Many companies tend to view supply chain circularity as merely a “feel-good” initiative, allowing them to tout their sustainability efforts without any genuine impact. However, as more organizations begin to embrace circular strategies, the real advantages of a circular economy are coming to light.
Modern supply chain professionals are increasingly seeking innovative methods to optimize company resources. The shift towards a circular supply chain model is driven by compelling reasons, and businesses that ignore this trend do so at their own risk.
So, what are the tangible benefits of adopting circular supply chain? What strong business rationale supports this shift? And how can organizations stay competitive in this evolving landscape?
In this discussion, we’ll explore a range of concrete benefits that companies are currently reaping from circular practices. Additionally, we’ll examine the future of supply chain management and how circularity is poised to become a vital component for business resilience and success.
What is a Circular Supply Chain?
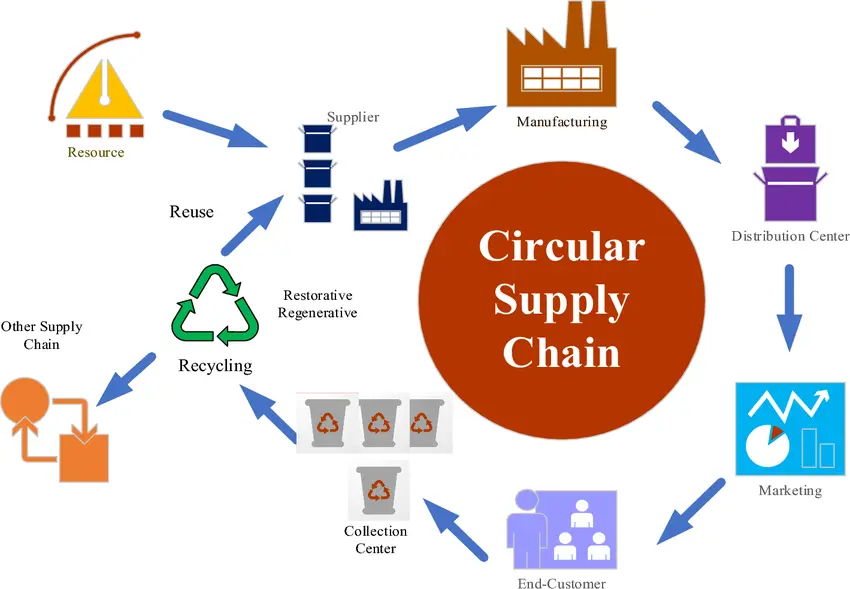
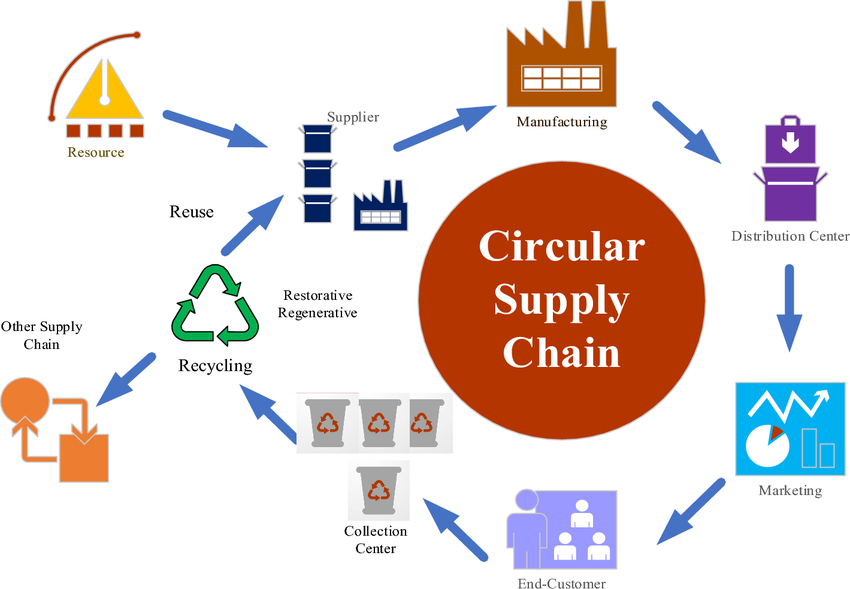
A circular supply chain focuses on maximizing the use of materials and products for as long as possible, rather than allowing them to become waste immediately. This in-trend model, manufacturers actively reuse raw materials like plastic, metal, cardboard, paper, steel, and glass.
They also refurbish and resell pre-owned items, offer rental options instead of outright sales, and opt for recycled pallets and other eco-friendly storage and packaging solutions. Similar to traditional supply chains, materials, and finished goods flow from suppliers to manufacturers, retailers, and ultimately to consumers.
For instance, cell phone manufacturers retrieve old devices to extract valuable metals like copper, gold, and tungsten, which are then repurposed for new phones. Beverage companies or their container suppliers often recycle plastic bottles and metal cans.
Additionally, some businesses choose to refurbish or repair products rather than recycle them outright.
