In today’s hyper-connected, efficiency-driven world, businesses across industries are under increasing pressure to offer complete visibility and control over their supply chains. Whether you’re in pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, electronics, or apparel, the need to track and trace products at every stage of their lifecycle is now a non-negotiable part of operations. This is where traceability using barcodes becomes not only relevant but foundational.

From enhancing inventory management to ensuring regulatory compliance and boosting consumer trust, traceability is proving to be a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective tool. But what makes barcodes the cornerstone of modern traceability systems? Let’s dive deep.
What Is Traceability and Why Does It Matter?
Traceability refers to the ability to track the movement of a product through the stages of production, processing, and distribution. It allows stakeholders to know exactly where a product came from, where it has been, and where it is going. This visibility is essential for:
- Quality control
- Recalls and risk management
- Regulatory compliance
- Counterfeit prevention
- Sustainability tracking
While there are various methods to achieve traceability—such as RFID, blockchain, and IoT—the most widely adopted and accessible approach remains traceability using barcodes.
The Evolution of Barcodes in Supply Chains
Barcodes have been around for decades, first used in retail environments in the 1970s. Over the years, their role has dramatically expanded into manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and more. They now form the digital backbone of many supply chain operations.
What has made traceability using barcodes so enduring? It’s a combination of simplicity, low cost, scalability, and universal acceptance. Almost every product you buy today—from a bottle of water to an industrial valve—has a barcode that provides essential data.
Why Barcodes Are the Foundation of Traceability
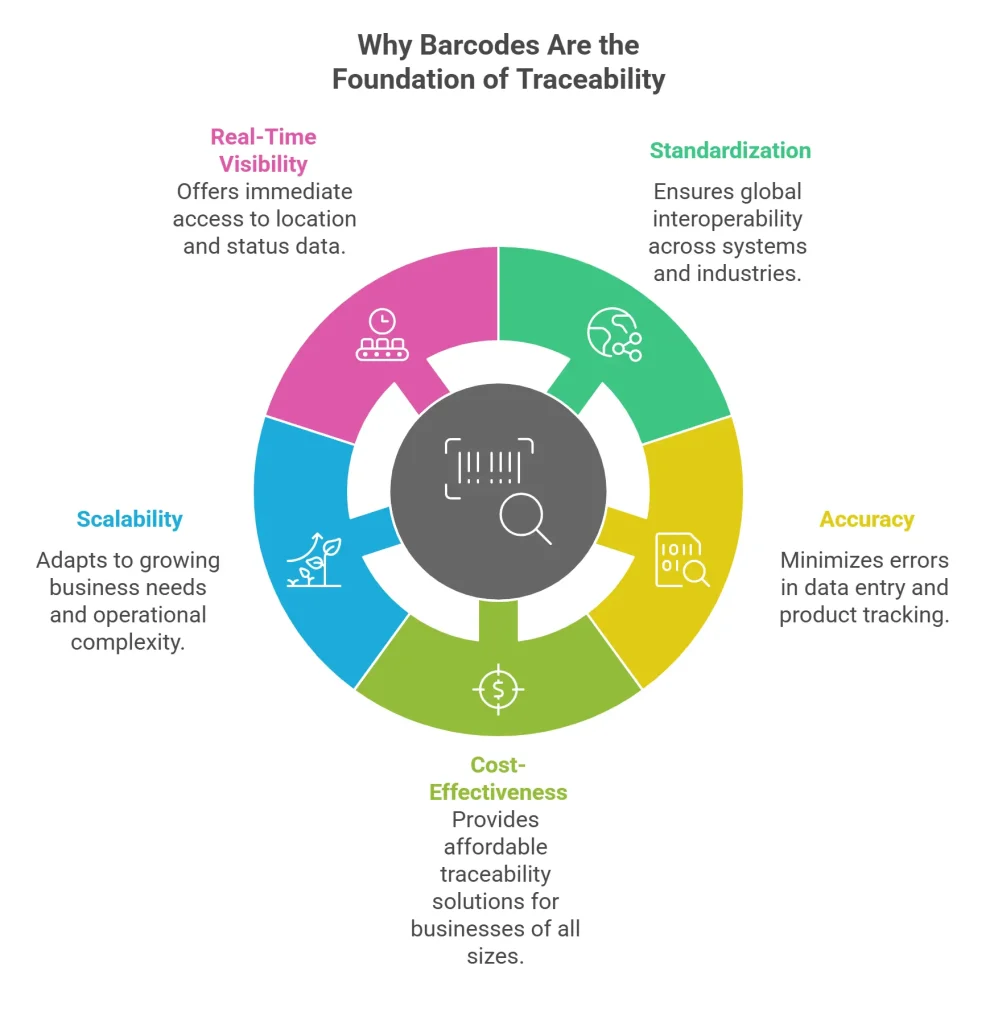
Here are the core reasons why barcodes in traceability form the bedrock of modern systems:
1. Standardization and Global Acceptance
Barcodes follow universally recognized standards, such as GS1, making them readable across systems, geographies, and industries. This ensures that your traceability system is not siloed but part of a globally interoperable ecosystem.
