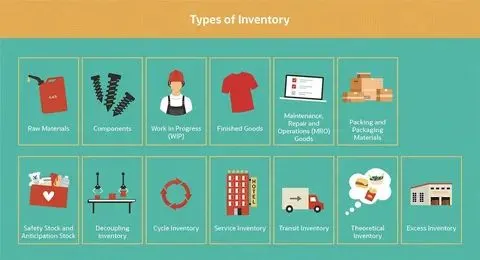
Inventory control is a crucial aspect of any business that deals with the production, distribution, or sale of physical goods. Effective inventory management ensures that a company has the right amount of stock on hand to meet customer demand while minimizing costs associated with holding excess inventory. There are various types of inventory control systems and methods available to businesses, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
In this blog, we will explore the different types of inventory control systems and methods, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages, to help businesses make informed decisions about which approach is best suited for their needs. Whether you are a small business owner or a large-scale manufacturer, this blog will provide valuable insights to optimize your inventory management practices and improve your bottom line.
What Do You Mean by Inventory Control?
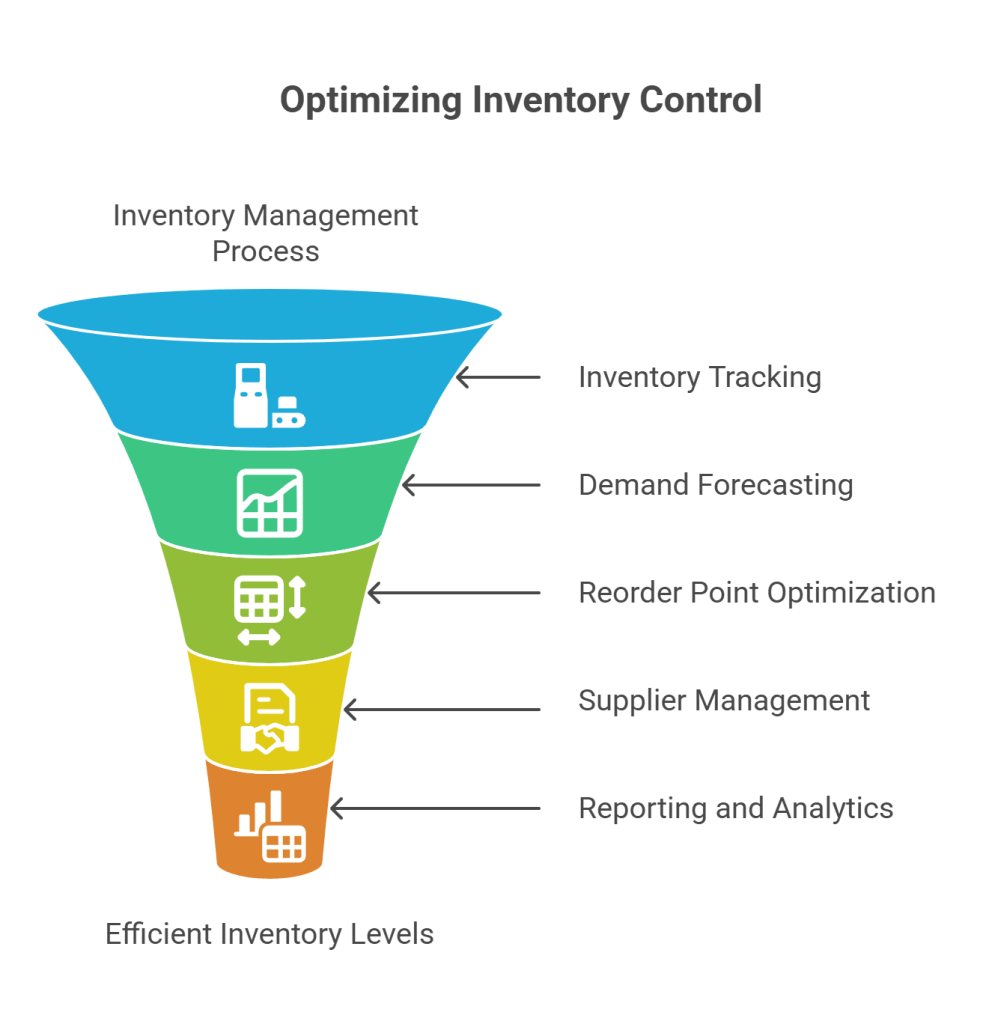
Inventory control refers to the process of managing and monitoring the flow of goods and materials in a business. It involves tracking inventory levels, determining reorder points, and optimizing inventory turnover to minimize costs and ensure that the business always has enough stock on hand to meet customer demand.
