Exploring the realm of effective supply chain management and inventory control, this blog delves into the pivotal domain of Good Warehousing Practices (GWP). In the dynamic landscape of modern business, optimizing warehouse operations has emerged as a strategic imperative.
This comprehensive guide navigates through GWP’s principles, strategies, and methodologies, illuminating how businesses can enhance efficiency, minimize errors, and ensure regulatory compliance within their warehousing processes.
From inventory optimization to streamlined workflows, join us to unravel the core facets of Good Warehousing Practices that empower organizations to achieve operational excellence and maintain a competitive edge.

GWP Meaning in Warehouse
Good Warehousing Practices (GWP) refer to the set of guidelines and procedures established to ensure efficient, safe, and organized warehouse operations. These practices are crucial for maintaining product quality, inventory accuracy, and overall operational excellence within a warehouse environment.
Some of the key features of GWP are listed below :
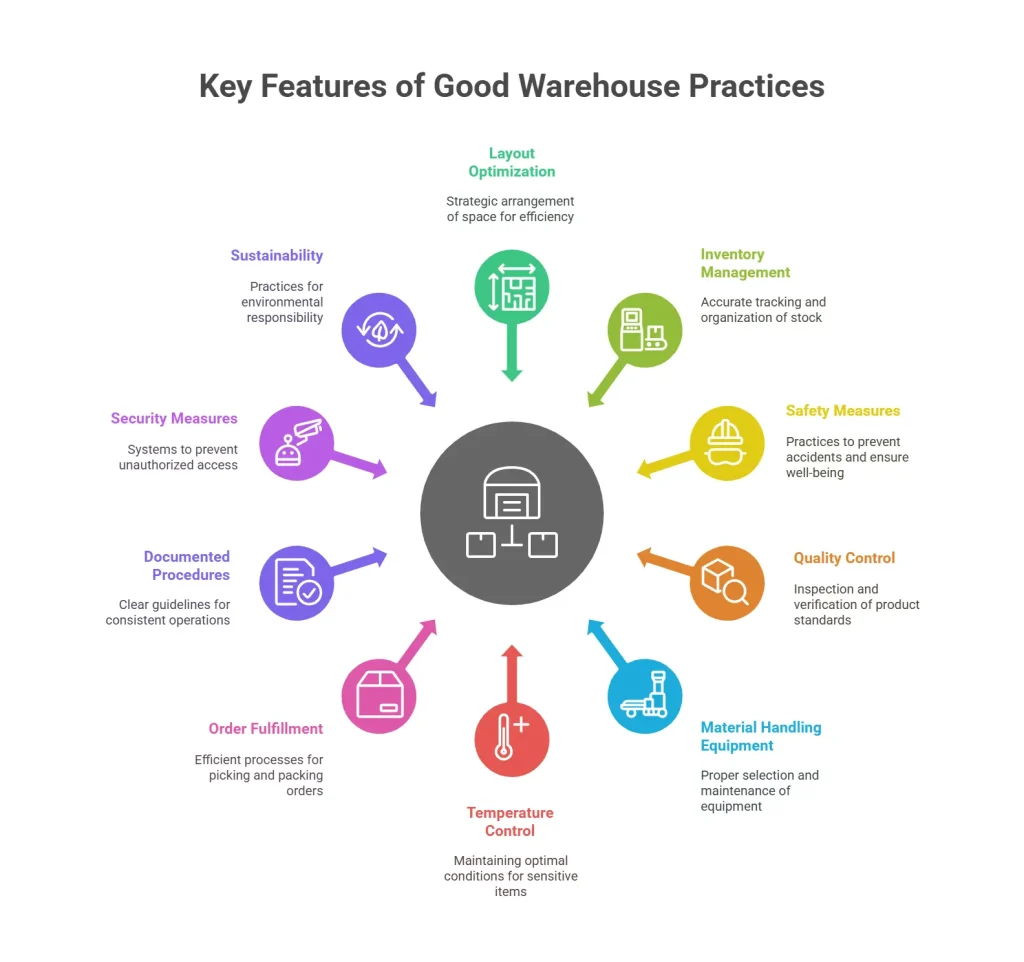
1. Layout and Space Utilization
A well-designed warehouse layout optimizes space utilization by strategically arranging storage areas, aisles, and workstations. By minimizing unnecessary travel distances and maximizing storage density, warehouse operations become more efficient. This layout also ensures that products with varying storage requirements (such as temperature-sensitive items or hazardous materials) are appropriately segregated and stored.
