Do you find it difficult to manage your inventory? Don’t worry, you are not alone. Almost half of all companies find it hard to optimize their assets and prevent theft, defects, or cyberattacks. Hence, the demand for RFID asset tracking is huge. You might be thinking – How does RFID tracking work? Fret not, we have you covered.
RFID technology collects important data about your assets that can be used to enhance your inventory management. The right use of tracking technology will help you increase the efficiency of your business.
Without further ado, let’s get to the details of the technology and understand its types, benefits, and more.

What is RFID Tracking?- A Closer Look
RFID asset tracking is a technological system to monitor and manage the physical assets of an organization. The core part of the technique includes using tags. The tags are small electronic devices that store and transmit data via radio waves. Asset tracking is a powerful technology that enables organizations to monitor and manage physical assets efficiently through the use of tags.
Asset tracking is an automated process where the attached tag sends all the relevant information to a server thereby saving time and increasing efficiency. The data includes information like the name of the machinery, condition, physical location, and amount.
Before you understand how does RFID tracking work, let’s try to get clear about the different types of RFID tags.
Different Types of RFID Tags- The Complete List
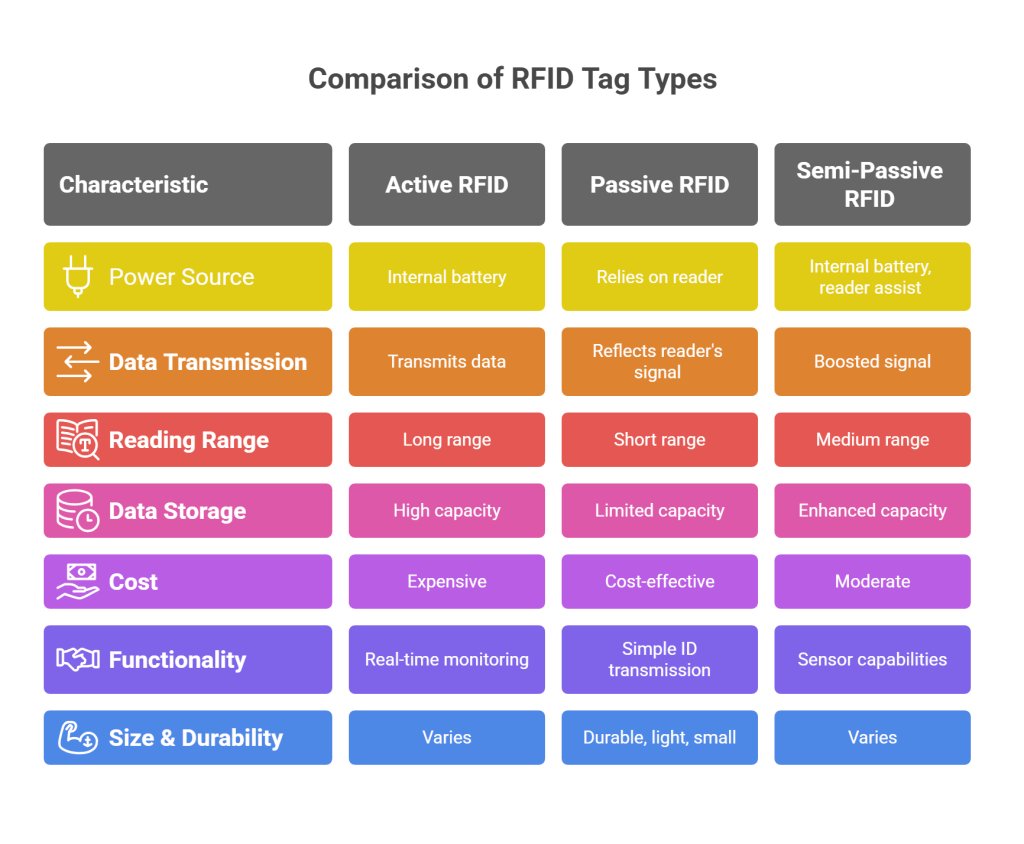
RFID technology is not a new concept and has been around for decades. When it comes to asset management RFID tracking, there are three types of tags that have different working mechanisms. Here is the complete list.
1. Active RFID Tags
Active tags have an internal power source like a battery that allows them to operate independently. They are consistent and have an extended frequency range. Active tags transmit their data to RFID readers. The reading range lies anywhere between a few meters to several hundred meters. Here are a few features of the tags.
