In today’s competitive market, businesses must effectively manage a product from its inception to its end-of-life. PLM is a strategic process that helps organisations streamline product development, enhance collaboration, and optimise supply chain operations.
But what is product lifecycle management exactly, and how does it impact supply chain efficiency? In this blog, we will explore the key aspects of PLM, its benefits, and its critical role in improving supply chain performance.
What Is Product Lifecycle Management?
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the systematic approach to managing a product’s lifecycle from ideation, design, and production to distribution, usage, and disposal. It integrates people, data, processes, and warehouse management systems to ensure efficient product development and operational effectiveness.
Companies that implement PLM gain better control over their product data, improve collaboration between teams, and reduce inefficiencies in supply chain operations. Understanding what is product lifecycle management helps organizations optimize workflows and reduce costs associated with production, logistics, and inventory management.
Product Lifecycle Stages
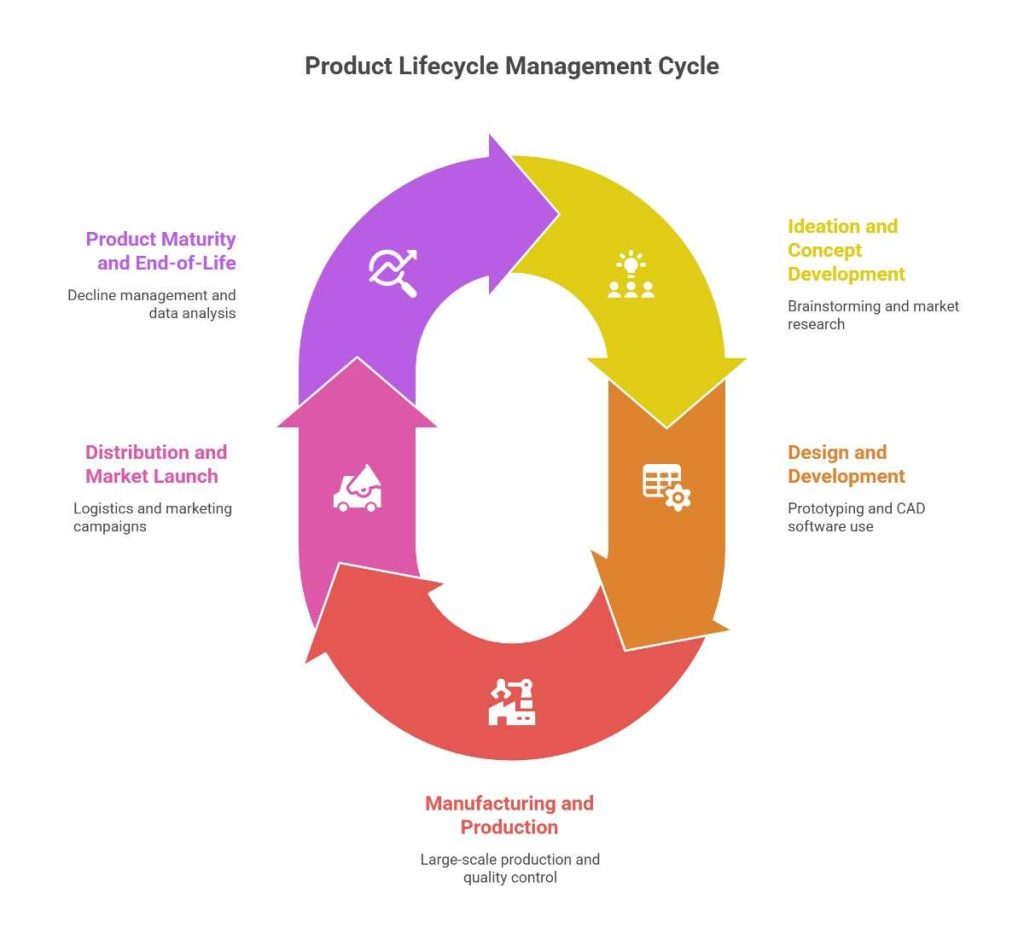
PLM consists of five primary stages that define a product’s journey:
1. Ideation and Concept Development
The first step is brainstorming ideas and researching market trends. Engineers, designers, and marketers collaborate to conceptualize a new product. Supply chain teams assess material availability and cost estimation.
2. Design and Development
- Prototyping, testing, and finalizing product designs take place in this phase.
- Companies use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software and digital simulations to enhance product development.
- PLM software integrates supply chain teams to ensure sourcing and procurement align with the design.
3. Manufacturing and Production
- The product moves from design to large-scale production.
