In a data-driven technological world, tracking and identifying objects, assets, and inventory are crucial for operational success. Among the most impactful technologies enabling seamless identification is RFID—short for Radio Frequency Identification. But many people still ask: What is an RFID scanner?

In this blog, we will explore the fundamentals of RFID scanners, how they function, and the industries that benefit from their widespread use.
What is an RFID Scanner?
Think of it like a tiny scanner that reads and analyses data stored on a tag using radio waves. When someone asks, What is an RFID scanner, the best answer is: it’s a contactless, automatic identification tool that helps track and monitor tagged items in real time.
Unlike barcode scanners, which require a line of sight, industrial RFID scanners can read multiple tags at once, even if they are not directly visible. This makes them ideal for environments where speed, accuracy, and automation are essential.
Components of an RFID System
Before diving deeper into how RFID scanners work, it’s important to understand the three key components of an RFID system:
- RFID Tag: This contains a microchip and antenna. The microchip stores data, and the antenna transmits it.
- RFID Reader/Scanner: This emits radio waves to communicate with the RFID tags and capture data.
- Antenna: Works in tandem with the reader to transmit and receive signals from the tag.
When you ask what is an RFID scanner, you’re essentially asking about the reader in this system that interprets tag data and transmits it to a software system for analysis or action.
How Does an RFID Scanner Work?
What is an RFID scanner? Understanding it also involves identifying the underlying technology.
Here’s how it works:
- Signal Transmission: The RFID scanner emits a low-power radio frequency signal through its antenna.
- Tag Activation: This signal activates nearby RFID tags (passive or active), which then respond with stored data.
- Data Capture: The scanner captures the returned signal and transmits the data to a centralized system, often through middleware or cloud-based platforms.
- Data Processing: Software processes the tag data to identify, track, or verify the object associated with the tag.
This process takes milliseconds, enabling real-time tracking and instant data availability.
Types of RFID Tags and Scanners
The functionality of RFID scanners often depends on the types of RFID tags they interact with. There are three main types of RFID tags:
- Passive Tags: No internal power source. Activated by the scanner’s signal.
- Active Tags: Battery-operated and can read information from long distances.
- Semi-Passive Tags: Have a battery but require a scanner to activate signal transmission.
Correspondingly, long-range RFID scanners may be:
- Handheld/RFID Hand Scanners: Portable and ideal for inventory audits or fieldwork.
- Fixed RFID Readers: Installed at entry/exit points to automate tracking.
- Mobile-Integrated Readers: Integrated with mobile devices for flexible, real-time access.
When you consider what is an RFID scanner, it can range from a basic handheld tool to an advanced, industrial-grade fixed reader.
Key Features of RFID Scanners
Here are some essential features that make RFID scanners indispensable:
- Multi-tag Reading: Can read hundreds of tags simultaneously.
- Long Read Range: Depending on tag type, it can scan from a few centimeters to over 100 feet.
- Durability: Industrial scanners can withstand extreme work conditions. They won’t break down in the middle of operating hours.
- Data Encryption: For secure communication and privacy.
- Integration Support: Compatible with ERP, WMS, and inventory software.
Each of these features contributes to the growing interest in the question: What is an RFID scanner and its applications in various sectors?
Where is RFID Scanning Used?
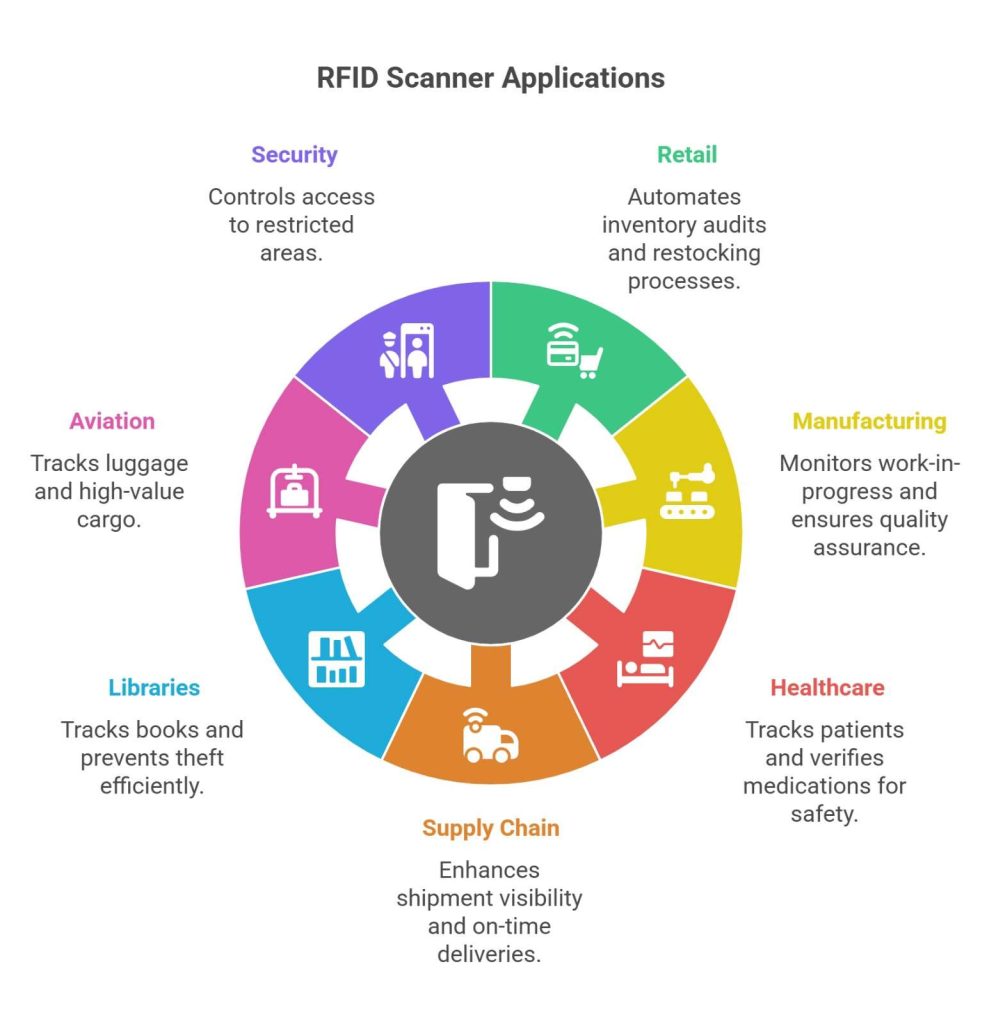
The real power of RFID becomes clear when you look at its wide range of use cases. What is an RFID scanner? Here’s where understanding it is practically valuable:
1. Retail and Inventory Management
Retailers use RFID scanners for inventory audits. This is done to reduce shrinkage and automate restocking processes. RFID scanners reduce manual work and enhance accuracy in stock management.
