
Introduction:
Embarking on the journey to start an FMCG business in India demands meticulous planning and a clear understanding of the FMCG business model. In a sector characterized by quick turnover and low-profit margins, comprehending the intricacies is paramount. The process begins with an in-depth analysis of market trends and consumer needs to choose the right product, aligning it with demand. For a deeper understanding of the latest trends in the FMCG industry, stay updated with evolving consumer preferences.
FMCG Business: Sales and Distribution Management
In the dynamic landscape of Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), the seamless orchestration of sales and distribution management is instrumental in driving success. FMCG products, characterised by their swift turnover and competitive pricing, necessitate a nuanced approach to capture consumer interest and foster brand loyalty.
1. Sales Strategy
A pivotal aspect of FMCG success lies in the development of a robust sales strategy. Understanding consumer behaviour, market trends, and competitive landscapes is paramount. By aligning product offerings with consumer preferences, companies can cultivate brand loyalty, fostering repeat purchases and sustained growth. For actionable insights, explore innovation in the FMCG sector and how it can set your business apart.
Inextricably linked with sales is the intricate web of sales and distribution management. A well-structured distribution network is imperative for ensuring products reach retailers promptly, reducing lead times, and enhancing on-shelf product availability. The synergy between sales and distribution is evident in the optimization of routes and channels, minimising transportation costs while maximising market reach. If you’re looking for practical steps, see how to start FMCG business (part 2).
2. Distribution Channels In FMCG Business
FMCG companies leverage a spectrum of distribution channels, from traditional wholesalers and retailers to modern e-commerce platforms. Building and maintaining strong relationships with distributors and retailers are critical elements for successful FMCG sales. This emphasis on relationships underscores the importance of clear communication and mutual understanding for sustainable business partnerships.
FMCG product distribution business is significant in making sure that the everyday essentials reach the consumer as fast and as efficiently as possible. This industry has a high level of success determined by good logistics, good supply chains and good market covers. As the competition intensity increases and people start to change their tastes and preferences, the use of technology and data-driven insights can be used to optimize the processes. Trust and consistency are the major attributes that determine success in the long-term in the FMCG product distribution business.
3. Supply Chain Management
Efficient supply chain management is foundational in the FMCG sector. Accurate demand forecasting and streamlined inventory management are pivotal in preventing stockouts and overstock situations. The integration of cutting-edge technologies such as RFID and IoT enhances supply chain visibility, enabling proactive responses to market fluctuations. Learn how FMCG automation and the latest trends are shaping the future of the industry.
One of the biggest challenges faced by fast moving goods company is ensuring transparency and traceability across the value chain. Discover the biggest challenges faced by the FMCG sector and how to overcome them. Companies must focus on track and trace solutions to deliver high-quality products, reduce wastage, and comply with regulations. For a comprehensive view, read about key challenges in the implementation of traceability initiatives for FMCG companies and why traceability is needed not just in plants, but across the value chain.
4. Managing Product Safety and Counterfeiting
Product safety and authenticity are critical in the FMCG industry. Counterfeiting remains a major challenge, impacting both consumer trust and brand reputation. Learn how to address product counterfeiting in the FMCG industry and what steps can be taken to mitigate these risks. In case of food safety challenges, see how FMCG companies can provide can provide greater visibility and resonse agility in the supply chain.
5. Technology Integration
In the contemporary FMCG landscape, technology integration is non-negotiable. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions, and data analytics tools play a pivotal role in providing insights for informed decision-making. Automation and hygienic processing equipment, such as hygienic conveyor systems, are essential for maintaining product quality and compliance with health standards. This technological integration optimises operations, enhancing customer satisfaction and driving business success.
6. Market Expansion
To fuel sustainable growth, fast moving goods company often explore avenues for market expansion. Whether entering new geographic regions, introducing product variants, or extending product lines, expansion strategies must align with market demands. The adaptability of the sales and distribution network is crucial in accommodating and capitalising on these strategic moves.
The intricate dance between sales strategies and distribution management defines success in the FMCG sector. This holistic approach, underpinned by consumer understanding, strong distribution networks, efficient supply chains, and technological integration, forms the bedrock for sustained growth and competitiveness in this fast-paced industry.
7. FMCG Manufacturing Company
Innovation, quality, and efficiency are the three strategic key drivers that enable an FMCG manufacturing company to keep up with the dynamic requirements of the consumers. In all the processes involved in sourcing raw materials to distribution of finished goods, precision and consistency is required. Productivity and cost reduction can be achieved through the employment of automation, sustainable practices and high technology. An effective FMCG manufacturing company is one that concentrates on producing quality products that are dependable and give the consumers confidence that the company appreciates their business.
