Industry 4.0 robotics or the 4th Industrial Revolution aims to integrate systems with people to make an increasingly efficient and intelligent production process.
This revolution promises the use of AI and ML to streamline and ease human operations. To achieve the expected results, automated strategies like the use of autonomous robots that have in common the connection they get from the Internet of Things.
So, as the use of robots and automated systems is growing, it is also possible to identify possible problems. It would help to understand the disruptive environment of this new age of technology.
Let’s see the revolution it has brought.
Autonomous Robots in Industry 4.0
4.0 The development of intelligent automation is reshaping today’s factories in the Autonomous robots in industry 4.0. precision The robot industry 4.0 is centered on precision, data connectivity and adaptive learning. Industrial robots also perform complex tasks with high precision and repeatability and with less human error.
Key Highlights:
Autonomous robots industry 4.0 has high productivity with real time monitoring.
Robot Industry 4.0: AI, IoT, and Analytics based Smart Operation.
Even assembly, welding, and packaging can seamlessly be managed by industrial robots.
Hands-on Training for Automation: An industrial robotics training in India hones the practical skills necessary to automate processes.
Industrial Robotics Training in India facilitates workforce equipped for tomorrow’s factories.
Some Examples of Industry 4.0 Robotics
Here are some of the innovations that Industry 4.0 robotics are going to bring around:
1. Increased Productivity
Robotics is pivotal in realising the goals of Industry 4.0, facilitating manufacturers in boosting productivity and refining product quality. By leveraging robots, manufacturers streamline intricate and repetitive tasks previously executed by humans.
Unlike human labour, robots operate incessantly, 24/7, sans the need for breaks, culminating in accelerated production rates, diminished cycle times, and amplified throughput, thus bolstering productivity.
2. Improved Quality
The incorporation of robotics in manufacturing processes elevates product quality by mitigating the likelihood of human error. Robots execute precise and accurate manoeuvres, resulting in fewer defects and variations during production, ensuring uniform quality of products and optimising responsiveness to customer demand.
Consequently, the seamless integration of robotics into manufacturing processes profoundly influences the attainment of Industry 4.0 objectives by enhancing efficiency and productivity, refining product quality, and optimising responsiveness to customer demand.
3. Reduced Costs
Implementing robotics in manufacturing processes results in a significant reduction in costs. By automating tasks requiring human labour, using robotics may lead to lower labour costs and fewer instances of scrap and rework.
Additionally, robots can operate in hazardous environments, reducing the need for costly safety equipment and fewer potential safety incidents. Such factors contribute to a more efficient use of resources and a reduction of overall manufacturing costs.
4. Enhanced Safety
Robots not only reduce costs but also improve safety in the workplace. They can perform tasks that are considered too hazardous for humans. It helps to minimise the need for human intervention in such situations.
By replacing humans in dangerous environments, using robots could result in fewer accidents. Also, robotics provide enhanced safety measures that can create a more secure place for employees.
5. Flexibility
Another advantage of industry 4.0 and robotics is the use of robotics to make operations more flexible for the manufacturers. You can reprogram the robots to perform different tasks so that manufacturers can quickly adapt to changing market demands.
This level of flexibility allows for a more agile and responsive manufacturing process. This usually results in the ability to produce customised products more efficiently. As a result, manufacturers can meet customer demands a lot faster and stay ahead of the competition.
6. Data Collection
By using advanced technology from the advanced robotics industry 4.0, manufacturers can collect large amounts of data from their manufacturing processes. This data is pivotal in improving the performance of manufacturing. It allows a reduction in downtime therefore increasing efficiency.
The data collected can also help with predictive maintenance, which results in fewer breakdowns and reduced downtime. Using robotics for data collection ultimately helps manufacturers make more informed decisions and optimise their processes for better performance.
7. Improved Working Conditions
By taking over hazardous, repetitive and physically demanding tasks, robots have a profound impact on the health and well-being of workers in the manufacturing industry. This makes the workplace safer which also leads to greater job satisfaction.
It also impacts a higher employee retention rate. Integrating robotics in manufacturing processes transforms how work is done. It provides a significant positive impact on human operations.
With autonomous robots industry 4.0, there is less risk of injuries and physical strain on workers. Integrating robotics in manufacturing is critical in archive the Industry 4.0 objectives. It brings numerous benefits including improved quality, more productivity, enhanced safety, flexibility, data collection and more.
However, it is also better to acknowledge the challenges of automation in Industry 4.0. While the benefits do not triumph over the challenges, it is better to know these risks before availing of the 4.0 technologies.
Embracing Challenges for Future Growth of Industry 4.0 Robotics
Despite the hurdles, the advantages of robotics in manufacturing surpass the challenges, cementing its status as a pivotal technology for the industry’s future. As the manufacturing terrain undergoes continual transformation, the seamless fusion of robotics and other Industry 4.0 technologies becomes indispensable for maintaining competitiveness and fulfilling customer expectations.
Moving ahead, let’s delve deeper into these challenges to devise effective strategies for overcoming them and unlocking the full potential of robotics in manufacturing.
