Retail Supply Chain Management plays a vital role in the success of any retail business. It involves all the complex steps and plans needed to move products from the makers to the buyers in the best way. In today’s tough market, staying ahead means having a well-organized supply chain that makes the most of the stock, cuts expenses, and makes customers happier.
In this blog, we will look into Retail Supply Chain Management and highlight important methods that can greatly boost the efficiency of your retail business. From inventory optimization and demand forecasting to technology integration and sustainable practices, we’ll unravel the essential elements that can transform your retail operations into a lean, agile, and customer-centric powerhouse.

What Is Retail Supply Chain Management?
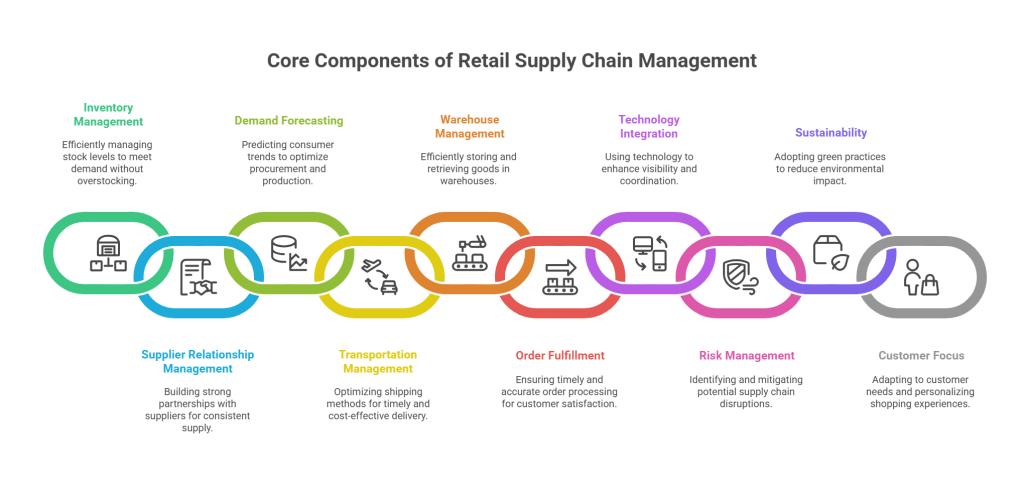
Retail Supply Chain Management involves carefully organizing, carrying out, and overseeing the movement of products and services from suppliers to retailers and, finally, to customers. It consists of a sequence of linked tasks to guarantee the smooth and economical transfer of items across different stages of the supply chain. Here are the top features of retail supply chain management in detail:
1. Inventory Management
This feature involves meticulous control over a retailer’s stock levels. Retailers must balance having enough inventory to meet customer demand without holding excessive stock that ties up capital and storage space. It necessitates sophisticated systems for tracking stock levels, real-time inventory visibility, and employing strategies such as just-in-time inventory management.
2. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
SRM is about cultivating strong, mutually beneficial partnerships with suppliers. This involves open communication, product quality and design collaboration, negotiating favorable terms, and developing contingency plans for potential disruptions in the supply chain. A robust SRM helps ensure a consistent and timely supply of goods.
3. Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting relies on historical data, market analysis, and even advanced machine learning algorithms. Retailers use these forecasts to anticipate consumer preferences and trends, adjusting their procurement, production, and inventory strategies accordingly. This minimizes the risk of stockouts and overstock situations.
4. Transportation Management
Efficient transportation management involves selecting the most cost-effective and timely shipping methods. It considers factors like shipment size, transportation mode (air, sea, road, or rail), carrier selection, route optimization, and real-time tracking to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
5. Warehouse Management
Warehouses play a pivotal role in the supply chain. Effective warehouse management includes optimizing layout, implementing automation and robotics for efficient storage and retrieval, and adopting inventory tracking systems. It ensures quick fulfillment of order while minimizing storage costs.
6. Fulfillment of Order
Timely and accurate order processing is essential for customer satisfaction. This involves streamlining order picking, packing, and shipping processes, often through automation. Retailers strive for reduced order-to-shipment times and error-free deliveries.
7. Technology Integration
Retail supply chains increasingly rely on technology for visibility and coordination. This includes using Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Transportation Management Systems (TMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, and data analytics tools to gain insights and optimize operations.