2. Inventory Management
Effective inventory management involves accurate tracking of stock levels, recording incoming and outgoing products, and utilizing modern inventory management software. Proper labeling, barcoding, and categorization of items simplify the retrieval process, reducing errors and delays. Regular cycle counts and occasional physical inventories maintain inventory accuracy and help identify discrepancies.
3. Safety Measures
Implementing safety practices is paramount in preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of warehouse personnel. This includes providing proper training on equipment usage, emergency procedures, and the safe handling of materials. Regular safety audits, fire drills, and hazard assessments help maintain a safe environment. Adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) should also be provided and used.
4. Quality Control
Quality control measures involve inspecting incoming products for damage, verifying their accuracy against purchase orders, and checking for defects. Implementing quality assurance processes ensures that only products meeting the required standards are accepted into the warehouse. Regular quality checks during storage and before shipment help maintain the integrity of the products.
5. Material Handling Equipment (MHE)
Selecting the right material handling equipment based on the type of products and layout is crucial. Proper training for operators is essential to prevent accidents and product damage. Routine maintenance of equipment ensures their optimal functioning, reducing downtime and minimizing disruptions to operations.
6. Temperature and Humidity Control
For warehouses storing temperature-sensitive items such as perishable goods or pharmaceuticals, maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels is critical. This might involve utilizing climate-controlled zones, monitoring systems, and emergency backup systems to prevent temperature fluctuations that could compromise product quality.
7. Order Fulfillment
Efficient order fulfillment processes involve strategic product placement, clear picking and packing instructions, and streamlined workflows. Technologies such as pick-to-light systems or voice-guided picking enhance accuracy and speed during order picking. Proper packing methods safeguard products during transit, reducing the likelihood of damage.
8. Documented Procedures
Well-documented procedures act as a guide for employees and ensure consistency in operations. These documents outline the steps for receiving, storing, and shipping goods, including safety protocols, quality control checks, and inventory reconciliation procedures. Clear documentation is crucial for employee training, especially for new hires.
9. Security Measures
Warehouses should be equipped with security measures like access control systems, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems. Implementing a restricted access policy prevents unauthorized personnel from entering sensitive areas. Regular inventory reconciliation and audits can help identify discrepancies that might indicate theft or other security breaches.
10. Sustainability
Implementing sustainable practices in warehouses contributes to environmental responsibility. This includes using energy-efficient lighting systems, optimizing heating and cooling, reducing waste through recycling programs, and employing eco-friendly packaging materials. Sustainability efforts not only align with social and environmental values but can also lead to cost savings over time.
By carefully incorporating these detailed features of Good Warehousing Practices, warehouses can achieve high levels of operational efficiency, product quality, and customer satisfaction. These practices collectively ensure that products are stored, handled, and shipped in a manner that preserves their value and meets customer expectations.
What Are the Good Warehousing Practices?