- Tags operate without relying on external power source
- They can continuously transmit data and help in real-time monitoring and tracking.
- The tags store more data related to the condition and temperature of an asset through the systematic use of sensors. Active tags are suitable for applications requiring massive data collection.
- They are able to transmit dynamic updates regarding the status of your inventory at regular intervals. For example, an alert is sent off immediately if any asset leaves its specified area.
- RFID tags are expensive due to the added cost of batteries and electronics. However, they provide the benefit of a long reading range and better functionality.
2. Passive RFID Tags
Passive tags do not have their own power source. They rely on RFID readers to send data using their radio waves. Here are some basic features of a passive tag.
- Passive tags do not have batteries and they are durable, light, and small. They do not rely on limited power sources.
- The tag uses radio-frequency waves from a reader or a scanner to transmit its unique ID and data back to the system.
- These tags are simple to recharge and have a small reading range.
- Passive tags do not complicated designs, so it’s easier to deploy them in large-scale applications and they are cost-effective.
- These tags are available in different sizes making them adaptable and flexible. For instance, a passive tag can be the size of a small grain or as big as a credit card.
3. Semi-Passive RFID Tags
Semi-passive tags have characteristics of both active and passive tags. These tags have their own internal power source but still rely partially on a reader’s energy to operate. Sei-passive tags are developed to provide benefits that neither passive nor active tags can deliver. Lister below are the semi-passive RFID features.
- Semi-passive tags use batteries to power sensors, data storage, and other components.
- The batteries give the tags added functionalities like environment sensors, motion sensors, and real-time calendar or clock functions.
- Semi-tags have a better reading range than passive tags. The battery boosts the tag’s response signal allowing it to read a greater distance from the reader.
- The tags are cheaper than active tags as they do not need large batteries to transmit data back to the scanner or reader.
Now, that you know the different types of tags and their basic functionalities, it’s time to circle back to the question – How does RFID tracking work?
Let’s look at the inner mechanism of technology in asset tracking.
How Does RFID Tracking Work?
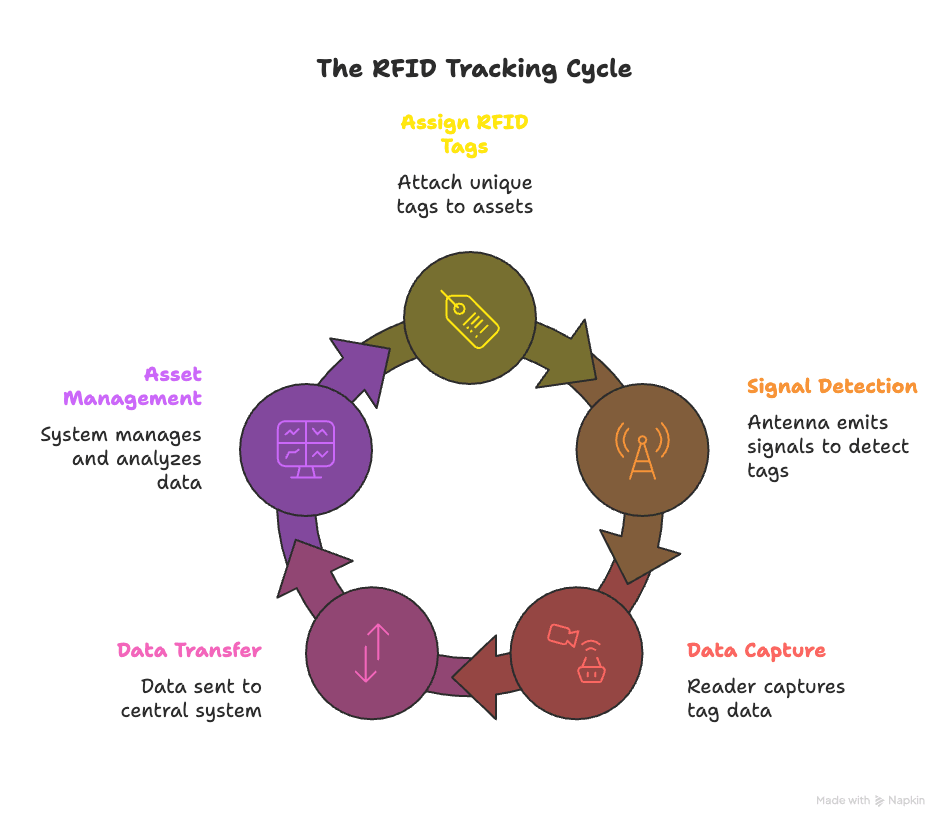
If you are wondering how does rfid tracking work, the process involves RFID tags, readers, antennas, and a centralized system to detect and manage asset information. Irrespective of the industry, the basic working principle of an tag is the same. The answer to the question – how does tracking work depends on the following 4 components.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology used to track and manage assets using radio waves. The fundamental principles behind RFID tracking remain consistent across industries such as retail, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. Here’s a clear, step-by-step breakdown of the process.