8. Risk Management
Supply chain disruptions can occur due to various factors, including natural disasters, political instability, or economic crises. Retail supply chain management involves identifying potential risks and developing contingency plans, diversifying suppliers, and maintaining safety stock to mitigate disruptions.
9. Sustainability and Green Practices
With growing environmental concerns, retailers are increasingly adopting green sustainable supply chain practices. This includes reducing waste, optimizing transportation routes to minimize emissions, and sourcing products from environmentally responsible suppliers.
10. Customer-Centric Focus
Ultimately, all supply chain efforts are aimed at satisfying customer demands. Retailers must continuously adapt to changing customer expectations, offering multiple delivery options (e.g., click-and-collect, same-day delivery) and personalizing the shopping experience through data-driven insights.
Effective retail supply chain management requires a holistic approach, combining these features into a well-coordinated and flexible strategy to adapt to market dynamics and meet customer expectations while optimizing costs and sustainability efforts.
Steps Involved in Retail Supply Chain Management
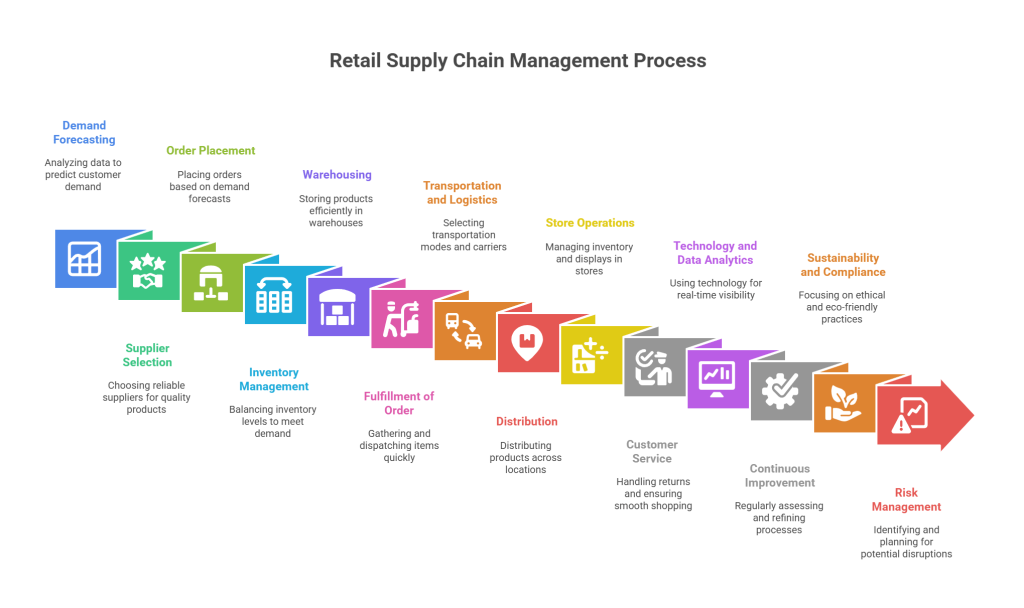
Retail supply chain management involves a series of interconnected steps to ensure the efficient flow of products from suppliers to customers. These steps are essential for meeting customer demands while minimizing costs and optimizing inventory. Below are the key steps involved in retail supply chain management:
1. Demand Forecasting
The process begins with understanding customer demand through data analysis, historical sales, market trends, and customer feedback. Accurate forecasting helps in planning inventory levels and production schedules, ensuring that a retailer can meet customer needs without overstocking or understocking products.
2. Supplier Selection and Management
Finding and partnering with trustworthy suppliers is critical. Retailers must choose suppliers who can provide quality products at fair prices and on time. Building strong supplier relationships helps ensure a consistent flow of goods and allows for collaborative problem-solving when disruptions occur.
3. Order Placement
Based on demand forecasts, retailers place orders with their chosen suppliers. The size and frequency of these orders are adjusted according to inventory turnover rates and lead times. This step is fundamental to ensuring that the right amount of stock is available when required.
4. Inventory Management
Balancing enough inventory to meet customer demand while avoiding excess stock is key. Retailers use strategies and tools such as ABC analysis and just-in-time (JIT) management to track stock levels accurately. Real-time inventory visibility is crucial in preventing overstocking that ties up capital and storage space.