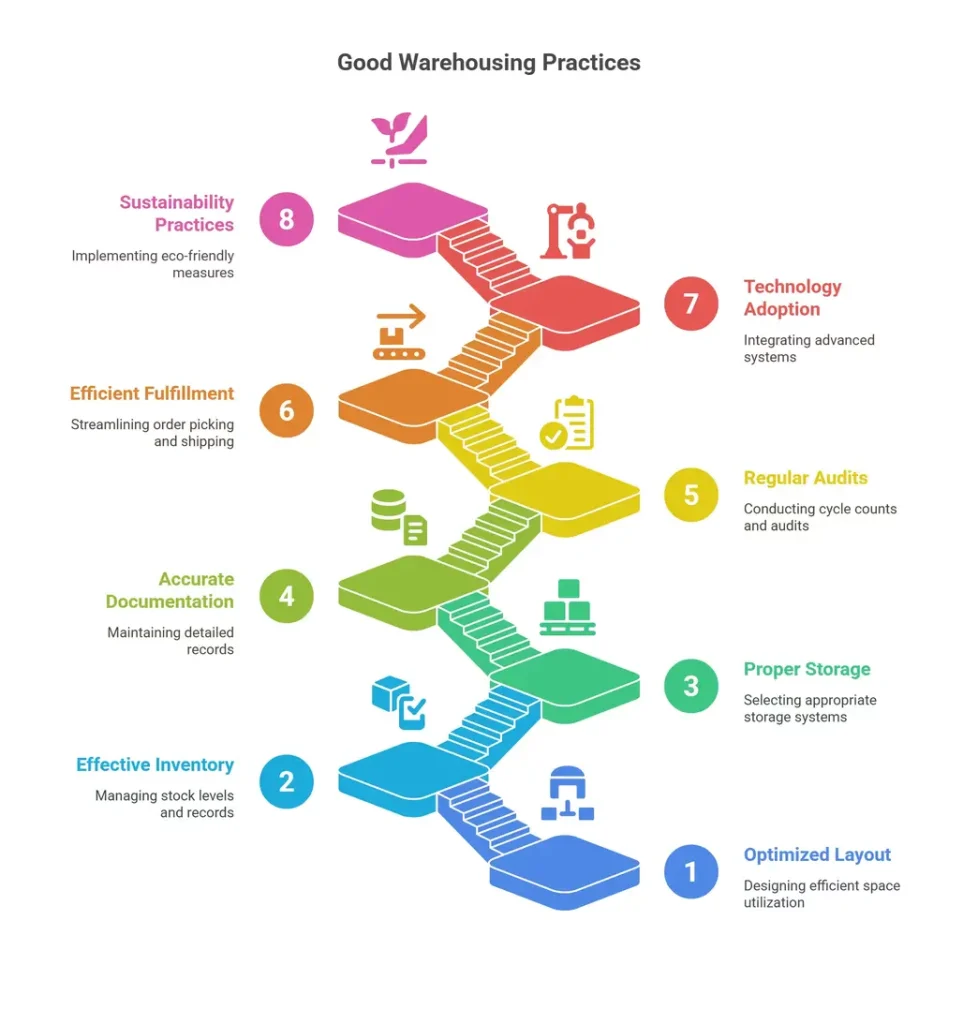
Good warehousing practices are essential for ensuring efficient and effective storage, handling, and distribution of goods. These practices help optimize space utilization, maintain product quality, and streamline operations. They involve proper inventory management, organized storage systems, effective communication, stringent safety measures, and adherence to regulatory standards.
By implementing these practices, warehouses can enhance productivity, minimize errors, reduce costs, and ultimately contribute to the overall success of supply chain management. Some of the key good warehousing practices are listed below :
1. Optimized Layout and Space Utilization
Designing an optimized layout involves analyzing product characteristics, demand patterns, and workflow to determine the most efficient arrangement. Employ techniques like ABC analysis to prioritize high-demand items for easy access. Utilize vertical space with mezzanines or multi-level racks. Create clear aisles and traffic paths to prevent congestion. Incorporate receiving and shipping areas that minimize cross-traffic and reduce handling.
2. Effective Inventory Management
Implement a combination of periodic and perpetual inventory counting methods. Utilize automated inventory systems to monitor stock levels in real-time. Set up reorder points to trigger replenishment orders. Implement safety stock for fluctuating demand. Use FIFO (First-In-First-Out) or FEFO (First-Expired-First-Out) methods for perishable goods. Maintain accurate records of SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) details, including dimensions, weight, and storage requirements.
3. Proper Storage Systems
Select storage systems that match the specific needs of your products. Pallet racking suits items with palletized loads, while bin shelving organizes smaller items. Use flow racks for high-turnover items, ensuring the oldest stock is picked first. Utilize cantilever racks for long or bulky items. Implement temperature-controlled storage for perishables or sensitive products.
4. Accurate Documentation
Detailed documentation includes receiving reports, put-away records, pick lists, packing slips, and shipping manifests. Each stage of the process should be documented accurately and in real-time. Barcode scanning and RFID technology can automate data entry, reducing manual errors. Maintain electronic records to facilitate quick retrieval and analysis of historical data.
5. Regular Cycle Counts and Audits
Perform regular cycle counts to reconcile discrepancies between recorded and actual inventory levels. Implement a cycle counting plan that covers all items over a specific timeframe. Conduct full physical audits periodically to ensure complete accuracy. Investigate discrepancies to identify root causes, such as data entry errors, theft, or damaged goods.
