In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing and production, maintaining quality standards is paramount to the success of any organization. One of the key pillars supporting this objective is inspection. In quality management, Inspection plays a pivotal role in ensuring that products meet specified requirements, adhere to industry standards, and fulfill customer expectations. Much like a detailed inspection trailer that provides an overview of a process, understanding different inspection types gives organizations a preview of how quality assurance unfolds across each production stage.
However, inspection is not a one-size-fits-all process; it encompasses various types tailored to specific needs and objectives. This blog aims to shed light on the different types of inspection and explore the crucial functions of quality management inspection.
Understanding these concepts will enable businesses to enhance their quality control measures, achieve operational excellence, and ultimately deliver superior products and services to their customers.

What Is Inspection in Quality Management ?
Inspection in quality management refers to the systematic examination, measurement, and evaluation of products, processes, or services to ensure they meet predefined quality standards. The inspection process in quality management involves examining and evaluating products, services, and procedures to ensure they meet established standards and comply with quality benchmarks.
It is a vital component of quality control, as it helps identify any deviations or defects that may affect the overall quality of a product or service. Key features of inspection in quality management include:
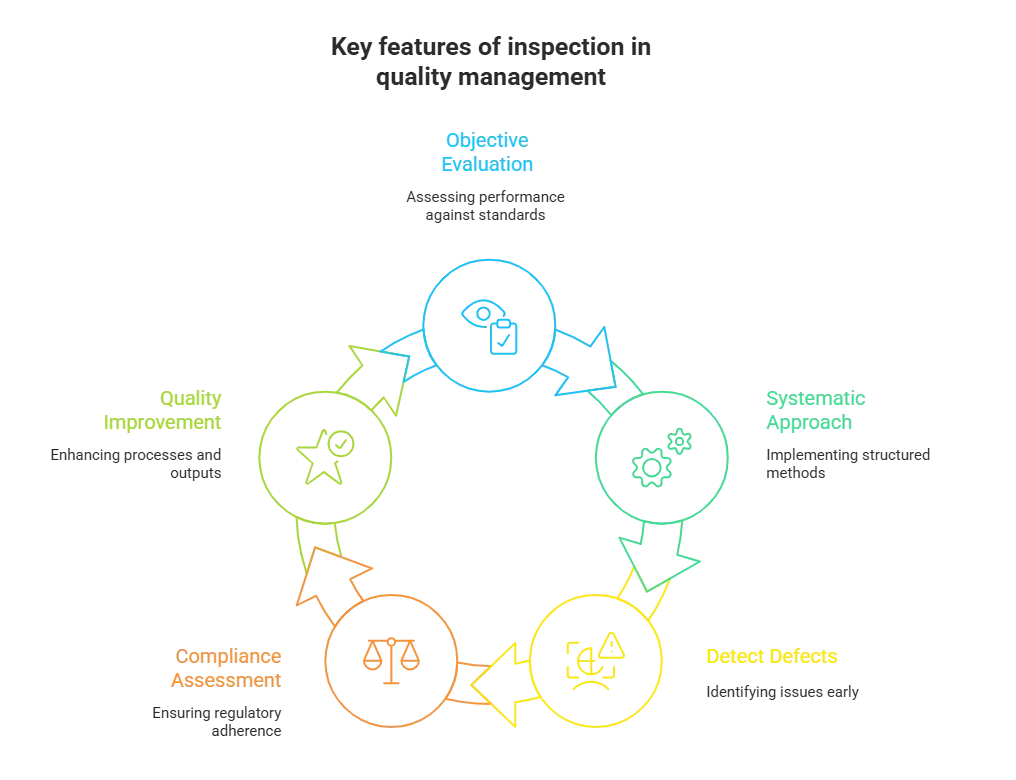
- Objective evaluation: Inspections are carried out based on predetermined criteria and specifications, ensuring an unbiased and objective assessment of the product or process.
- Systematic approach: Inspections follow a structured and systematic approach, involving the use of standardized procedures and checklists to ensure consistent evaluation across different items or batches.
- Detecting defects: The primary purpose of the inspection is to identify and detect defects or non-conformities in products, processes, or services. This allows for corrective actions to be taken to improve quality and prevent further issues.
- Compliance assessment: Inspections verify whether the product or process complies with relevant regulations, standards, and customer requirements. This helps ensure that the organization is meeting the necessary quality and safety guidelines.
- Quality improvement: Inspection findings provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement efforts. By analyzing inspection results, organizations can identify trends, root causes of defects, and areas for improvement, leading to enhanced quality and efficiency in the long run.
Overall, inspection plays a crucial role in quality management by enabling organizations to monitor and control the quality of their products, processes, and services, ensuring customer satisfaction and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Types Of Inspection in Quality Management
Inspection plays a crucial role in quality management by ensuring that products, processes, and services meet the required standards and specifications. It involves systematically examining and evaluating various aspects of a product or process to identify any deviations or defects.
There are numerous types of inspections employed in quality management to address different stages and aspects of production. Here are ten common types:
- Receiving Inspection: This type of inspection occurs upon receipt of raw materials, components, or finished goods to verify their quality and conformance to specifications.
- In-Process Inspection: Conducted during the manufacturing process, this inspection ensures that products meet quality standards at each stage and helps identify any potential issues early on.