5. Warehousing
After receiving shipments, products are stored in warehouses or distribution centers. Efficient warehouse management involves organizing inventory for easy retrieval, reducing order processing times, and keeping storage costs to a minimum through optimal layout designs and, often, automation.
6. Fulfillment of Order
When customers make a purchase, the retailer must quickly gather, pack, and dispatch the items. Effective order fulfillment systems, often automated, help reduce errors and ensure that products are delivered to customers on time, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
7. Transportation and Logistics
Selecting the right transportation modes and carriers is essential. Retailers consider shipment size, the cost-effectiveness of different transportation modes (air, sea, road, or rail), carrier reliability, route optimization, and real-time tracking to ensure that products reach stores or customers efficiently.
8. Distribution
Products must be distributed across various locations, whether through a central distribution center or a network of regional warehouses. Effective distribution planning ensures that inventory is available where needed, reducing lead times and travel costs.
9. Store Operations
Within retail stores, processes such as receiving deliveries, stocking shelves, and organizing displays are crucial. Store operations ensure that inventory is managed on the ground level to maintain consistent product availability and enhance the shopping experience.
10. Customer Service
Handling returns, addressing inquiries, and ensuring a smooth shopping experience are key elements of retail supply chain management. High levels of customer service build trust and loyalty while ensuring that the entire process—from order placement to delivery—is error-free.
11. Technology and Data Analytics
Modern retail supply chains rely on technology for real-time visibility and coordination. Systems such as inventory management software, RFID tags, IoT sensors, and data analytics tools help track stock levels, forecast trends, and drive informed decision-making across all stages of the supply chain.
12. Continuous Improvement
Regular assessment and refinement of supply chain processes ensure that operations remain competitive. Retailers should consistently analyse performance metrics, identify areas for cost reduction, and implement strategies that adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
13. Sustainability and Compliance
Many retailers now focus on sustainable and ethical practices. This involves sourcing products from eco-friendly suppliers, reducing waste, and complying with environmental and social regulations. Sustainable practices not only help protect the environment but also appeal to increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
14. Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying potential disruptions—such as supply shortages, natural disasters, or political instability—and developing contingency plans. By maintaining safety stock, diversifying suppliers, and leveraging technology to monitor risks, retailers can minimize the impact of unforeseen events on their operations.
When you do a good job handling these things, stores can make sure stuff comes from suppliers to buyers without any issues, save money, make customers happier, and stay competitive in the ever-changing retail world.
Strategies to Improve Your Retail Business Efficiency
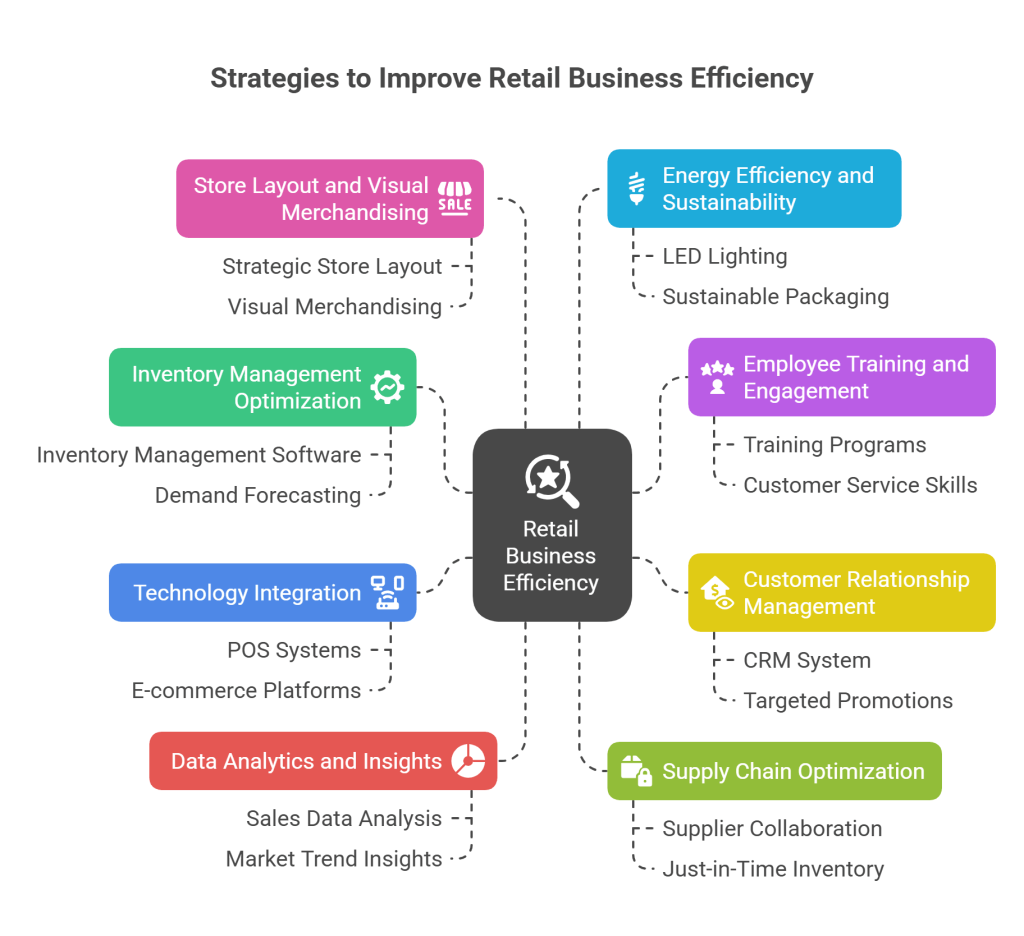
Improving the efficiency of your retail business is crucial in today’s competitive market. Streamlining your operations can not only enhance customer satisfaction but also boost profitability. Here are eight strategies to achieve just that:
1. Inventory Management Optimization
Efficiently managing your inventory is essential. Utilize inventory management software to track stock levels, forecast demand, and automate reordering processes. This minimizes overstocking and understocking issues, reducing costs and ensuring products are readily available when needed.
2. Employee Training and Engagement
Well-trained and motivated employees can significantly impact efficiency. Invest in training programs to enhance product knowledge and customer service skills. Engaged employees are more likely to go the extra mile, leading to better customer experiences and increased sales.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Implement a CRM system to better understand and cater to customer preferences. This enables personalized marketing efforts, improving customer retention and boosting sales through targeted promotions and recommendations.
4. Technology Integration
Embrace technology to streamline processes and enhance the shopping experience. This includes adopting point-of-sale (POS) systems, e-commerce platforms, and mobile payment options. Integrating these technologies reduces manual work, speeds up transactions, and meets evolving customer expectations.
5. Data Analytics and Insights
Leverage data analytics tools to gain actionable insights from sales data, customer behavior, and market trends. Data-driven decisions can help you optimize pricing, product assortments, and marketing strategies, ultimately boosting sales and profitability.
6. Supply Chain Optimization
Collaborate with suppliers to improve the efficiency of your supply chain. Establish clear communication channels and consider just-in-time inventory practices to minimize carrying costs and reduce the risk of obsolete stock.
7. Store Layout and Visual Merchandising
Carefully design your store layout to enhance the customer shopping experience and encourage impulse purchases. Strategic visual merchandising and signage can lead to higher sales by directing customer attention to featured products and promotions.
8. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Embrace energy-efficient technologies and environmentally friendly practices within your retail enterprise to both reduce costs and appeal to eco-conscious patrons. Implementing measures such as utilizing LED lighting, optimizing heating and cooling systems for efficiency, and adopting sustainable packaging options can enhance operational efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and position your business for competitiveness in a challenging market.
Challenges in Retail Supply Chain Management
Retail supply chain management is a complex and dynamic field that ensures products reach consumers efficiently and seamlessly. It involves a series of interconnected processes, from procurement and inventory management to distribution and customer service.
Amidst this intricate web of operations, retailers face several significant challenges that can impact their overall performance and profitability. Here, we delve into the top challenges in retail supply chain management:
1. Demand Forecasting and Planning
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for retailers to maintain optimal inventory levels. Predicting consumer preferences, seasonal trends, economic fluctuations, and unexpected events remains a challenge. Misjudging demand can lead to excess inventory or missed sales opportunities.
2. Inventory Management
Striking a balance between too much and too little inventory is essential. Overstocking consumes capital and storage space, while understocking results in lost sales and unhappy customers. Retailers need smart inventory strategies to meet demand efficiently without increasing costs.
