In today’s hyper-connected world, technology continues to evolve how we interact with objects, products, and information. One of the most transformative technologies quietly powering various industries is RFID—short for Radio-Frequency Identification. Whether it’s tracking inventory in a warehouse, locating luggage at an airport, or verifying the authenticity of a luxury product, RFID is everywhere. But what is RFID, really? Let’s explore this exciting technology.

What is RFID?
To put it simply, what is RFID? RFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identification, a wireless communication technology that uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags store electronic data, which is sent to the reader for analysis and information display.
The system comprises three main components:
- RFID Tags: Microchips embedded with antennas that store data.
- RFID Readers: Devices that send and receive signals to and from the tags.
- Antenna: Acts as the communication link between a tag and a reader.
This combination allows for seamless data collection and identification across a wide range of environments.
How Does RFID Work?
What is RFID? You have understood its basic definition. Next, let’s dive into how it works.
An RFID system operates through radio waves. The reader is responsible for transmitting radio signals to the tag. Once activated, the tag transmits the signal back to the reader. This information is then processed and interpreted by a software system.
There are two primary types of RFID tags:
- Passive RFID Tags: These don’t have their own power source and rely on the reader’s signal to activate. They’re cost-effective and used for tracking low-value items.
- Active RFID Tags: These have a built-in battery and can send signals independently. They’re used for high-value items or in environments requiring long-range tracking.
History and Evolution of RFID Systems
The journey of the Radio Frequency Identification Device dates back to World War II, when radar technology was used to identify friendly aircraft. However, it wasn’t until the 1970s that RFID started gaining commercial traction. In the 1990s and 2000s, RFID saw a boom with retail giants like Walmart implementing it for inventory control.
Today, RFID is deeply embedded in industries ranging from healthcare and logistics to fashion and agriculture.
So, what is RFID in a historical context? It’s a technology with military roots that has evolved into a cornerstone of modern data tracking in indian supply chains.
RFID Applications in Real Life
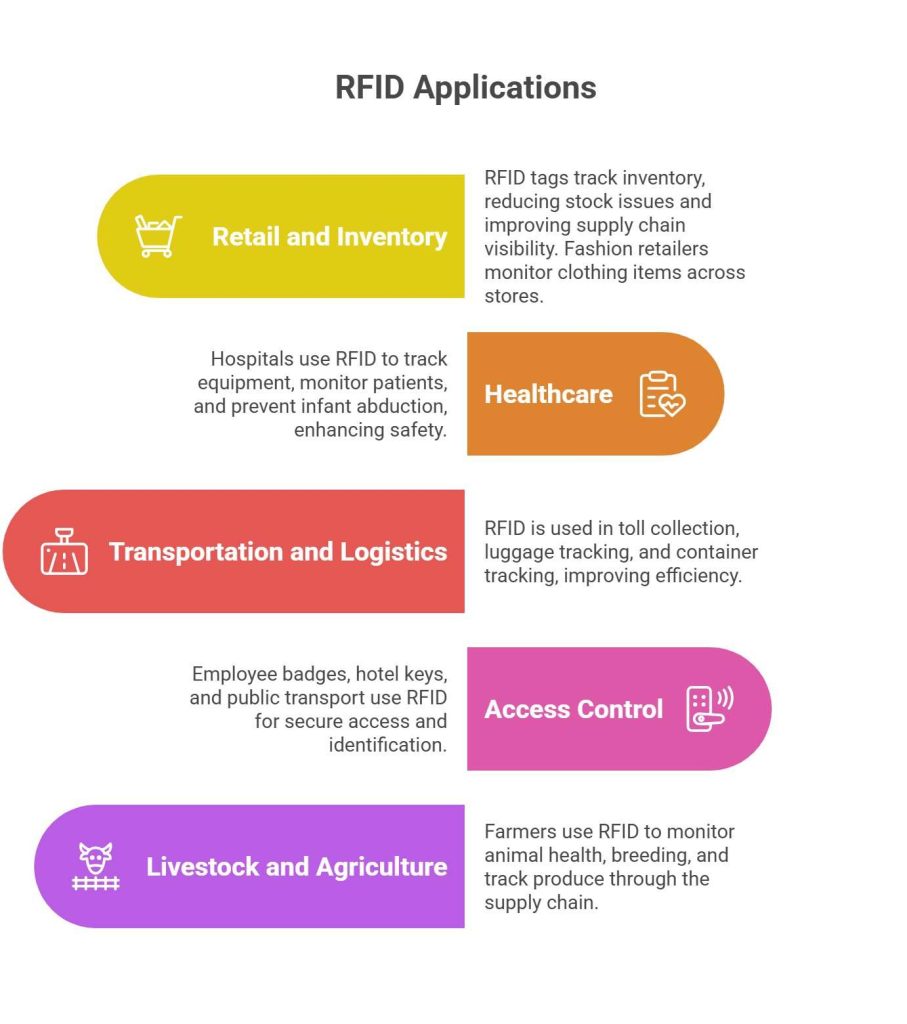
To truly understand what RFID is, we need to explore its vast applications:
1. Retail and Inventory Management
RFID tags help retailers track inventory in real time, reducing out-of-stock issues and improving supply chain visibility. For example, fashion retailers use RFID to monitor clothing items across stores and warehouses.