- Final Inspection: Performed after the completion of production, it involves a comprehensive examination of finished products to ensure they meet all quality requirements before they are released for distribution.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Typically applied to the first production run of a new product, FAI ensures that the initial batch meets all customer requirements and design specifications.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC involves continuous monitoring and inspection of a production process using statistical techniques to identify variations and maintain process stability.
- Attribute Sampling: This inspection technique involves randomly sampling a batch of products and determining whether each unit meets a predefined set of criteria or standards.
- Variable Sampling: In this type of inspection, measurements are taken on randomly selected samples from a batch, and statistical analysis is used to assess the quality level of the entire batch.
- 100% Inspection: As the name suggests, every individual item in a batch is inspected thoroughly to ensure compliance with quality standards. This method is time-consuming and resource-intensive but guarantees comprehensive scrutiny.
- Dock Audit: Performed when products are ready for shipping, dock audits involve checking the accuracy of product quantities, packaging, labeling, and overall shipment quality.
- Process Audit: This type of inspection focuses on assessing the effectiveness of production processes and identifying areas for improvement. It involves a systematic review of procedures, documentation, and adherence to quality standards.
These are just a few examples of the many types of inspections used in quality management. Choosing the appropriate inspection method depends on the specific requirements of the industry, product, and production process, aiming to ensure consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
Different Quality Control Techniques in Supply Management
Quality control techniques play a crucial role in supply management, ensuring that products or services meet the desired quality standards. These techniques help identify and eliminate defects, minimize errors, and maintain consistency throughout the supply chain. Here are five commonly used quality control techniques:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC involves the use of statistical methods to monitor and control production processes. It helps detect variations and trends in data, allowing manufacturers to take timely corrective actions.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma aims to reduce defects and improve overall quality by following a structured problem-solving approach known as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). It focuses on achieving near-perfect processes and outputs.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): FMEA is a systematic approach to identifying and prioritizing potential failures in a product or process. By analyzing the effects and causes of failures, organizations can implement preventive measures to mitigate risks.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Total Quality Management is a management philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and involvement of all employees. It emphasizes a holistic approach to quality control, involving every aspect of the organization.
- Lean Manufacturing: Lean principles aim to eliminate waste and improve efficiency in manufacturing processes. Techniques such as value stream mapping, just-in-time production, and 5S methodology are used to optimize workflows and reduce non-value-added activities.
These quality control techniques, among others, contribute to enhancing product and service quality, reducing costs, and fostering customer satisfaction in supply management.
Conclusion
Types of inspections in quality management include receiving inspection, in-process inspection, final inspection, and periodic inspection. The important functions of quality management inspection include ensuring product conformance, identifying defects, monitoring process effectiveness, and maintaining customer satisfaction. Since the introduction of modern inspection frameworks like those implemented in various industries after The Inspection 2022 reforms, organizations have been able to achieve higher operational accuracy and accountability.
In conclusion, inspections play a crucial role in quality management by ensuring that products meet established standards, minimizing defects, and improving overall quality.
Qodenext, a leading quality management software provider, can assist by offering comprehensive inspection solutions. In a broader sense, inspection processes have evolved to become as detailed and methodical as creative productions like The Inspection A24—aiming for precision, compliance, and continuous improvement.
Their software streamlines inspection processes, enhances data collection and analysis, and enables proactive quality control, ultimately helping businesses improve their product quality and customer satisfaction.
FAQ
1.What is the primary purpose of inspection in quality management?
The main purpose of inspection in quality management is to systematically examine and evaluate products, processes, or services to ensure they meet predefined quality standards. Inspections help identify defects, verify compliance with specifications, and provide feedback for quality improvement.
2.How do receiving and final inspections differ in the quality control process?
Receiving inspection checks the quality and conformance of raw materials or components upon arrival, preventing defective inputs from entering production. Final inspection is performed after production is complete to ensure finished goods meet all quality requirements before distribution or delivery to customers.
3.What is the role of in-process inspection in manufacturing?
In-process inspection involves ongoing checks at various stages during manufacturing. Its role is to catch defects early, ensure that each step meets quality standards, and prevent costly rework or scrap by addressing issues as soon as they arise.
4.Why is 100% inspection not always used in quality management?
While 100% inspection reviews every item for defects, it is often resource-intensive and time-consuming. For large batches or low-risk products, statistical sampling methods are preferred to balance quality assurance with efficiency.
5.How do process audits contribute to continuous improvement in quality management?
Process audits systematically review production procedures, documentation, and adherence to standards. They help identify inefficiencies, ensure compliance, and uncover root causes of issues—driving continuous improvement in operations.
6.What are some commonly used quality control techniques in supply management?
Key quality control techniques include Statistical Process Control (SPC), Six Sigma, Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Total Quality Management (TQM), and Lean Manufacturing. Each technique focuses on reducing defects, eliminating waste, and optimizing processes.
7.How does inspection support customer satisfaction and business competitiveness?
Regular inspections ensure that only products and services meeting required standards reach customers, reducing returns, complaints, and recalls. Consistent quality builds trust, enhances brand reputation, and gives companies a competitive advantage in the marketplace.






