Ever wonder what it takes to manufacture, monitor, and ship a product to a customer’s doorstep? Supply chain planning is helping your business meet customer demand in the most efficient way possible. It includes manufacturing raw materials, monitoring production, and balancing the supply-demand curve of multiple products.
Modern supply chains need to be agile, robust, and resilient to tackle unpredictable global events. If you’re tackling inefficient logistics, we’ve got your back. In this article, we’ll explore the scope of planning in supply chain management, including its best practices, strategies, and more.
Let’s go!

What is Supply Chain Planning?
The purpose of this planning is to coordinate the transfer of goods, services, and finances across multiple stakeholders. It involves forecasting demand, managing inventory, scheduling production, and ensuring seamless transportation. The goal is to balance supply and demand most cost-effectively while meeting customer expectations.
This planning process is a critical component of supply chain management, focusing on long-term objectives and day-to-day operations to avoid disruptions, minimize costs, and maximize efficiency.
Key Components of Supply Chain Planning
The best supply chain processes help you optimise, coordinate, and build resilience. Here are the key components listed below.
1) Demand Planning
Accurate demand forecasting is essential to reduce stockouts and overstock situations. It involves analyzing market trends, historical data, and customer behavior. Learn more about demand forecasting in supply chain management.
2) Inventory Planning
Balancing inventory levels is essential to avoid excess holding costs and ensure product availability. Effective inventory planning aligns stock levels with demand forecasts.
3) Production Planning
This ensures that manufacturing resources are used efficiently to meet demand. It involves scheduling production activities, allocating resources, and managing capacity.
4) Distribution Planning
Distribution planning focuses on optimising the movement of goods from warehouses to customers. It includes route optimisation, transportation mode selection, and ensuring timely deliveries.
5) Supply Planning
This component involves coordinating with suppliers to ensure that raw materials and components are available as needed, avoiding production delays.
7 Strategies for Effective Supply Chain Planning
Achieving desired business goals requires careful planning, strategies, and execution. It’s all about responding tactically to market conditions. Here are the 7 basic strategies to ace your supply chain management plan.

1) Collaborative Planning
Collaboration among supply chain partners, including suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, ensures better visibility and coordination. Sharing real-time data helps in aligning goals and reducing inefficiencies.
2) Agile Planning
Agility in supply chain planning and control allows businesses to quickly adapt to changes in demand or supply. This strategy focuses on flexibility and responsiveness to minimise disruptions.
3) Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
IBP aligns supply chain planning and analytics with broader business objectives, including financial and operational goals. It is a holistic approach to ensure that all departments work collectively to plan the path ahead.
4) Scenario Planning
This strategy involves preparing for various potential scenarios, such as demand surges, supply shortages, or geopolitical risks. Real-world events are simulated in real time using AI tools to prepare emergency plans.
5) Lean Supply Chain Planning
Lean logistics focuses on reducing waste and maintaining a balance between resource allocation and budget. It emphasizes continuous improvement and efficiency across all supply chain processes. For a deeper dive, see TQM in supply chain management.
6) Technology-Driven Planning
Leveraging advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT enhances forecasting accuracy and decision-making. Real-time analytics provide actionable insights for better supply chain management and planning product demand.
7) Sustainability-Driven Planning
Integrating sustainability into planning helps reduce environmental impact and aligns with corporate social responsibility goals. This includes optimizing transportation, reducing waste, and sourcing responsibly. Learn about circular supply chain strategies.
The Supply Chain Planning Process
Supply chain demand planning helps businesses anticipate demand to maximise profits. Here are the six critical steps of the supply chain process.
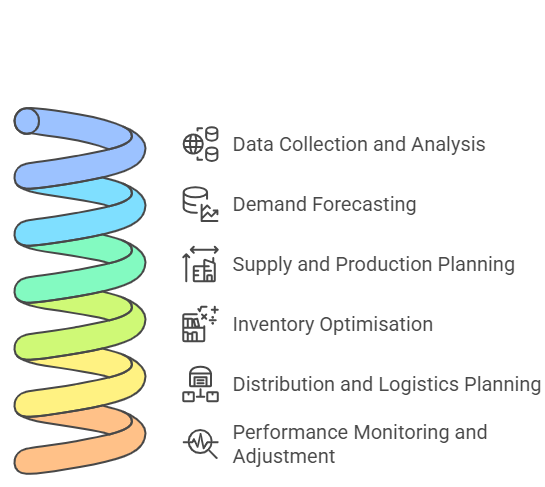
Step 1: Data Collection and Analysis
The process begins with gathering data from various sources, including historical sales data, market trends, and supplier performance. Analyzing this data provides insights into demand patterns and supply chain efficiency.