FMCG Business Model
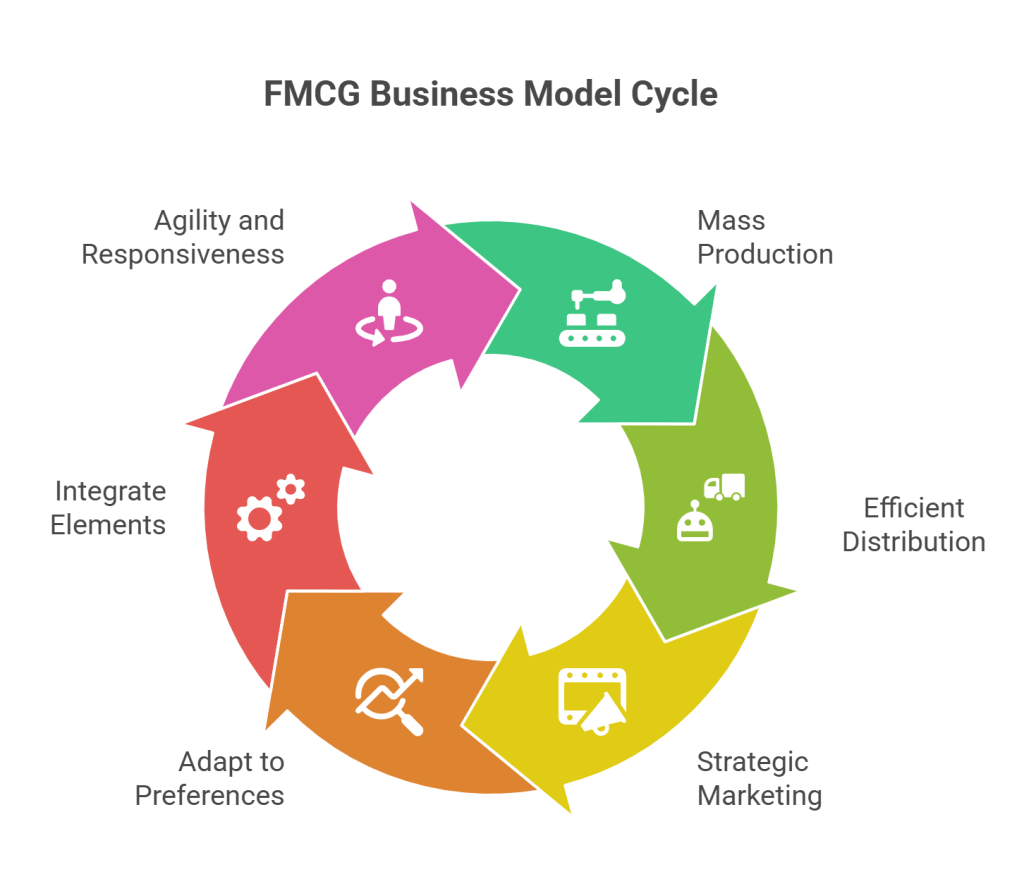
Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) refer to a wide range of frequently purchased consumer products with high turnover rates. The FMCG business model is built on a combination of large-scale production, efficient distribution, and strong marketing strategies — all designed to meet constant consumer demand.
1. Focus on Mass Production and Economies of Scale
At the heart of the FMCG business model is mass production. Companies aim to manufacture goods in large volumes to reduce the cost per unit. This approach helps them achieve economies of scale, making it possible to offer products at competitive prices while still maintaining healthy profit margins. Cost-effectiveness is crucial in FMCG, where price-sensitive consumers drive purchase decisions.
2. Efficient Distribution Network
Distribution plays a critical role in the FMCG model. To meet demand quickly and consistently, companies need a widespread and efficient supply chain. This often means partnering with wholesalers, retailers, and logistics providers to ensure fast movement of goods from factories to store shelves. Timely delivery and availability are key to winning in this space.
3. Strong Marketing and Brand Building In FMCG Business
Marketing and branding are central to success in FMCG. Companies invest heavily in advertising, promotional campaigns, and in-store visibility to create strong brand recognition. Frequent exposure to a brand builds trust and encourages repeat purchases. A loyal customer base is one of the strongest assets in the FMCG industry.
