For many years, barcodes have been a fundamental technology for inventory management, retail, and logistics. All the same, 3D barcodes are changing what we need to think about, and how we use barcodes. 3D barcode scanner offer improved functionality and information capacity compared to conventional barcodes, with applications across multiple sectors. In this post, we will discuss 3D barcodes, different types, examples, and how they transform the barcode domain.

What Is 3D Barcode?
A three-dimensional (3D) barcode is a barcode with depth or height in addition to length and width dimensions. And since this includes both the vertical and horizontal plane, these bar codes can hold more data than common 1D or 2D bar codes. They are different from flat-printed ones in that they can be etched, embossed, or even engraved on diverse media, which makes them suitable for industries that need durable and versatile tagging solutions.
How Do These 3D Barcode Work?
Like regular ones, these barcodes store information, but they can hold and access a greater amount. These barcodes encode complex data into small spaces using advanced barcode scanner 3D models. These codes are used in scanners or barcode generator software, which makes it a suitable technology for applications where robust data encoding is needed.
3D Barcode Types
To fulfill diverse practical requirements, different versions of 3D barcodes have been developed. Here are the most common:
1. Embossed 3D Barcodes
These raised barcodes are commonly used in metal or plastic components for manufacturing and aerospace industries.
2. Etched 3D Barcodes
Etched barcodes are engraved into the material, ensuring they can withstand environmental factors without wearing out.
3. Molded 3D Barcodes
These are integrated into the materials at the time of production, such as in a car or medical devices. Molded Provides integrated inside the product, very safe without worry of damage and removal.
4. QR-Based 3D Barcode
These are based on the principles of QRs and store large amounts of product information, URLs, or similar information in a 3D-Barcode format. This ability to bridge the gap between physical and digital space has made them a force in retail and marketing applications.
Examples of 3D Barcode in the Real World
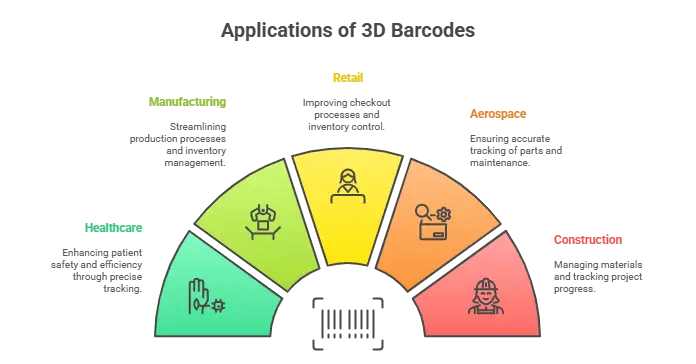
1. Healthcare
Traceability is ensured by utilizing these barcode labels on the medical devices in question, complying with the regulatory standards. Based on this, surgical implements embedded with 3D barcodes can be tracked during their lifetime, confirming the details of their sterilization and history of use.
2. Manufacturing
Additionally, embossed or etched barcodes impressed on machinery parts provide durability to track functional units of a part. Manufacturers can track production processes and ensure quality control, while barcodes are also used to optimize inventory management.
3. Retail
Interactive marketing campaigns and customer engagement through QR-based 3D barcodes. These codes can be scanned by shoppers to get information about products, reviews, or promotional offers, creating an engaging retail experience.
4. Aerospace
Other technologies used to assist in production include 3D stickers to monitor critical components that experience high temperatures or extremes. Turbine blades and other aircraft components are commonly encoded with high-durability barcodes that survive high temperatures and pressure.
5. Construction
Voice Recognition—you must have heard about it in the movies; it is also used in construction in the form of these barcodes, which can be pasted in the material like steel beams or pre-fabricated elements and can help ensure they are assembled in the right way and the right place, as well as helping keep track of the materials on site.