Step 2: Demand Forecasting
Using statistical models and advanced forecasting tools, businesses predict future demand. This step is crucial for aligning supply and production with market needs.
Step 3: Supply and Production Planning
Based on demand forecasts, supply and production plans are developed. This involves determining the quantities of raw materials needed, scheduling production runs, and allocating resources efficiently.
Step 4: Inventory Optimisation
Optimising inventory ensures your business operates risk-free without costly stock holding. This involves setting reorder points, safety stock levels, and inventory turnover targets.
Step 5: Distribution and Logistics Planning
This step ensures that finished products are delivered to customers right at their doorstep. It includes planning transportation routes, selecting carriers, and coordinating warehouse operations.
Step 6: Performance Monitoring and Adjustment
Continuous monitoring of supply chain performance helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as order fulfilment rates, inventory turnover, and transportation costs are tracked. Based on this data, adjustments are made to improve planning accuracy. Check out supply chain KPIs for more.
Benefits of Effective Supply Chain and Planning
- Cost Reduction: Optimised planning minimises costs related to inventory, transportation, and production.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Ensures timely delivery and product availability, enhancing the customer experience.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlines operations, reduces waste, and maximises resource utilisation.
- Risk Mitigation: Anticipates potential disruptions and develops contingency plans.
- Better Decision-Making: Data-driven insights support informed and strategic decision-making.
Conclusion
Supply chain planning serves as the backbone of inventory and logistics, seamlessly bridging the gap between supply and demand for raw materials and finished goods. From supplier management and consumer analytics to recycling initiatives and real-time data-driven decisions, every step in the supply chain plays a vital role in business success. By embracing strategies that foster collaboration, prioritize sustainability, and leverage advanced technologies—especially machine learning—organizations can adapt swiftly to evolving market dynamics and secure a competitive edge.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your supply chain? Contact QodeNext today for expert insights and innovative solutions tailored to your business needs.
FAQs
1. Why is supply chain planning important?
Planning in supply chain is vital for balancing supply and demand, optimizing costs, and ensuring customer satisfaction. It helps businesses stay competitive and adapt to market changes efficiently.
2. How does technology improve supply chain planning?
Advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT enhance forecasting accuracy, improve decision-making, and provide real-time insights for better supply chain visibility.
3. What is demand planning in the supply chain?
Demand planning is forecasting customer demand for a specific period. It involves predicting future trends based on historical analysis, market trends, and economic conditions.
4. How can businesses improve their supply chain and planning?
Businesses can improve by adopting advanced planning technologies, fostering collaboration, leveraging real-time data, and continuously monitoring performance to make data-driven adjustments.
5. How does planning in supply chain contribute to sustainability?
It helps businesses adopt more sustainable practices by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and improving energy efficiency in production and transportation. It also facilitates sourcing from sustainable suppliers and minimizes the carbon footprint of logistics operations.
6. What role does cross-functional collaboration play in supply chain and planning?
Cross-functional collaboration ensures that all departments are aligned with the expectations and work towards common objectives. It improves communication, enhances visibility, and creates more accurate and efficient plans.
7. What is supply chain planning?
Supply Chain Planning is the process of organizing and managing the flow of goods, information, and money from suppliers to customers. It involves forecasting demand, planning production, managing inventory, and scheduling deliveries to make sure products are available when and where customers need them, while keeping costs low.
8. What is SAP planning strategy?
SAP Planning Strategy (in SAP ERP or S/4HANA) is a set of rules or methods that tell the system how to plan production and inventory for each product. It helps decide whether to make products based on customer orders (make-to-order), based on forecasts (make-to-stock), or using a mix of both. The planning strategy controls things like how sales orders and forecasts interact, how inventory is managed, and how production is triggered. You assign a planning strategy to each product in SAP, and this determines how the system plans and produces that item.