2. Accuracy and Efficiency
Manual data entry is prone to errors, leading to inventory mismatches, incorrect shipments, and compliance issues. Barcode scanning, on the other hand, offers near-perfect accuracy. This makes traceability using barcodes an ideal method for error-free product tracking.
3. Cost-Effective Traceability
Compared to RFID and IoT, barcode systems are far more affordable. Barcode printers and scanners are inexpensive, and even smartphones can be equipped to read them. This allows even small and medium enterprises to implement robust traceability without breaking the bank.
4. Scalability for All Sizes
Whether you’re a local artisanal soap maker or a global automotive parts supplier, barcodes can be scaled to match the complexity of your operations. As your business grows, your traceability using a barcode system can grow with it. The best barcode scanners adapt and scan according to your requirements.
5. Real-Time Visibility
Barcodes enable real-time data capture and updates at every stage of the supply chain. This is especially useful in dynamic environments like eCommerce, where speed and precision are crucial. Real-time traceability using barcodes ensures immediate access to location, quantity, and status data.
Key Industries Benefiting from Barcode Traceability
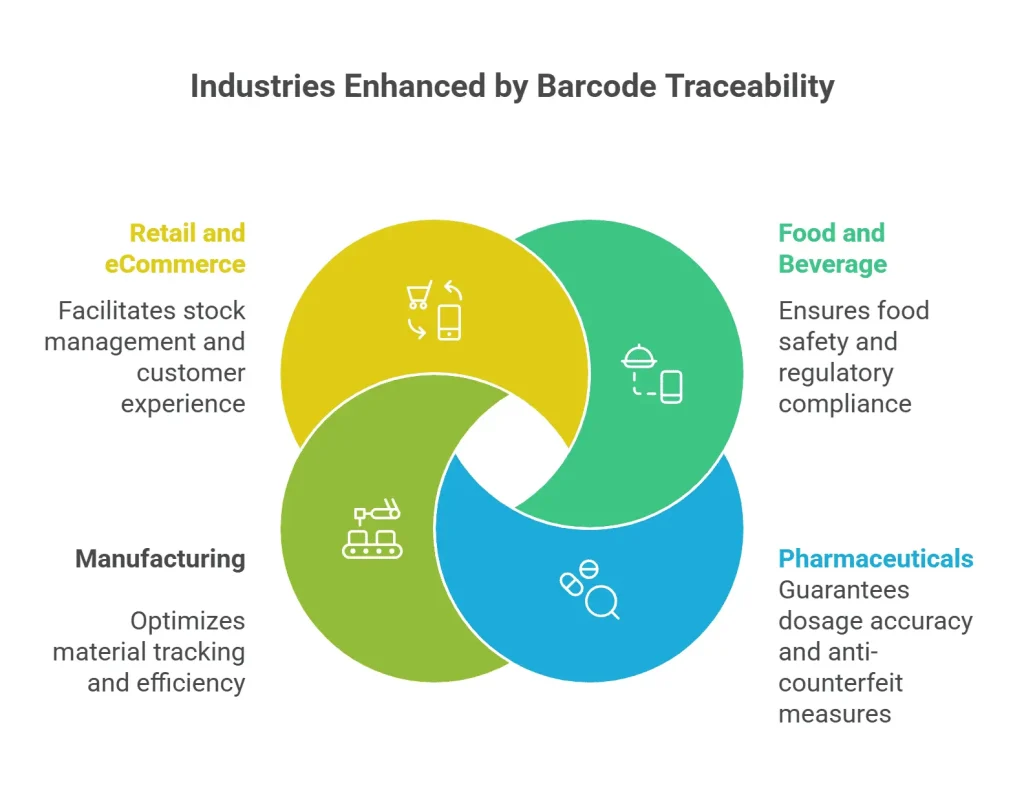
1. Food and Beverage
Barcodes help track perishables from farm to fork, ensuring food safety, recall management, and regulatory compliance.