Effective inventory control helps businesses avoid stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and improve their overall efficiency. Some of the top features of inventory control include:
- Inventory tracking: This involves monitoring inventory levels in real time and keeping track of inventory movements, such as receipts, transfers, and sales. By tracking inventory levels, businesses can ensure they have enough stock on hand to meet customer demand, avoid stockouts, and minimize excess inventory.
- Forecasting and demand planning: Accurately forecasting demand is crucial to optimizing inventory levels and ensuring that businesses have enough stock on hand to meet customer demand without overstocking. Demand planning involves analyzing past sales trends, current market conditions, and other factors to predict future demand and plan inventory accordingly.
- Reorder point optimization: Determining the optimal reorder point helps businesses avoid stockouts while minimizing excess inventory. The reorder point is the inventory level at which a business needs to place an order for more stock. By optimizing the reorder point, businesses can ensure they always have enough stock on hand without overstocking and tying up cash in excess inventory.
- Supplier management: Managing relationships with suppliers is critical to ensuring the timely delivery of goods and materials and maintaining optimal inventory levels. Businesses need to develop strong relationships with their suppliers and negotiate favorable terms to ensure they receive timely deliveries of high-quality goods and materials at the best possible prices.
- Reporting and analytics: Inventory control software typically provides a range of reporting and analytics tools that help businesses track key metrics such as inventory turnover, stockouts, and excess inventory. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs. Reporting and analytics also help businesses track the effectiveness of their inventory control processes and make adjustments as needed.
Popular Types of Inventory Control
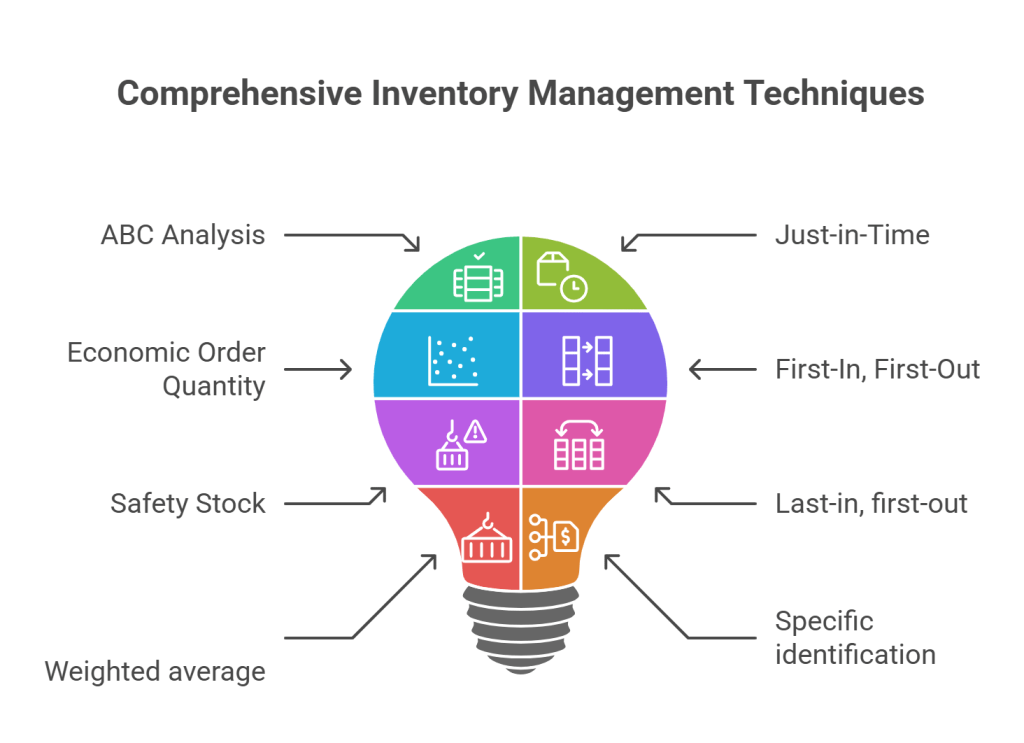
Inventory control refers to the process of managing the inventory levels of a company. Effective inventory control can help businesses save money and improve their operational efficiency. There are several types of inventory control methods that businesses can use to manage their inventory levels. Here are the top 5 types of inventory control:
- ABC Analysis: ABC analysis is a technique that helps businesses prioritize their inventory items based on their importance. This technique categorizes inventory items into three groups: A, B, and C, based on their value. A-items are high-value items that account for a large percentage of the total inventory value, while B-items are moderate-value items that account for a moderate percentage of the inventory value, and C-items are low-value items that account for a small percentage of the total inventory value. By prioritizing inventory items based on their importance, businesses can focus on managing the most important items while reducing the risk of stockouts.