2. Manufacturing
RFID has many benefits in apparel manufacturing plants. RFID scanners monitor work-in-progress, track parts, and ensure quality assurance. They play a vital role in enabling smart manufacturing and traceability.
3. Healthcare
Hospitals use RFID scanners for patient tracking, asset management, and medication verification—critical areas where safety and timing matter.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics
RFID enhances shipment visibility, minimizes human errors in scanning, and ensures on-time deliveries. Knowing what is an RFID scanner helps logistics providers improve operational transparency.
5. Libraries and Archives
RFID replaces traditional barcodes in tracking books, files, and sensitive archival material, offering faster check-ins and better theft prevention.
6. Aviation and Travel
Airlines use RFID tags for luggage tracking to prevent loss or misrouting. It also helps in monitoring high-value cargo and equipment.
7. Security and Access Control
RFID scanners control access to restricted areas in corporate offices, data centres, and educational institutions, enhancing safety and monitoring.
Benefits of Using RFID Scanners
What is an RFID scanner? Now that we’ve answered it, here are the key advantages:
- Speed: Scans hundreds of items in seconds.
- Accuracy: Minimizes manual errors.
- Automation: Eliminates the need for line-of-sight scanning.
- Scalability: Easy to scale across multiple departments or locations.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces labor costs and theft in the long run.
Conclusion
So, what is an RFID scanner? It’s more than just a reader—it’s a powerful tool for automating identification, improving accuracy, and enabling real-time visibility across industries. Whether you’re in retail, manufacturing, healthcare, or logistics, RFID scanners can revolutionise the way you manage and track your assets.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, the relevance of the RFID scanner only continues to grow. Investing in RFID technology today means securing accuracy, efficiency, and scalability for tomorrow. Want a secure, robust RFID tracking solution? Contact Qodenext today.
FAQS – What is an RFID Scanner?
1. What is an RFID scanner, and how is it different from a barcode scanner?
Barcode scanners can only detect limited data, but RFID tracking scanners are equipped with smart sensors to read multiple layers of information. RFID scanners can scan multiple tags at once and from longer distances.
2. How is an RFID scanner used in logistics?
In logistics, RFID scanners track shipments, monitor cargo movement, and improve accuracy in warehouse operations, reducing errors and speeding up processes.
3. Can an RFID scanner read through materials like cardboard or plastic?
Yes, RFID scanners can read through non-metallic materials, unlike barcode scanners that need visual access to the code.
4. How do RFID scanners work?
The scanners decode the information stored inside RFID tags. They can capture data from long distances without a direct line of sight.
5. Is it difficult to integrate RFID scanners into existing systems?
No, modern scanners are designed to integrate with ERP, WMS, and other enterprise platforms, making implementation smooth and scalable. Buy RFID scanners from trusted sources to gain maximum benefit.
6. Do RFID scanners require a power source to operate?
Yes, RFID scanners (also called readers) need a power source to generate and transmit radio frequency signals that interact with RFID tags. Most fixed RFID readers are plugged into an electrical supply, while handheld models may use rechargeable batteries for portability.
7. Can RFID scanners be used outdoors and in harsh environments?
Absolutely. Many industrial RFID scanners are specifically designed for rugged environments. These devices are built to withstand dust, moisture, vibration, and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for factories, warehouses, and outdoor logistics operations.
8. Is data from RFID scanning secure and private?
Modern RFID systems use secure communication protocols and encryption to protect sensitive information. Data privacy can be ensured by limiting access, using password protection, and encrypting both tag and reader transmissions, especially in applications like healthcare and access control.
9. What is the typical range of an RFID scanner?
The read range depends on the type of RFID technology and the tag used. Passive RFID scanners typically have a range from a few centimeters up to about 25 feet, while active RFID systems can achieve ranges of over 100 feet or more.
10. Can RFID scanners interfere with other wireless devices?
RFID scanners are regulated to operate within specific frequency bands to minimize interference. However, in environments crowded with multiple wireless technologies (like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth), careful planning and frequency coordination are recommended to prevent signal disruption.