3. Supply Chain Visibility
Retailers often work with multiple suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics partners. Without real-time visibility across the entire supply chain, it becomes difficult to manage disruptions or inefficiencies. Access to up-to-date insights enables better, faster decision-making.
4. Supplier Relationships
A reliable supply chain depends on strong supplier relationships. Challenges such as inconsistent quality, delays, and ethical concerns can weaken these relationships. Open communication and long-term collaboration are key to maintaining supplier trust and performance.
5. E-commerce Integration
With the rapid growth of online shopping, retailers must integrate e-commerce with physical store operations. This includes synchronized inventory, streamlined order fulfillment, and consistent customer service—each of which presents operational complexities.
To navigate these challenges successfully, retailers must leverage cutting-edge technology, harness the power of data analysis, and explore innovative approaches to enhance the performance of their supply chains. Additionally, they should maintain a relentless focus on understanding and meeting their customers’ evolving wants and needs.
This proactive approach to integrating technology and adapting to shifting customer preferences will position retailers to thrive in an increasingly digital and customer-centric marketplace.
Conclusion
To sum up, managing the supply chain in retail is crucial for making a store work well. It involves different plans and actions to make sure products move smoothly from the makers to the buyers. By implementing effective inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics, retailers can minimize costs, reduce lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
To further enhance your retail business efficiency, consider partnering with Qodenext. Our cutting-edge supply chain solutions leverage advanced technology and data analytics to streamline operations, improve inventory visibility, and boost overall performance. Take the next step towards a more efficient and profitable retail business by contacting us today for a personalized consultation and to explore how Qodenext can help you achieve your supply chain management goals.
FAQs on Retail Supply Chain Management
1. What is Retail Supply Chain Management?
Retail Supply Chain Management refers to the coordination of processes involved in moving products from suppliers to retail shelves and ultimately to customers. It includes inventory control, procurement, logistics, warehousing, and customer service—all aimed at ensuring timely, cost-effective delivery of goods.
2. Why is inventory management important in retail supply chains?
Inventory management ensures that retailers maintain optimal stock levels—enough to meet customer demand without overstocking. Poor inventory control can lead to stockouts, excess holding costs, and unsatisfied customers. Tools like ABC analysis and just-in-time (JIT) methods are commonly used.
3. How does demand forecasting improve retail supply chain efficiency?
Accurate demand forecasting enables retailers to predict future customer needs using historical data, trends, and analytics. This helps in planning inventory, purchasing, and marketing strategies, ultimately reducing wastage and improving service levels.
4. What are the key technologies used in modern retail supply chains?
Technologies such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Transportation Management Systems (TMS), RFID tracking, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and ERP platforms enhance visibility, accuracy, and operational efficiency across the supply chain.
5. What role does customer service play in supply chain success?
Customer service is a critical component that ensures returns, complaints, and inquiries are managed effectively. A responsive and well-integrated customer service function builds trust, drives loyalty, and supports a seamless end-to-end customer experience.
6. How can retailers deal with supply chain disruptions?
Retailers can mitigate disruptions through proactive risk management, such as diversifying suppliers, maintaining safety stock, and creating contingency plans. Technologies like real-time tracking and predictive analytics can also aid in early detection and response.
7. How can retail businesses improve their supply chain sustainability?
Sustainable retail supply chains focus on reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and ethically sourcing products. Strategies include optimizing transportation routes, using eco-friendly packaging, and collaborating with green-certified suppliers.
8. What is the importance of supplier relationship management (SRM)?
Strong SRM ensures timely procurement, consistent quality, and cost control. It also supports innovation, risk mitigation, and long-term collaboration, which are vital for a resilient and agile retail supply chain.
9. What are common challenges in retail supply chain management?
Major challenges include demand unpredictability, inventory mismanagement, lack of supply chain visibility, supplier issues, and difficulties integrating e-commerce operations with physical retail channels.
10. How can Qodenext help improve retail supply chain efficiency?
Qodenext provides advanced supply chain solutions powered by automation, data analytics, and real-time inventory visibility. Retailers can partner with Qodenext to optimize operations, reduce costs, and build a more responsive and customer-centric supply chain.