- Just-in-Time (JIT): Just-in-Time inventory control is a technique that involves ordering inventory only when it is needed. JIT helps businesses reduce inventory holding costs and improve cash flow. This technique requires a high level of coordination between the supplier and the business, as inventory is only ordered when it is needed and must be delivered promptly. By implementing JIT, businesses can improve their supply chain efficiency and reduce the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Economic Order Quantity is a formula that helps businesses determine the optimal order quantity for a given item. The formula takes into account the cost of placing an order, the cost of holding inventory, and the demand for the item. The goal of EOQ is to find the order quantity that minimizes the total cost of ordering and holding inventory. By using EOQ, businesses can reduce their inventory holding costs while ensuring that they always have enough inventory on hand to meet demand.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO): First-In, First-Out is an inventory control method that assumes that the first items purchased are the first items sold. This technique is commonly used for perishable items or items with a limited shelf life. By using FIFO, businesses can ensure that they are selling the oldest items first, reducing the risk of spoilage or expiration. FIFO is a simple and effective technique for managing inventory, especially for businesses that deal with perishable or time-sensitive items.
- Safety Stock: Safety stock is a buffer inventory that businesses keep on hand to ensure that they always have enough inventory to meet unexpected demand. Safety stock is based on the lead time for an item (the time it takes to receive an order once it has been placed) and the demand variability (the likelihood that demand will fluctuate). By keeping safety stock on hand, businesses can reduce the risk of stockouts and ensure that they always have enough inventory to meet demand, even in the case of unexpected spikes in demand.
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO): This method assumes that the last items purchased are the first items sold. In other words, the most recently acquired inventory is sold first. LIFO is commonly used in industries where the cost of goods is rising, such as the oil and gas industry. LIFO results in a lower valuation of inventory, as the cost of goods sold is based on the most recent and therefore highest-priced items in stock. This can result in a lower tax burden, as the profit margin is lower due to the higher cost of goods sold.
- Weighted average: This method takes the average cost of all inventory items in stock and applies it to the cost of goods sold. This method is useful for companies with large inventories of identical items. Weighted average results in a moderate valuation of inventory, as the cost of goods sold is based on the average price of all items in stock. This method can result in a more stable profit margin, as it smooths out fluctuations in the cost of goods sold.
- Specific identification: This method identifies the cost of each item in stock and applies it to the cost of goods sold. This method is useful for companies with a small number of high-value items in stock. Specific identification results in the most accurate valuation of inventory, as the cost of goods sold is based on the actual cost of each item in stock. This method can result in a more volatile profit margin, as it is subject to fluctuations in the cost of individual items.
In summary, each of these inventory control techniques offers unique benefits and can help businesses manage their inventory levels more effectively. By implementing one or more of these techniques, businesses can reduce inventory holding costs, improve cash flow, and ensure that they always have enough inventory on hand to meet demand.