The Four Essential Components of RFID Tracking
- RFID Tags
Small devices affixed to assets, each storing unique electronic data about the item. - RFID Reader (or Scanner)
A device that detects and reads the information transmitted from RFID tags. - Antenna
Facilitates communication between the tag and the reader, transmitting signals to locate nearby tagged assets. - Centralized Computer System with Asset-Tracking Software
Securely collects, manages, and analyzes the data from the reader, allowing for asset tracking and management.
Step-by-Step Process of RFID Tracking
To understand how does rfid asset tracking work, it’s essential to look at the components involved and the data flow from tag to software.
- Step 1: Assigning RFID Tags to Assets
Each RFID tag is programmed with a unique identifier linked to a specific asset. These details might include the asset’s type, location, and history. - Step 2: Signal Detection
The antenna emits radio signals. When an RFID tag enters its detection range, it receives the signal and responds, transmitting its stored information. - Step 3: Data Capture and Reading
The RFID reader receives the reply from the tag via the antenna and extracts the unique asset data encoded on the tag. - Step 4: Data Transfer and Asset Management
The data from the reader is sent to a centralized software system, which organizes and displays the information, providing real-time status updates and asset locations.
The Value of RFID Tracking
Explaining how does rfid location tracking work, antennas send radio signals that trigger tags to transmit their location data back to readers for real-time tracking.
Understanding how tracking works empowers organizations to:
- Gain instant visibility into asset status and location
- Collect data automatically, minimizing errors
- Enhance security and improve accountability
- Streamline workflows through efficient asset monitoring
This process helps businesses maintain control over their assets, optimize inventory management, and improve decision-making throughout the supply chain.
You know the mechanism and the importance of RFID technology. So, let’s move to the benefits of RFID asset tracking.
Benefits of RFID Tracking System
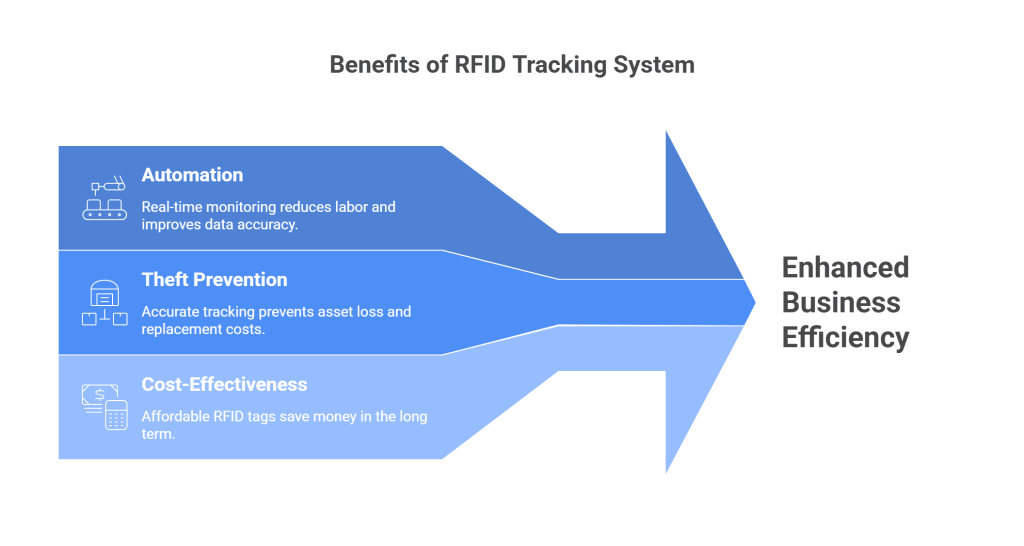
Physical assets are the core part of your business. That’s why maintaining a proper tracking system will allow you to meet the increasing expectations of customers and stakeholders. Systematic asset management helps you reduce overhead expenses, build trust, maximize product efficiency, and improve customer experience. That said, take a look at the key benefits of an RFID tracking system.