4. Adapting to Changing Consumer Preferences
The FMCG sector is fast-moving not just in product turnover, but also in changing consumer tastes. Businesses must continuously monitor market trends and customer preferences. This requires constant investment in market research and data analysis to refine products and introduce innovations quickly. Being responsive and agile is essential for long-term relevance.
5. Integration of Production, Distribution, and Marketing
The strength of the FMCG business model lies in its ability to integrate production, distribution, and marketing into a seamless cycle. Each element feeds the other — mass production supports cost efficiency, efficient distribution ensures availability, and strategic marketing drives demand. This integrated approach is what keeps FMCG businesses competitive.
6. Agility and Responsiveness as a Success Factor
In such a fast-paced industry, companies must be nimble. Consumer preferences can shift quickly due to trends, seasons, or global events. FMCG companies that succeed are those that can quickly adjust their product lines, marketing strategies, or supply chain operations in response to change.
The FMCG business model revolves around three key pillars: large-scale production, robust distribution, and strategic marketing. By keeping costs low, products available, and customers engaged, companies can thrive in a highly competitive environment. The ability to adapt and respond to market changes is not just an advantage — it’s essential for success in the ever-evolving FMCG industry.
FMCG Business: supply chain challenges
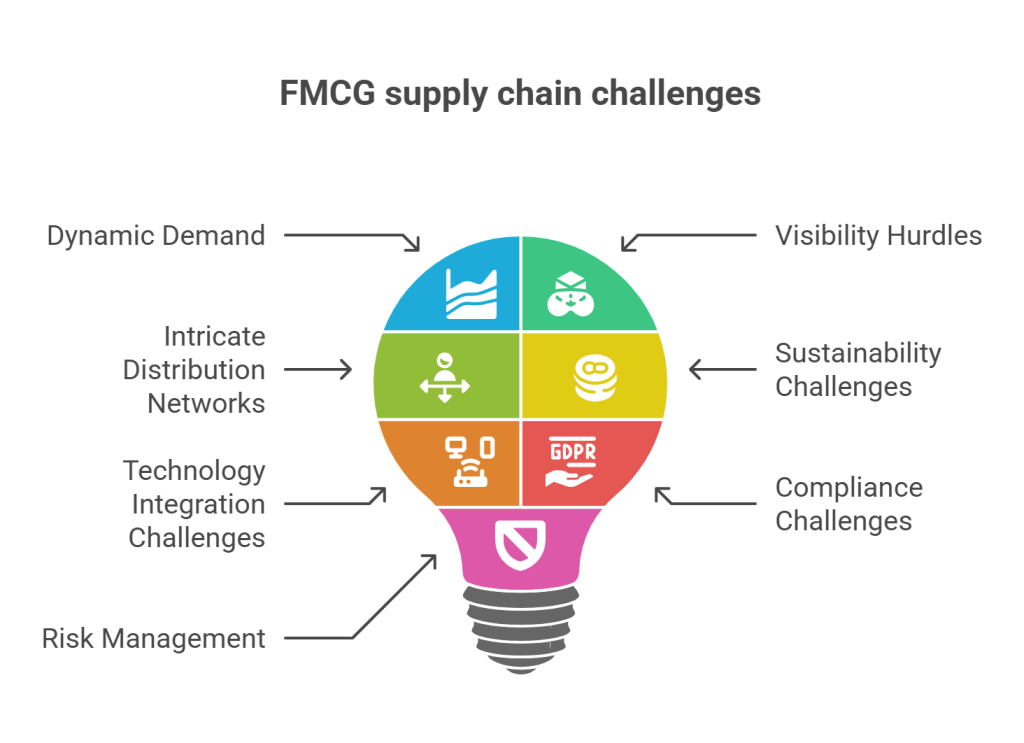
1. Dynamic Demand in FMCG Supply Chain Management:
The FMCG sector frequently contends with swift and unpredictable shifts in consumer demand. This volatility poses challenges in accurately forecasting demand and managing inventory effectively. Companies must adopt flexible supply chain strategies to promptly adapt to fluctuations and mitigate the risk of stockouts or surplus inventory.
2. Visibility Hurdles in FMCG Supply Chains:
Achieving comprehensive visibility across the entire FMCG supply chain proves challenging due to the involvement of multiple stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Inadequate real-time data and visibility hinder decision-making processes, impeding the ability to respond swiftly to changes in demand or supply disruptions.
