Embrace the power of ERP with Qodenext and pave the way for a prosperous future.
FAQs
1. What is ERP in operations management?
ERP in operations management integrates various business functions into a unified system to streamline workflows, improve communication, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
2. How does ERP improve supply chain management?
ERP systems enable demand forecasting, automate replenishment, and provide real-time tracking of inventory and orders, helping maintain optimal stock levels and reduce disruptions.
3. What role does ERP play in financial management within operations?
ERP automates invoicing, tax compliance, and financial reporting, reducing errors and ensuring transparent and accurate financial operations.
4. How does ERP support human resource management (HRM)?
ERP manages employee recruitment, onboarding, training, performance evaluations, and payroll operations, aligning workforce management with business goals.
5. Can ERP systems provide real-time data analytics and reporting?
Yes, ERPs offer real-time dashboards and customizable reports, empowering users to monitor operational metrics and make data-driven decisions instantly.
6. What is the benefit of a centralized database in ERP?
A centralized database ensures consistent, accurate data across departments, eliminating duplication and enabling seamless collaboration.
7. How does ERP facilitate customer relationship management (CRM)?
ERP-integrated CRM modules track customer interactions and preferences, supporting personalized marketing and improved customer service.
8. Is ERP useful for managing inventory across multiple locations?
Yes, ERP systems enable centralized control of inventory in multiple warehouses or stores, optimizing stock allocation in response to demand patterns.
9. What are some examples of ERP software suited for operations and inventory management?
Popular ERP platforms include SAP ERP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Infor CloudSuite, Epicor ERP, and Acumatica.
10. How does mobile access enhance ERP functionality in operations management?
Mobile and remote access allow authorized personnel to update and access ERP data on the go, enabling quicker decision-making and operational flexibility.