- Supply chain management ensures raw materials are procured on time and production schedules are met.
- What is the product lifecycle without quality assurance? At this stage, quality control and compliance checks are vital.
4. Distribution and Market Launch
- Logistics and warehouse management ensure the product reaches distributors and retailers.
- Marketing campaigns drive demand while supply chain teams focus on optimizing inventory distribution.
5. Product Maturity and End-of-Life
- As demand declines, companies must decide whether to update, discontinue, or replace the product.
- Reverse logistics, recycling, and waste management strategies play a role in sustainable product lifecycle management.
- Data analytics from previous sales and customer feedback guide future product improvements.
Each of these stages influences supply chain operations, making PLM a critical component of business success.
How PLM Enhances Supply Chain Efficiency
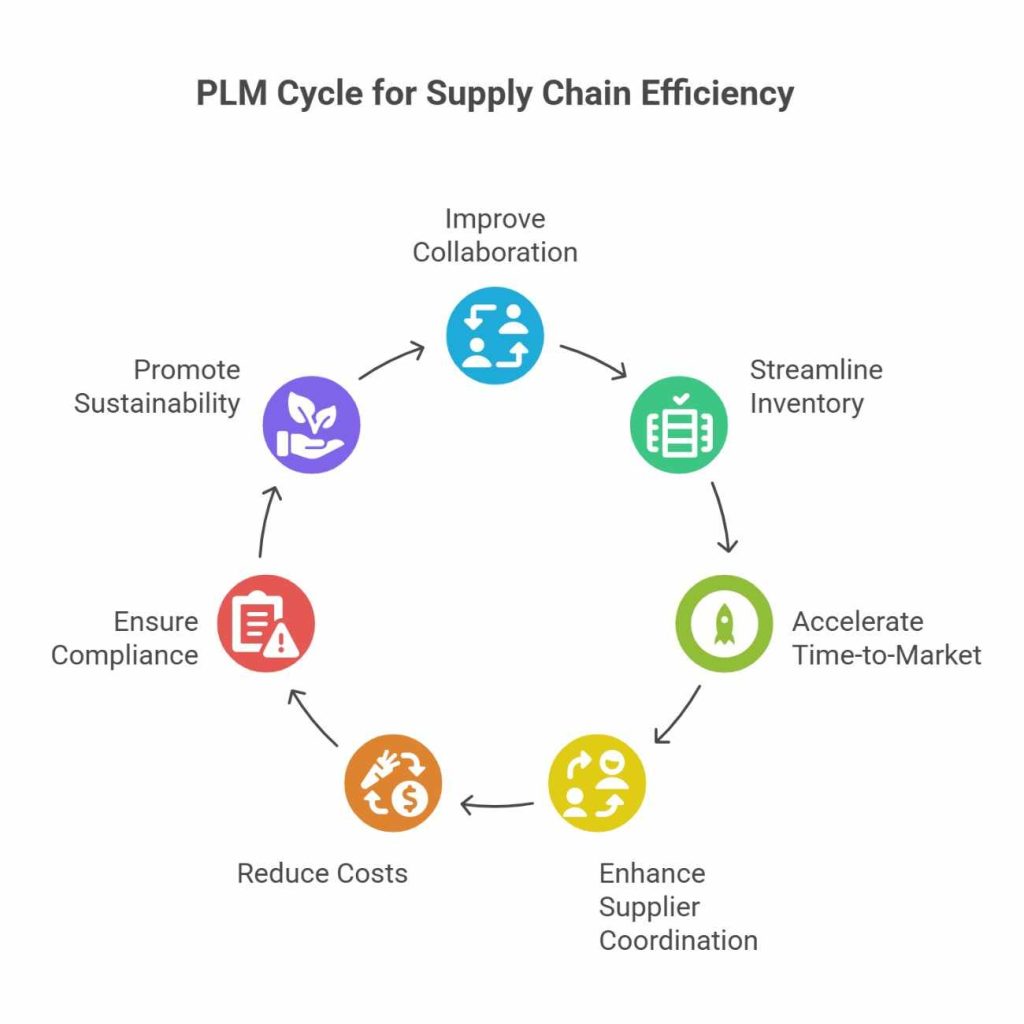
What is product lifecycle management? This question is clear, so let’s explore how it enhances supply chain efficiency.
1. Improved Collaboration and Communication
PLM integrates cross-functional teams, ensuring engineers, designers, suppliers, and logistics teams work together seamlessly. This minimizes miscommunication and delays in product development and distribution.