2. Pharmaceuticals
In life-saving sectors, traceability using barcodes ensures dosage accuracy, expiry monitoring, and anti-counterfeit measures.
3. Manufacturing
Track raw materials, WIP (Work-in-Progress), and finished goods across facilities to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
4. Retail and eCommerce
Barcodes enable seamless stock management, automated checkouts, and enhanced customer experiences.
How Traceability Using Barcodes Works
Typical traceability using a barcode system includes:
- Barcode Generation – Each unit, batch, or pallet is labelled with a unique barcode.
- Scanning and Data Capture – Barcodes are scanned at key touchpoints: receiving, storage, production, packaging, and shipping.
- Data Integration – The scanned data is fed into a centralized system (ERP, WMS, or TMS) for tracking and analysis.
- Real-Time Monitoring – Live dashboards show product location, status, and movement history.
- Reporting and Compliance – Complete audit trails help in quality assurance, recalls, and regulatory documentation.
Real-World Example: Traceability in Pharma
A pharmaceutical company uses traceability using barcodes to monitor each vial from production to patient. Each barcode includes details such as batch number, manufacturing date, and expiry date. If a batch is found to be defective, it can be swiftly recalled with minimal risk and zero guesswork.
The Role of 2D and QR Barcodes
Traditional 1D barcodes carry limited information. Newer 2D codes (like Data Matrix and QR codes) are now being used to pack more data into a smaller footprint. These can include URLs, geo-location, timestamps, and more.
This evolution makes traceability using barcodes even more powerful, allowing companies to share detailed product information directly with consumers, regulators, or downstream partners.
Future of Traceability Using Barcodes
As technology evolves, barcodes are expected to integrate with AI, blockchain, and IoT. But rather than being replaced, barcodes will complement these systems as the initial data capture mechanism. Imagine barcodes initiating a blockchain transaction or triggering a smart contract. This synergy will enhance the accuracy and trustworthiness of the foundation of traceability.
FAQs: Traceability Using Barcodes
1. Can barcodes really provide complete traceability?
Yes. When implemented properly, barcode traceability can track products across their entire lifecycle—from raw materials to end-user delivery.
2. Is barcode traceability suitable for small businesses?
Absolutely. One of the biggest advantages of barcode traceability is its affordability and ease of implementation for businesses of any size.
3. How does barcode traceability help with recalls?
It allows companies to identify affected batches instantly and trace their distribution path, making product recalls swift and accurate.
4. Are barcodes secure enough for sensitive industries like pharma?
Yes. When combined with serialization and secure data management systems, traceability can meet strict regulatory and safety standards.
5. What’s the difference between barcodes and RFID in traceability?
Barcodes are optical and require line-of-sight, whereas RFID uses radio waves. Barcodes are cheaper and simpler to implement, making traceability the preferred choice for most companies.
Conclusion
In an era where transparency is the currency of trust, traceability using barcodes provides the tools businesses need to meet consumer expectations, regulatory demands, and operational goals. Its low cost, global acceptance, and compatibility with emerging tech make it not just a solution—but the foundation—for modern traceability systems.
Whether you’re trying to prevent counterfeits, manage recalls, improve inventory, or build brand trust, traceability is the starting point of your digital transformation journey. Contact Qodenext today.






