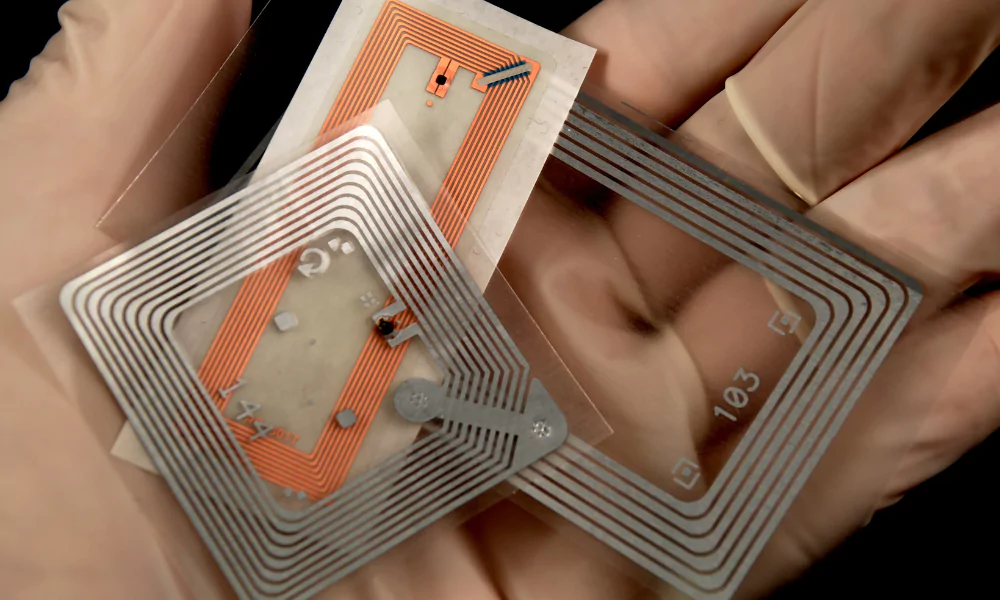
Tiny RFID tags, like smart stickers, are transforming inventory management. These tags have chips and antennas that use radio waves to unlock information about what they’re attached to.
They can send data wirelessly, so you don’t need a direct scan, and each tag has a unique code for computers to track easily. But RFID’s reach extends far beyond inventory.
These versatile tags come in various forms, passive tags, active tags, and semi-passive tags. Naturally, their uses spread over various markets and jobs, and this blog is all about them.
This blog talks about the different types of RFID tags and their uses around the warehouse. First, let’s understand how it works. Then, we’ll delve into tag types, functionalities, and their impact on warehouse management.
Let’s begin!
How Does an RFID System Work?
Behind the scenes of efficient inventory management lies RFID technology. This system utilizes radio waves to streamline object identification and data capture. It works like a well-managed team, here’s a detailed breakdown of its core components and how they work:
1. RFID Tags
Tags act as miniature data carriers, often resembling small stickers. Embedded with chips and antennas, they store relevant information and transmit it wirelessly upon receiving a radio signal.
2. RFID Readers
Functioning as interrogators, these devices emit radio waves to activate tags within their range. Once activated, the tag transmits its data back to the reader. Readers can be fixed or mobile depending on the application.
3. Antenna
This component serves as a bridge for communication, transmitting and receiving radio waves between the reader and the tag.
There are different types of readers based on their frequencies. Let’s explore some of them next.
Frequency in RFID Tags
RFID technology operates across different frequencies, each with its advantages and limitations. Low Frequency (LF) RFID systems, spanning 30KHz to 300KHz, offer short reading ranges but excel in environments with metals or liquids.
However, the size of these waves, also known as frequency, plays a crucial role in an RFID system’s performance. Here’s a breakdown of the three main frequency bands used in RFID technology, each offering advantages and disadvantages:
1. Low Frequency (LF) RFID
- Frequency Range: 30KHz to 300KHz (commonly 125 KHz or 134 KHz)
- Reading Range: Short (around 10 cm)
- Reading Speed: Slow
- Interference Resistance: Very high
Pros: Excellent resistance to external interference from metal or liquids, making it ideal for harsh environments.
Cons: Limited reading range and slow data transmission restrict its use to applications requiring short-range identification, such as access control systems or animal tags. Additionally, the lack of a global standard can create compatibility issues.