6. Efficient Order Fulfillment
Optimize order picking strategies based on order volume and item characteristics. Batch picking groups orders with similar items, minimizing travel time. Zone picking assigns specific areas to individual pickers, reducing congestion. Implement pick-to-light or pick-to-voice systems to guide pickers accurately. Consider wave picking for combining orders and minimizing trips.
7. Advanced Technology Adoption
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) integrate various operations, including inventory management, order processing, and shipping. Implement RFID or barcode scanning for real-time tracking of goods. Automated conveyors, sortation systems, and robotic picking improve order accuracy and reduce labor costs. TMS streamlines transportation by optimizing routes and carrier selection.
8. Employee Training and Safety
Comprehensive training covers equipment operation, safety protocols, emergency procedures, and proper material handling techniques. Conduct regular safety training sessions to reinforce best practices. Equip employees with personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensure proper equipment maintenance. Establish safety committees to address concerns and continuously improve safety measures.
9. Quality Control
Implement quality checks upon receiving goods to identify any damage or discrepancies against purchase orders. Inspect products for defects, expiration dates, and compliance with quality standards before shipment. Use sampling techniques for large quantities. Document quality control processes and outcomes for reference and improvement.
10. Sustainability Practices
Integrate sustainability into every aspect of warehousing. Use energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems. Implement waste segregation and recycling programs for packaging materials. Collaborate with suppliers to minimize excess packaging. Optimize transportation routes to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions. Evaluate opportunities for renewable energy sources, such as solar panels.
By meticulously implementing and customizing these detailed warehousing practices, businesses can achieve operational excellence, maintain high customer satisfaction, adapt to changing market demands, and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient supply chain ecosystem.
Conclusion
Embracing Good Warehousing Practices (GWP) and efficient supply chain management is paramount. These practices optimize storage and distribution processes and ensure product quality and safety. By adhering to GWP, companies can reduce operational errors, minimize inventory discrepancies, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, as businesses strive for excellence in warehousing, solutions like Qodenext emerge as invaluable assets. Qodenext’s expertise in streamlining warehousing operations, implementing advanced tracking systems, and offering data-driven insights makes it a pivotal partner in achieving GWP. Elevate your warehousing practices with Qodenext – a step toward precision, reliability, and success.
FAQs: Good Warehousing Practices (GWP)
1. What are Good Warehousing Practices (GWP)?
Good Warehousing Practices (GWP) are a set of standardized procedures and guidelines that ensure efficient, safe, and organized storage, handling, and distribution of goods within a warehouse.
2. Why are Good Warehousing Practices important?
GWP helps maintain product quality, minimize errors, ensure employee safety, improve inventory accuracy, and enhance overall warehouse efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3. What role does warehouse layout play in GWP?
A well-planned layout maximizes space utilization, reduces unnecessary movement, ensures smooth workflow, and accommodates different product requirements like temperature-sensitive or hazardous materials.
4. How does GWP help in improving inventory management?
GWP ensures accurate stock tracking through barcoding, labeling, real-time inventory systems, and regular audits—minimizing stockouts, overstocking, and inventory discrepancies.
5. What safety measures should be implemented in a warehouse?
Warehouses should include safety training, proper use of PPE, regular audits, hazard assessments, fire drills, and clear emergency protocols to prevent accidents and protect staff.
6. How do Good Warehousing Practices ensure product quality?
GWP includes quality control checks during receiving, storage, and dispatch to ensure only defect-free, accurate, and undamaged goods are handled and delivered.
7. What is the role of Material Handling Equipment (MHE) in GWP?
MHE helps in safely and efficiently moving products. Proper equipment selection, operator training, and maintenance reduce product damage and operational delays.
8. How does GWP contribute to faster order fulfillment?
GWP enhances order picking accuracy and speed through smart placement strategies, picking technologies like voice picking or pick-to-light, and standardized packing processes.
9. What documentation is required in warehousing operations?
Key documents include receiving logs, inventory records, pick lists, packing slips, and shipping manifests, all of which ensure transparency, traceability, and consistency.
10. Are sustainability practices part of GWP?
Yes, GWP encourages eco-friendly practices like energy-efficient lighting, recycling programs, optimized HVAC use, and sustainable packaging to reduce environmental impact and cost.