1. Automation
Businesses need to adapt fast and reduce labor time. Automated tracking systems like RFID tags monitor the movement of goods in real-time. This allows asset managers to get accurate updates from the asset tracking database. The entire data collection process is automated, so there is no human intervention.
Asset managers can track the stock levels, supply chain, shipment of goods, and costly delays in operations. This eliminates the need for manual spreadsheets that save employee labor and improve productivity.
2. Prevent Theft and Loss of Assets
Replacing physical assets is not easy and it takes away all the revenue of businesses. Many assets get lost, misplaced, or stolen which can cause serious damage to the daily operations of your business. Deploying RFID readers and antennas throughout multiple checkpoints of your inventory helps to track the exact location of your assets.
Accurate location data prevents replacement costs and improves the efficiency of your business.
3. Return on Investment( ROI)
Tags are cheaper so all types of businesses can deploy the tools. It is cost-effective, long-lasting, and has revolutionized the manufacturing, logistics, and retail industries. The tags and the software are easy to install and will help you save money in the long term.
Conclusion
To conclude, RFID is an important cog in your business wheel. Ask yourself – How does RFID tracking work? This can help you get a clear picture of your business operations. The technology is highly effective in asset management, streamlining daily workflows, and improving employee performance.
Do you want to integrate RFID solutions into your business? Get in touch with Qodenext to take your asset management to the next level.
Also read: What is Shipping Label and how it works?
To summarize, tags are a boon for businesses to become agile and efficient. Now, let’s move to frequently asked questions about how does tracking work.
FAQs – How Does RFID Tracking Work?
1. Can mobile phones detect RFID?
Yes, smartphones with NFC (Near-Field Communication) functionality can detect certain types of RFID devices, particularly those operating in compatible frequency ranges such as high frequency (HF). NFC-equipped phones typically cannot read UHF RFID tags, which are more common in industrial asset tracking.
2. What is the lifespan of RFID tags?
Tags are engineered for durability, with passive tags often lasting 10–20 years or more under normal operating conditions. However, the actual lifespan depends on environmental factors such as exposure to sunlight, temperature extremes, and mechanical wear.
3. What can interrupt or interfere with RFID?
Common sources include heavy metals, water, harsh chemicals, electromagnetic interference from nearby equipment, and overheating. Proper tag selection and placement help mitigate these issues.
4. Is RFID better than GPS for asset tracking?
RFID and GPS serve different purposes. RFID is more cost-effective for indoor asset tracking or when tracking assets within defined areas, while GPS is suited for outdoor, long-distance tracking. The best technology depends on your specific business needs.
5. How accurate is RFID tracking?
Accuracy depends on several factors including tag type, reader quality, antenna placement, and the surrounding environment. Passive RFID typically tracks assets precisely within a defined zone, but cannot provide exact “X, Y” coordinates like GPS.
6. Can RFID tags be reused and reprogrammed?
Most tags (especially passive and semi-passive types) can be reprogrammed and reused, provided they remain intact and functional. This feature enables flexibility and cost savings over time.
7. How many RFID tags can be read at once?
RFID systems can read hundreds of tags per second, making them ideal for bulk inventory operations. Anti-collision protocols in modern readers ensure efficient multi-tag capture without significant performance loss.
8. Where is RFID asset tracking used?
RFID systems are widely used in retail, manufacturing, healthcare, supply chain logistics, access control, and even in tracking livestock or library books. Essentially, any sector that needs quick, accurate, and contactless identification of assets benefits from RFID.
9. What information is stored on an RFID tag?
Tags typically store a unique asset ID, but may also include data like asset name, status (e.g., condition, maintenance records), last known location, and manufacturer. More advanced tags can handle sensor data such as temperature or motion.
10. What are the main limitations or challenges with RFID?
Key challenges include signal interference, tag placement issues, environmental obstacles, varied read ranges, interoperability among different standards, and upfront costs for system implementation. Careful planning and site surveys help overcome these drawback