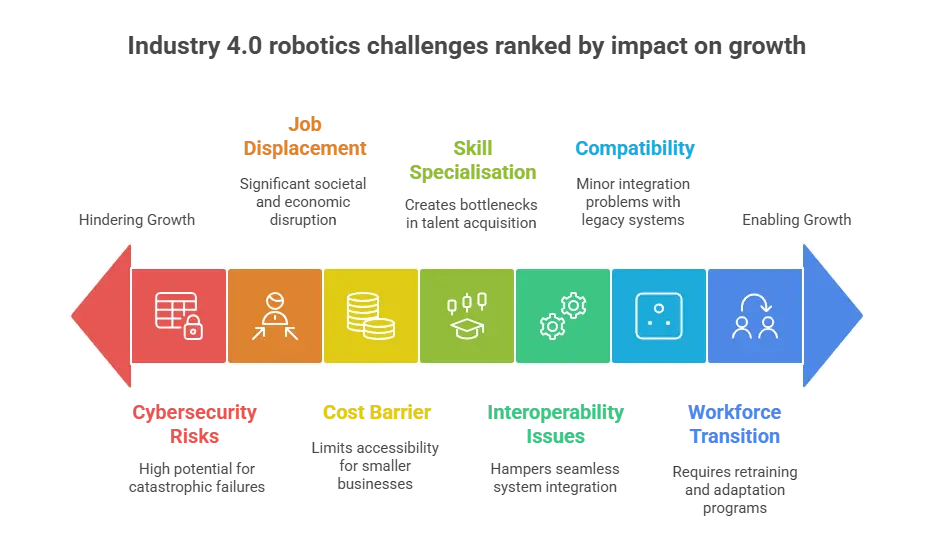
1. Workforce Transition
The integration of advanced technologies like robotics necessitates upskilling the workforce to adapt to new roles and tasks. Addressing skill gaps and ensuring smooth transitions for employees amidst technological disruptions poses a significant challenge for Industry 4.0 and robotics implementation.
2. Cost Barrier
Acquiring and sustaining the robotics era provides a formidable impediment. The preliminary funding for deploying robots can be prohibitive, and continual upkeep charges can escalate rapidly.
3. Skill Specialisation
Effective integration of robotics in production hinges on specialised knowledge in programming, renovation, and troubleshooting. However, securing gifted employees poses an extremely good venture because of the scarcity of competently skilled individuals in these domain names.
4. Interoperability Issues
Integrating diverse technologies and systems within Industry 4.0 frameworks often leads to interoperability challenges. Ensuring seamless communication and compatibility between different devices, platforms and software solutions becomes crucial for maximising the efficiency and effectiveness of interconnected manufacturing processes. Overcoming it requires standardised protocols and robot integration strategies for industry 4.0 and robotics.
5. Job Displacement
Incorporating robotics into manufacturing workflows may displace human workers, prompting apprehensions regarding job stability. This poses a substantial concern, particularly for workers whose skill sets become obsolete due to task automation.
6. Compatibility
Challenges in Robotics Integration: Merging robotics technology with established manufacturing processes poses difficulties. Ensuring compatibility among various machines and software systems presents a notable obstacle, often demanding further investments in new technologies.
7. Cybersecurity Risks
As more manufacturing processes become automated in industry 4.0 robotics, there will always be a risk of cybersecurity. Robots and other connected devices are vulnerable to cyber attacks, leading to significant data breaches and financial losses.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning and implementation. Companies must have a comprehensive strategy in mind to address all the potential difficulties of integrating industry 4.0 robotics.
Conclusion
In embracing Industry 4.0 and robotics, we witness transformative benefits like improved productivity, enhanced safety, and data-driven insights. Yet, challenges such as workforce transitions, cost barriers, and cybersecurity risks necessitate careful consideration.
For expert solutions in industry 4.0 robotics in navigating these complexities and realising the full potential of next-gen technologies for supply chain management, visit Qodenext.
FAQs: Pioneering Industry 4.0 Robotics:
1. What is the role of robots in Industry 4.0?
Robotics in the industry can help to execute data-driven analytics and insights effectively. This progression is vital for transitioning from traditional manufacturing methods to intelligent, data-centric operations.
2. How does Industry 4.0 automation increase productivity?
It optimises productivity by streamlining interactions between stages. The 3D models allow, for example, to realise the deployment of a production unit, the difficulties inherent to the manufacture of devices and their maintenance.
3. What are the risks of adopting Industry 4.0?
Transitioning to Industry 4.0 poses risks: automation may redefine job roles, necessitating skill investments; internet-connected sensors increase cyber attack susceptibility, and scaling projects may fall short of projected returns.
4. How can manufacturers better scale Industry 4.0 projects from initial pilots?
Scaling Industry 4.0 initiatives requires: defining clear processes, gaining managerial support, and, with limited resources, introducing a minimum viable product, gathering feedback, and possibly expanding the workforce through recruitment or training.