3. Intricate Distribution Networks in FMCG Supply Chains:
FMCG companies often grapple with intricate distribution networks involving numerous intermediaries. This complexity results in inefficiencies, extended lead times, and heightened logistics costs. Streamlining distribution channels and optimising the network becomes paramount to enhance the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
4. Sustainability Challenges in FMCG Supply Chains:
The FMCG sector faces growing pressure to address sustainability concerns, encompassing environmental impacts and ethical sourcing. Balancing sustainability objectives with cost-effectiveness proves challenging, particularly when implementing eco-friendly packaging or responsibly sourcing materials.
5. Integration Challenges of Technology in FMCG Supply Chains:
Integrating cutting-edge technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), and blockchain into FMCG supply chains presents challenges. Seamless implementation of these technologies necessitates substantial investment, skill development, and overcoming resistance to change within the industry.
6. Compliance Challenges in FMCG Supply Chains:
Adhering to regulations and compliance standards, particularly concerning product safety and labelling, poses a significant challenge for FMCG companies. Ensuring products meet legal requirements across diverse markets adds complexity to the supply chain management process.
7. Risk Management in FMCG Supply Chains:
FMCG supply chains are vulnerable to various risks, including natural disasters, geopolitical issues, and global economic uncertainties. Developing robust risk management strategies is imperative to minimise the impact of unforeseen events on supply chain continuity.
FMCG supply chain challenges encompass a spectrum of issues, from dynamic demand and visibility obstacles to sustainability and technology integration. Successfully addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach that combines advanced technologies, streamlined processes, and proactive responsiveness to market dynamics. Navigating these intricacies is vital for FMCG companies to sustain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving consumer goods landscape.
Best Supply Chain Practices In FMCG Business
Effective supply chain management is crucial for success in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry. Implementing best practices ensures the seamless flow of products from manufacturers to consumers, optimising efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The supply chain management in FMCG industry in India is an intricate web that enables products to get to consumers quickly and effectively. It requires cooperation between producers, distributors, and vendors to keep the flow of products consistent. With increasing consumer expectations and fast-paced digitization, companies are leveraging sophisticated logistics and automation. Efficient supply chain management in FMCG industry in India brings efficiency in operation, cost saving and brings sustainable long term business growth.
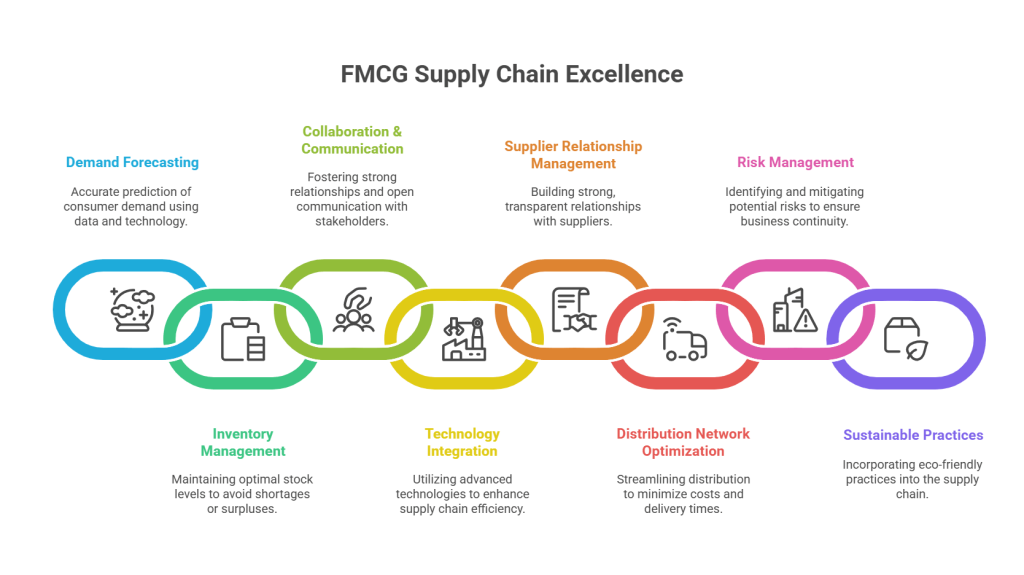
1. Demand Forecasting:
In the FMCG sector, accurate demand forecasting is paramount. Regularly assess historical data, market trends, and consumer behaviour to predict demand accurately. Utilise advanced forecasting tools and technologies to enhance precision in anticipating product requirements.
2. Inventory Management In FMCG Business:
Maintaining optimal inventory levels is key to avoiding stock outs or overstock situations. Employ just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices to reduce holding costs while ensuring product availability. Regularly review stock levels, and establish robust communication channels with suppliers for timely replenishment.
