
Understanding lead time in the supply chain is crucial for businesses striving for efficiency. Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. It encompasses various stages, including manufacturing, transportation, and handling. Effective management of lead time can significantly impact customer satisfaction, inventory management, and overall operational performance. In this blog, we delve into the nuances of lead time in supply chain management, exploring strategies to minimize delays and enhance productivity.
What Is Lead Time In Supply Chain
Lead time is a critical concept in supply chain management, representing the time it takes for an order to be fulfilled from the moment it is placed to when it is delivered to the customer. This metric plays a pivotal role in inventory management, production planning, and overall operational efficiency within a supply chain.
Definition of Lead Time:
Lead time encompasses various stages of the supply chain, including procurement, manufacturing, transportation, and distribution. It begins when a customer places an order and ends when the product is delivered to the customer’s doorstep. Essentially, it reflects the elapsed time from order initiation to order fulfillment.
Components of Lead Time:
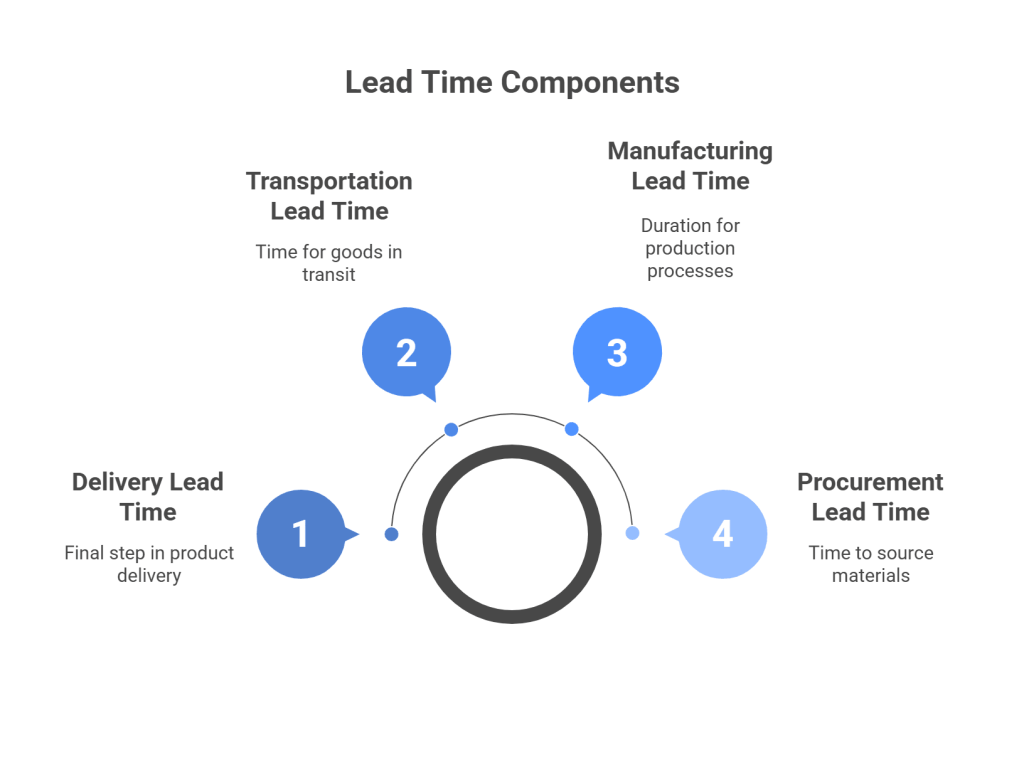
1. Procurement Lead Time:
This refers to the time taken to source raw materials or components from suppliers. It includes the time required for order processing, supplier communication, and transportation.
2. Manufacturing Lead Time:
This denotes the duration needed to convert raw materials into finished products. It involves production processes, quality control measures, and any potential delays.
3. Transportation Lead Time:
This signifies the time taken to transport goods from the manufacturing facility to distribution centers or directly to customers. It includes transit time and any delays in transit.
4. Delivery Lead Time:
This represents the time taken to deliver products from distribution centers to customers’ locations. It includes order processing time, picking, packing, and shipping.