Conclusion
Inventory control is an essential component of efficient supply chain management, and there are various types of inventory control methods used by businesses. These include just-in-time (JIT), first-in, first-out (FIFO), and last-in, first-out (LIFO) among others. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the most appropriate approach depends on the nature of the business.
Qodenext’s SETU is a cloud-based inventory management system that can help businesses automate and streamline their inventory control processes. It offers features such as real-time inventory tracking, automated reorder points, and advanced analytics that provide insights into inventory performance. With Qodenext SETU, businesses can optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Contact Qodenext today and take the first step in improving your inventory control.
FAQ’s-Types of Inventory Control and Methods
1. What is inventory control and why is it important?
Inventory control refers to the process of monitoring and managing a company’s stock levels to ensure the right quantity of goods is available to meet customer demand. It helps minimize excess inventory, prevent stockouts, and optimize the overall supply chain. Effective inventory control leads to reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, and better operational efficiency.
2. What are the key features of a good inventory control system?
A robust inventory control system typically includes features such as:
- Inventory tracking in real-time
- Forecasting and demand planning based on sales trends
- Reorder point optimization to avoid stockouts
- Supplier management for timely procurement
- Reporting and analytics to monitor performance and identify inefficiencies
These components work together to ensure a balanced inventory approach that supports business growth.
3. What is ABC analysis and how does it help in inventory management?
ABC analysis categorizes inventory into three groups based on their value:
- A-items: High-value products with low frequency
- B-items: Moderate-value, moderately used
- C-items: Low-value, high-frequency items
By focusing more resources and attention on A-items, businesses can optimize stock control for their most critical inventory, reducing overall holding costs and improving service levels.
4. How does the Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory method work?
Just-in-Time (JIT) is an inventory strategy where stock is ordered and received only when needed for production or sales. It minimizes holding costs and frees up warehouse space. However, JIT requires excellent coordination with suppliers to avoid delays or stockouts. It’s best suited for stable production environments with predictable demand.
5. What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and why is it used?
EOQ is a mathematical formula used to determine the most cost-effective order quantity by balancing the cost of ordering and holding inventory. It helps businesses:
- Avoid overstocking or understocking
- Minimize total inventory costs
- Ensure smooth operations by maintaining optimal stock levels
EOQ is especially useful for items with regular demand patterns.
6. What is the difference between FIFO and LIFO methods?
- FIFO (First-In, First-Out) assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, which is ideal for perishable goods or items with a shelf life.
- LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) assumes the most recently added inventory is sold first. It is often used in industries facing rising costs, as it reduces taxable income by attributing higher costs to goods sold.
The choice between FIFO and LIFO depends on product type, accounting practices, and industry regulations.
7. What is safety stock and how is it calculated?
Safety stock is extra inventory maintained to prevent stockouts caused by demand variability or supplier delays. It is calculated based on:
- Average demand during lead time
- Variability in demand and lead time
- Desired service level
Keeping safety stock helps businesses remain resilient during supply chain disruptions and ensures product availability.
8. What is the weighted average inventory method?
The weighted average method assigns an average cost to all units in stock, regardless of purchase date. It’s suitable for businesses with homogeneous products or large quantities of similar items. This method simplifies accounting and provides a stable view of inventory value over time.
9. When is specific identification used in inventory control?
Specific identification tracks the actual cost of each inventory item individually. It is typically used for high-value, low-volume items such as luxury goods, machinery, or vehicles. This method provides the most accurate valuation of inventory but requires detailed tracking and is not practical for large-scale operations.
10. How can Qodenext SETU help in optimizing inventory control?
Qodenext SETU is a cloud-based inventory management system designed to streamline inventory control processes. It offers:
- Real-time inventory visibility
- Automated reorder points
- Supplier coordination tools
- Data-driven analytics for inventory optimization
With SETU, businesses can improve inventory accuracy, reduce holding costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability when and where it’s needed.