3. Collaboration and Communication:
Foster strong collaboration with suppliers, distributors, and retailers. Establish open lines of communication to promptly address any challenges or changes in demand. Implementing a robust communication system enhances visibility across the supply chain, facilitating quick decision-making and responsiveness.
4. Technology Integration in FMCG Business:
Leverage cutting-edge technologies, such as RFID, IoT, and advanced analytics, to streamline supply chain processes. Integrating these technologies enhances real-time visibility, traceability, and overall efficiency. Invest in a robust and adaptable IT infrastructure to support the seamless exchange of information.
5. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM):
Nurture strong relationships with suppliers through transparent communication and mutual cooperation. Regularly assess supplier performance and provide feedback for continuous improvement. A collaborative approach with suppliers helps in maintaining the quality and consistency of the raw materials or products sourced.
6. Distribution Network Optimization:
Optimise the distribution network to minimise transportation costs and delivery lead times. Regularly review the network’s efficiency and explore opportunities to enhance it. Utilise data analytics to identify the most cost-effective routes and distribution centres.
7. Risk Management:
Identify and assess potential risks within the supply chain, including geopolitical, economic, or natural disasters. Develop contingency plans to mitigate these risks and ensure business continuity. Regularly update risk management strategies to adapt to the evolving business environment.
8. Sustainable Practices in FMCG Business:
Incorporate sustainable and eco-friendly practices into the supply chain. Consider environmentally friendly packaging, energy-efficient transportation, and ethical sourcing of raw materials. Embracing sustainability not only aligns with consumer preferences but also contributes to long-term cost savings.
Adopting these best practices in demand forecasting, inventory management, collaboration, technology integration, supplier relationship management, distribution network optimization, risk management, and sustainable practices can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the FMCG supply chain. Regularly reassess and refine these practices to stay agile and responsive to the dynamic nature of the industry.
Conclusion:
Every FMCG business in India cannot be established just on great product, but with strategic planning, a strong supply chain and comprehensive consumer behaviour knowledge. Whether it is maximization of sales and distribution to adoption of new technologies and product safety, all these are a part of sustainable growth.
Remaining agile, customer-focused, and regulatory is beneficial to the brands. By implementing the proper approach and intelligent technology application through the help of QodeNext, companies will be able to optimize their performance, build strong brand names, and gain long-term consumer loyalty in the highly competitive Indian FMCG market.
FAQs in FMCG Business :
1. How to Start FMCG Business in India?
To start an FMCG business in India, begin with thorough market research, identify target demographics, secure funding, and establish a robust business plan. Focus on how to start FMCG business with a clear vision.
2. What is the Ideal FMCG Business Model?
The ideal FMCG business model involves a mix of manufacturing, distribution, and retail partnerships. Adopting a direct-to-consumer approach and e-commerce integration can enhance success.
3. How to Manage FMCG Sales and Distribution Effectively?
Implement a robust sales and distribution management system. Leverage technology for real-time tracking, optimise route planning, and establish strong relationships with distributors and retailers. The article will discuss how to start FMCG business while ensuring efficient sales and distribution.
4. What Challenges Exist in the FMCG Supply Chain?
FMCG supply chain challenges include perishable goods handling, demand volatility, and timely delivery. Address these challenges with agile supply chain practices to ensure product availability and minimise wastage.
5. Best Supply Chain Practices in FMCG Business?
Implement best supply chain practices such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and collaboration with suppliers. A streamlined supply chain enhances efficiency and customer satisfaction, a crucial aspect of how to start FMCG business successfully.
6. How to Overcome FMCG Supply Chain Challenges?
Overcoming supply chain challenges involves adopting technology, building strong partnerships, and continuous monitoring. The article will delve into specific strategies on how to start FMCG business while navigating and overcoming supply chain hurdles.
7. Why Choose Qodenext for Your FMCG Business?
Qodenext, a leading brand in the FMCG industry, provides innovative solutions for efficient supply chain management, robust sales strategies, and business growth. Explore how Qodenext can elevate your FMCG venture.
8. How do I build a distribution network?
Begin with local distributors and small scale stores. Use e-commerce platforms to expand your reach and ensure consistent product availability.
9. How do I prevent counterfeits?
Use QR codes, secure packaging, and educate customers. Technology like RFID can help trace your supply chain.
10. What are common mistakes to avoid?
Avoid poor demand planning, weak branding, ignoring marketing, and expanding too quickly. Start small, test, and scale gradually.