3D Barcode and Scanning Technology
The 3D barcode scanner technology is transforming the accuracy of data capture and its speed. A 3D barcode scanner allows you to scan embossed or debossed barcodes on materials like metal or plastic. For generating 3D barcode systems, depth sensing imaging and laser sensors are used.
Key Points:
- Build 3D barcode solutions to increase product traceability.
- Barcode scanning technology provides rapid and reliable identification in manufacturing and distribution.
- Finger barcode scanner gadgets enable projects such as secure, user-specific authentication.
- Advanced barcode technology and finger bar code scanner products improve security, effectiveness and accuracy of information for workflows in many industries.
Changing The 3D Barcode Industry
1. Enhanced Data Capacity
Where traditional barcodes have lower data storage capacity, these barcodes enable far higher storage of data, accommodating more sophisticated datasets. This ability is especially valuable in sectors that need to maintain extensive documentation, including healthcare and logistics.
2. Increased Durability
These barcodes are resistant to harsh environments and, can be engraved or embossed and thus, suitable for industrial and outdoor applications. They’re very resilient too so you don’t have to replace them very often which saves you money.
3. Versatile Application
3D barcodes can be applied on virtually any surface from metals to ceramics, giving a great deal of flexibility. This versatility allows adapting them in various sectors; from consumer electronics; to aerospace engineering.
4. Improved Security
Authentication capabilities may be layered into a barcode to help avoid counterfeiting and ensure data integrity. Locked Barcodes on high-value items, as an example, are a secure seal against fraud;
How to Create 3D Barcode
Specialized 3D barcode generator software is needed to create these barcodes. Here are the steps:
- Software Selection: Use trusted software that can handle the type of barcode you need and is compatible with how you plan to use them.
- Data to Encode: The information you want to encode This can be the serial numbers, product specifications, or URLs.
- Select Material: Define what sort of material and production type used (ex. engraving or embossing) Selection based on application, environment, etc.
- Generate and Test the 3D model of Speedy Checkout: Implement a barcode scanner to test output Testing verifies that the barcode is readable and operates correctly in practical situations.
Future Trends in 3D Barcode Technology
The barcode arena is rapidly evolving with developments in AI and IoT creating possibilities to follow:
- Smart Packaging: The new 3D barcodes enable interactive packaging solutions. These packages may offer consumers dynamic content like tutorials or recipes that enhance the product purchase.
- Integrating with AR: The use of these barcodes for Augmented Reality (AR) is enhancing customer experience. Scan of a bar code to unlock AR features such as product guide and tour.
- Blockchain Integration: They are used to connect physical goods with digital blockchain journals, enhancing traceability. This is especially true in the area of supply chain management, where transparency is the order of the day.
- Pretreatment method: The method for pretreating surfaces before them can impact the quality of the final product.
Frequently Asked Questions in 3D barcode
1. What is a 3D barcode?
A 3D barcode is a type of data code system that uses a three-dimensional form to improve the amount of data that can be stored and is more robust than traditional 1D and 2D barcodes.
2. Can I print these barcodes at home?
Although you can use basic 3D barcode generator software, industrial equipment is often needed to create durable 3D barcodes.
3. What is it used for?
Healthcare, aerospace, manufacturing , and retail are examples of industries that are leading the way in adopting these barcodes.
4. How are these barcodes read?
To precisely decode these codes, they must be scanned using specialized scanners (Other Barcode Scanner 3D Models).
5. Instead of traditionally flat codes, what are the benefits of using these barcodes?
They provide benefits such as greater data capacity, durability, versatility, and improved security features.
Conclusion
Firstly, these 3D barcode scanner are a revolutionary advancement in barcode technology, enabling unique features and possibilities. This shift in thinking gradually leads industries to embrace such a proposition, an ever-expanding landscape of efficiency, security, and interactivity. From industrial production to retail interaction, they are revolutionizing how data is encoded and retrieved, paving the way for the future.
Unravel the potential of it now and become part of this growing technological arena. Reach out to Qodenext now.