Top 3 Circular Supply Chain Strategies:
1. Coordination with Waste Collection Systems
Waste collection systems play a vital role in circular supply chain strategies, serving several important functions. However, they also pose a significant challenge in creating effective circular supply chain solutions due to their need to cover large areas.
This is essential for collecting returned products from consumers and delivering them to recycling, refurbishing, or repair facilities—especially important for online purchases. Additionally, it can be difficult for companies to ensure that their waste collection methods gather enough goods and materials in a cost-effective way.
To address these challenges, leading organizations are taking steps to improve existing waste collection systems. Companies focused on e-commerce are leveraging enhanced carrier networks and smart technologies to create seamless global return solutions.
This enables them to collect products from consumers, regardless of location, and direct these returns to their warehouses or to manufacturing or recycling facilities, depending on their needs, once a sufficient and cost-effective volume has been gathered.
Moreover, software with Application Programming Interface (API) integration adds a new layer of visibility to circular supply chains. With API, businesses can connect their management systems for warehouses, recycling, and manufacturing, providing a comprehensive overview of how returns are utilized alongside data from the entire supply chain.
This technology allows businesses to analyze trends and identify areas for improvement by distilling data from all points in their supply chain.
2. Increasing Technology Accessibility and Availability
Another barrier to advancing circularity is the lack of supporting tech infrastructure, particularly in remote areas. This infrastructure is crucial for enhancing supply chain visibility and optimizing transportation routes.
Currently, delivery providers struggle to optimize their routes in many rural locations due to the absence of real-time data. This limitation affects the efficiency of deliveries and pickups, which, in turn, increases transportation-related CO2 emissions.
Today’s advanced circular supply chain solutions offer some level of route optimization, allowing businesses to strategically place their inventory closer to consumers. In the near future, leading solution providers are expected to incorporate advanced routing algorithms.
These algorithms will automatically determine the most efficient locations for returned goods. They will consider factors such as proximity to warehouses or processing facilities and the types of materials involved.
3. Satisfying Regulatory Reporting Requirements:
Modern logistics technology serves as a crucial link between all parts of the supply chain. Data is collected from every stage, including manufacturing, warehousing, last-mile delivery, and returns. Advanced visibility portals create a unified data experience, enabling brands to quickly identify trends and make optimizations using intelligent automation.
Technology partners are addressing emissions reporting challenges by developing unified emissions tracking tools within their portals. These features allow e-commerce businesses to monitor CO2 emissions throughout the transportation and warehousing stages of their supply chains.
Despite the complexities of implementing circular supply chains, organizations can lead in efficiency and sustainability by partnering with the right technology solution providers. This collaboration not only helps achieve business and financial objectives but also supports environmental goals, paving the way for a more sustainable supply chain and future.
Barriers to Circular Supply Chain Strategies:
In many traditional supply chains, the focus has been on increasing product variety and centralizing production to achieve two key objectives: enhancing performance through the specialization of parts and improving economic efficiency through economies of scale. This often involves using specialized materials and designs that enhance functionality and operating large manufacturing plants that can distribute products over wide areas, sharing fixed costs through extensive distribution networks.
However, because most supply chains have optimized for these goals, transitioning to circular business models can be prohibitively expensive, at least in the short term. Effective recycling and remanufacturing of products or components would require collection systems that cover vast distances, retrieving items from where they are used and bringing them back to manufacturing sites.
Additionally, due to the specialization of parts, it can be challenging to gather enough volume of specific components to make recycling viable. This process might necessitate breaking down materials to their basic metals, silicon, or hydrocarbons, complicating the recycling of the many different types of plastics.
In the long run, technological advancements are emerging that could facilitate a shift toward greater circularity. For instance, you can now purchase a home 3D printer for around $1,000, which can create a variety of plastic shapes tailored to your specifications.
Meanwhile, metal 3D printing is rapidly improving in both performance and affordability, enabling the production of shapes that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. As 3D printing becomes more widely adopted, decentralization in supply chains could become more cost-effective.
While initial assembly plants for complex products may still need to remain centralized for some time, it is feasible that spare parts could be decentralized and produced closer to the point of use.
FAQs: Top 3 Circular Supply Chain Strategies
What are the benefits of a circular supply chain?
A circular supply chain reduces waste, lowers costs, enhances resource efficiency, promotes sustainability, and increases brand loyalty by appealing to environmentally conscious consumers while driving innovation and resilience.
Which role is prioritized in a circular supply chain?
In a circular supply chain, the role of collaboration is prioritized. Stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers, must work together to optimize resource use and improve recycling efforts.
How to make sure a circular supply chain flows better?
To enhance flow, implement advanced technologies for tracking, optimize logistics and distribution networks, promote transparency among stakeholders, and foster partnerships to streamline recycling and refurbishing processes effectively.
Conclusion
Adopting circular supply chain strategies is essential for fostering sustainability while enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. At Qodenext, we are dedicated to supporting businesses in this transition, providing innovative solutions that ensure competitiveness and resilience in an ever-evolving market. Together, we can drive meaningful change for a sustainable future