2. High Frequency (HF) RFID
- Frequency Range: 3 to 30 MHz (commonly 13.56 MHz)
- Reading Range: Moderate (between 10cm and 1 meter)
- Reading Speed: Moderate
- Interference: Moderately affected by metals and liquids
Pros: Offers a balance between reading range and data speed compared to LF. Commonly used for ticketing, payments, and data transfer applications, such as contactless cards.
Cons: More susceptible to interference than LF, limiting its effectiveness in certain environments. The reading range is still relatively short compared to UHF.
3. Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID
- Frequency Range: 300MHz to 3GHz (commonly 860 to 960 MHz, with regional variations)
- Reading Range: Long (up to 12 meters or more)
- Reading Speed: Very fast
- Interference: Highly susceptible
Pros: UHF boasts the longest reading range and fastest data transmission speed among the three frequencies. This makes it ideal for large-scale inventory management, supply chain tracking, and applications requiring long-distance identification.
Additionally, advancements in technology have improved UHF tag performance in environments with potential interference from metals or liquids. UHF also benefits from a global standard (EPC Global Gen2) ensuring broader compatibility.
Cons: Susceptible to interference, requiring careful system design for optimal performance in complex environments. Compared to LF and HF tags, UHF tags are generally cheaper and easier to manufacture.
Choosing the right RFID frequency depends on your specific application. Consider factors like reading range, data speed, interference levels, and cost to determine the optimal solution for your needs.
As technology continues to develop, we can expect further improvements in UHF performance and a wider range of applications for all RFID frequencies. Let’s next learn how the frequencies play an important role in deciding the usage of the different tags.
Types of RFID Tags Based on Frequency
Not all RFID tags are created equal! These workhorses come in three main types, each with its strengths:
1. Passive RFID Tags
The most affordable option is powered by the reader’s signal. Ideal for short-range applications like access control or item tracking in controlled environments. They operate in various frequencies (Low Frequency, High Frequency, Ultra High Frequency) depending on the specific need.
2. Active RFID Tags
In contrast to their passive counterparts, active tags pack an internal battery, allowing them to broadcast a signal continuously. This translates to significantly extended reading ranges and the ability to transmit additional sensor data, such as temperature or pressure.
Active tags typically operate in the UHF (ultra-high frequency) or microwave frequency range, catering to applications requiring long-range asset tracking or real-time monitoring in complex environments.
3. Semi-Passive RFID Tags
These tags bridge the gap between passive and active technologies. They contain a small battery that powers an internal chip, allowing them to respond to a reader’s signal with a stronger response compared to passive tags.
FAQs: Different Types of RFID Tags and their Applications
What are the major features of RFID tags?
They store unique IDs, eliminating the need for line-of-sight scanning like barcodes. They communicate wirelessly with readers, transmitting data for identification and tracking purposes. Many are very helpful in logistics operations in warehouses as well.
What is the range of RFID tags?
RFID tag range varies based on type (passive, active, semi-passive) and frequency. Passive tags have shorter ranges (cm to meters), while active tags with internal batteries offer extended ranges (tens of meters). Effective reading distance is determined by the tag-reader combination.
Can RFID tags be reused?
Reusability depends on the tag type. Generally, passive tags are disposable due to their low cost. Some active tags with replaceable batteries can be reused. However, evaluating factors like tag cost, data security needs, and environmental impact is crucial when deciding on reusability.
Can I block RFID tags?
Certain materials like metal shielding can block RFID signals, preventing readers from detecting tags. However, complete blocking depends on the shielding material, tag frequency, and reader power. RFID-blocking sleeves or wallets are available to protect specific items like credit cards containing RFID chips.
How long do RFID tags last?
The lifespan of an RFID tag depends on the type and its environment. Passive tags, often encased in epoxy, can last for years. Active tags with batteries typically have a defined lifespan based on battery life and usage patterns. The manufacturer’s specifications provide the most reliable information on individual tag durability.
Can RFID tags be used to track location?
While basic RFID tags primarily identify objects, some specialized tags can be used for location tracking. These tags might leverage additional technologies like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth to provide more precise location data within a designated area. However, traditional GPS is still more effective for outdoor, real-time location tracking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different types of RFID tags and their applications is pivotal for optimizing inventory management and enhancing operational efficiency. Passive, active, and semi-passive tags suit diverse environments and applications.
As technology evolves, RFID continues to revolutionize industries worldwide, with advancements like those offered by Qodenext empowering businesses to harness the full potential of RFID technology for streamlined operations and improved asset tracking.