2. Healthcare
Hospitals use RFID solutions to track medical equipment, monitor patient movement, and even prevent infant abduction. It enhances safety and operational efficiency.
3. Transportation and Logistics
RFID is used in toll collection systems, luggage tracking at airports, and container tracking in shipping yards.
4. Access Control
Employee badges, hotel room key cards, and public transport systems use RFID for secure access and identification.
5. Livestock and Agriculture
Farmers use RFID tags to monitor animal health, breeding patterns, and track produce through the supply chain.
In each of these cases, the question “what is RFID” gets answered not just in theory but in visible, impactful action. RFID real-world applications will keep increasing in the future.
Benefits of RFID – Uses and Applications
Understanding what RFID is also means understanding why it’s widely adopted. Here are some key benefits:
- Increased Accuracy: Reduces manual errors in inventory or asset tracking.
- Time Efficiency: Automated scans are much faster than barcode or manual entries.
- Real-Time Data: Provides instant visibility into item location and status.
- Security: Helps prevent theft, counterfeiting, and unauthorized access.
- Scalability: Easily integrates into existing enterprise systems.
Challenges of RFID Implementation
While RFID has many advantages, it’s not without challenges:
- Cost: Initial setup, especially with active tags, can be expensive.
- Signal Interference: Metal surfaces and liquids can disrupt radio signals.
- Privacy Concerns: Unauthorized scanning of RFID tags can lead to data breaches.
- Data Overload: Managing and analyzing massive volumes of data requires a robust infrastructure.
Despite these challenges, industries continue to embrace RFID, making the question “What is RFID?” more relevant than ever.
RFID vs Barcodes
A common point of confusion when asking what RFID is is how it differs from traditional barcodes.
| Feature | RFID | Barcode |
| Line of Sight | Not required | Required |
| Wired | Up to 100 meters (Active) | Few inches |
| Data Storage | Large (up to several KBS) | Minimal |
| Durability | High (embedded or coated) | Easily damaged |
| Speed | Much faster | Slower, manual scanning |
RFID offers superior functionality, especially for complex, high-speed environments.
The Future of RFID
Looking ahead, RFID is expected to play a pivotal role in the Internet of Things (Iot), where connected devices communicate autonomously. It is also integral to blockchain-based traceability systems, smart packaging, and AI-powered analytics.
So when we ask what RFID is, we’re not just looking at a tracking system—we’re looking at a technology shaping the future of automation and transparency.
Conclusion
So, what is RFID? It’s a transformative, invisible layer of technology that enables faster, smarter, and more efficient tracking and communication across industries. From retail to healthcare, RFID is quietly driving automation and accuracy in places we often overlook.
By understanding what RFID is, you’re not just learning about a technology—you’re exploring a system that’s redefining how the world moves, tracks, and connects. For advanced supply chain tracking solutions, contact Qodenext today.
FAQS – What is RFID?
1. What is RFID, and how is it used in daily life?
RFID is a sensor technology that tracks goods, shipments, and inventory. It’s used in toll booths, metro cards, contactless payments, and even tracking your Amazon delivery.
2. What is RFID in supply chain management?
In supply chains, RFID enables real-time tracking of goods, reduces shrinkage, and enhances inventory management by automating data collection.
3. Can RFID work without the internet?
Yes, RFID systems can work without internet access. However, internet connectivity enhances its capabilities for remote monitoring and data analytics.
4. Is RFID secure?
While generally secure, RFID systems can be vulnerable to unauthorized scanning if not properly encrypted or shielded. Secure protocols and physical safeguards are recommended.
5. Are passive and active RFID tags the same?
No. Passive tags rely on the reader’s signal to power up, while active tags have their own battery and transmit data independently over longer distances.
6. What kinds of items or materials can interfere with RFID performance?
Materials like metal and liquids can block or disrupt RFID radio waves, causing poor tag readability or no reading at all. Specialized tag designs and system configurations help mitigate these issues in challenging environments such as warehouses, manufacturing floors, or healthcare settings.
7. How far can RFID tags be read from?
Read distance varies depending on tag type and frequency: passive tags usually work from a few centimeters to several meters, while active tags with batteries may be read from 100 meters or more, making them suitable for asset tracking over large areas.
8. Are RFID systems easily scalable for growing businesses?
Yes, RFID systems are highly scalable. New tags, readers, and software modules can be added as needed, allowing businesses to expand coverage or capabilities without replacing entire infrastructures.
9. What maintenance do RFID systems typically require?
Maintenance is generally low but includes routine software updates, cleaning and inspection of readers and antennas, and battery replacement for active or semi-passive tags to ensure optimal and reliable operation.
10. Can RFID technology be integrated with other business systems?
Absolutely. RFID data can be seamlessly integrated with ERP, warehouse management, point-of-sale, and other enterprise systems to enable real-time analytics, automated workflows, and smarter decision-making across operations.