2. Streamlined Inventory Management
By analysing demand forecasts and production schedules, PLM helps businesses optimise inventory levels. This prevents overstocking or stockouts, reducing carrying costs and wastage.
3. Faster Time-to-Market – Uses of PLM
A well-managed PLM system accelerates product development and distribution. By automating workflows and reducing manual errors, businesses can introduce new products faster and gain a competitive edge.
4. Enhanced Supplier Coordination
PLM improves supplier relationships by providing real-time updates on material requirements and production changes. This reduces lead times and enhances procurement efficiency.
5. Cost Reduction in Manufacturing and Logistics
With accurate product data and efficient planning, PLM improves traceability in manufacturing, reduces rework costs, and optimises transportation logistics, resulting in significant cost savings.
6. Better Compliance and Quality Control
Regulatory compliance is essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, automotive, and electronics. PLM ensures all products meet quality standards and regulatory requirements, reducing legal risks and recalls.
7. Sustainable Supply Chain Management
As sustainability becomes a priority, PLM helps companies design eco-friendly products, reduce waste, and implement circular economy strategies like product recycling and remanufacturing.
By addressing these factors, PLM significantly enhances supply chain efficiency, making it a vital investment for modern businesses.
Implementing PLM in Your Business
To fully benefit from PLM, companies must integrate it into their existing supply chain systems. Here are some key steps:
1. Choose the Right PLM Software
Selecting a robust PLM platform that aligns with your industry and supply chain needs is essential. Popular product lifecycle management tools include:
- Siemens Teamcenter
- PTC Windchill
- Dassault Systèmes ENOVIA
- Oracle Agile PLM
2. Integrate PLM with Supply Chain Management (SCM) Systems
PLM should be seamlessly connected with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain Management (SCM) software to ensure a smooth procurement process.
3. Train Teams and Standardize Processes
Proper training and workflow standardization help employees maximise PLM benefits and maintain consistency in product management.
4. Utilize Data Analytics for Decision-Making
PLM systems collect vast amounts of data on product performance, customer feedback, and supply chain logistics. Businesses should leverage this data to refine operations and improve product lifecycle strategies.
5. Monitor and Optimise Continuously
Regular evaluation and updates to PLM processes ensure businesses remain agile in an evolving market.
By implementing these steps, companies can leverage what is product lifecycle management for improved efficiency, profitability, and sustainability.
PLM vs. ERP: Understanding the Differences
PLM and ERP integration play crucial roles in business operations, but they serve different purposes. PLM focuses on managing a product’s lifecycle from initial design to disposal, ensuring efficient collaboration, innovation, and regulatory compliance throughout its development. It primarily supports engineering, research, and design teams by centralising product-related data.
On the other hand, ERP streamlines business processes such as procurement, production, inventory management, and finance, ensuring smooth operations and resource allocation across departments. In essence, PLM drives product innovation and design, while ERP optimises business execution and supply chain efficiency, making them complementary rather than interchangeable.
Conclusion
What is product lifecycle management? Understanding it is essential for businesses looking to enhance their supply chain efficiency. By optimising product development, improving collaboration, and reducing costs, PLM ensures a seamless transition from product ideation to end-of-life management.
Companies that successfully implement PLM gain a competitive advantage by reducing time-to-market, minimising waste, and improving overall operational efficiency. Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, leveraging PLM can help you stay ahead in today’s dynamic business environment. Do you want to transform your traceability operations? Get in touch with Qodenext today.
FAQs – What is Product Lifecycle Management?
1. What is product lifecycle management in simple terms?
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the process of managing a product from its conception and design to production, distribution, and disposal. It helps businesses optimize product development and streamline supply chain operations.
2. How does PLM improve supply chain efficiency?
PLM enhances supply chain efficiency by improving collaboration, reducing costs, optimizing inventory, and accelerating time-to-market. It also ensures regulatory compliance and sustainable resource management.
3. Can small businesses benefit from PLM?
Yes, small businesses can use cloud-based PLM solutions to improve product management, supplier coordination, and operational efficiency.
4. What industries use PLM?
Industries like manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and fashion rely on PLM to streamline product development and supply chain operations.
5. Is PLM the same as ERP?
No, PLM focuses on managing a product’s lifecycle, while ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) manages business processes like finance, HR, and inventory. However, integrating PLM with ERP improves overall business efficiency.
6. What are the key challenges in implementing PLM?
Some common challenges include high initial costs, resistance to change, software integration issues, and the need for employee training. However, the long-term benefits outweigh these challenges.