Importance of Lead Time:
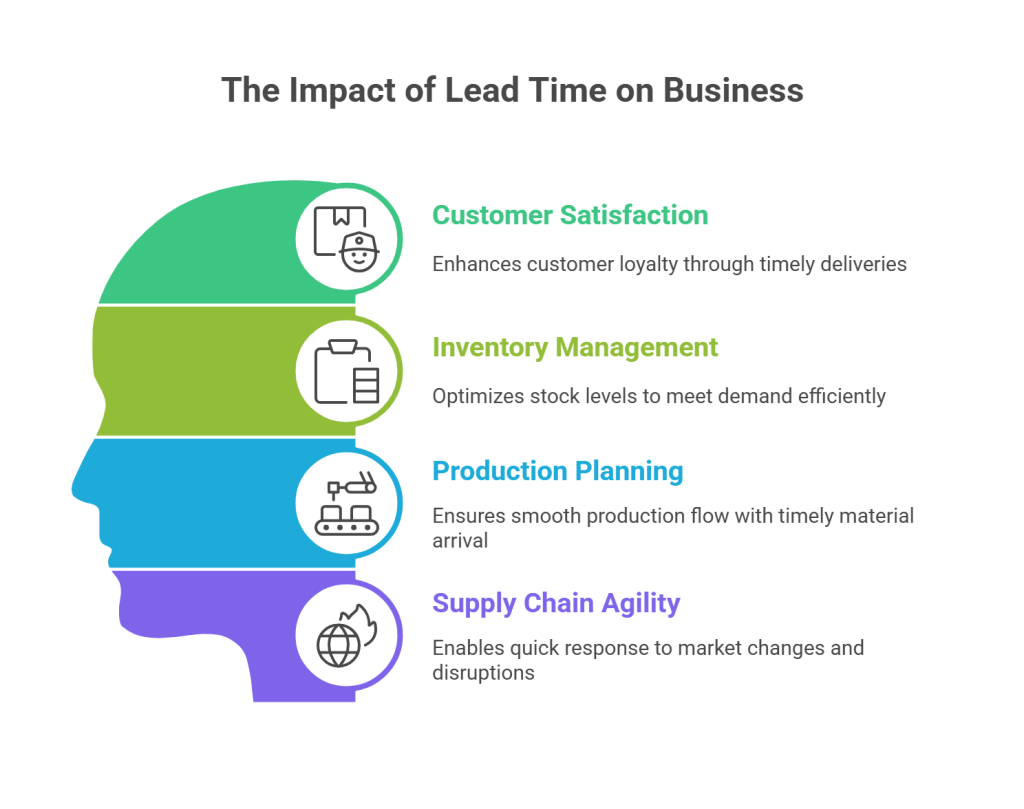
Lead time may sound like a technical term, but in reality, it plays a big role in how smoothly businesses run and how happy customers feel. Whether you’re running a small online store or managing a large supply chain, understanding and managing lead time is crucial to staying competitive.
1. Customer Satisfaction
Imagine ordering a product online and getting it at your doorstep within two days. That quick delivery leaves a positive impression, right? Shorter lead times make this possible. When businesses fulfill orders faster, customers are more satisfied—and happy customers are more likely to return and recommend the brand. In today’s world where instant gratification is the norm, meeting delivery expectations is key to building trust and loyalty.
2. Smarter Inventory Management
Lead time directly affects how businesses manage their inventory. If you know how long it takes to restock products, you can plan more accurately. This means you’re less likely to face awkward stockouts where shelves are empty, or end up with excess inventory gathering dust. With accurate lead time forecasting, companies strike the right balance—having enough stock to meet demand without wasting money or space.
3. Efficient Production Planning
In manufacturing, knowing lead times helps in setting realistic production schedules. When raw materials arrive on time, production lines keep moving smoothly. But if materials are delayed, everything slows down, leading to idle workers, wasted time, and delayed deliveries. By understanding lead times, businesses can plan ahead and minimize disruptions—ensuring that products are made efficiently and on time.
4. Greater Supply Chain Agility
Markets change fast—new trends emerge, customer demands shift, and unexpected disruptions happen (think COVID or natural disasters). Companies with shorter, well-managed lead times are better equipped to respond quickly. They can ramp up production, switch suppliers, or restock fast-moving items without delay. This kind of flexibility helps businesses stay competitive and resilient, no matter what challenges come their way.
Factors Affecting Lead Time:
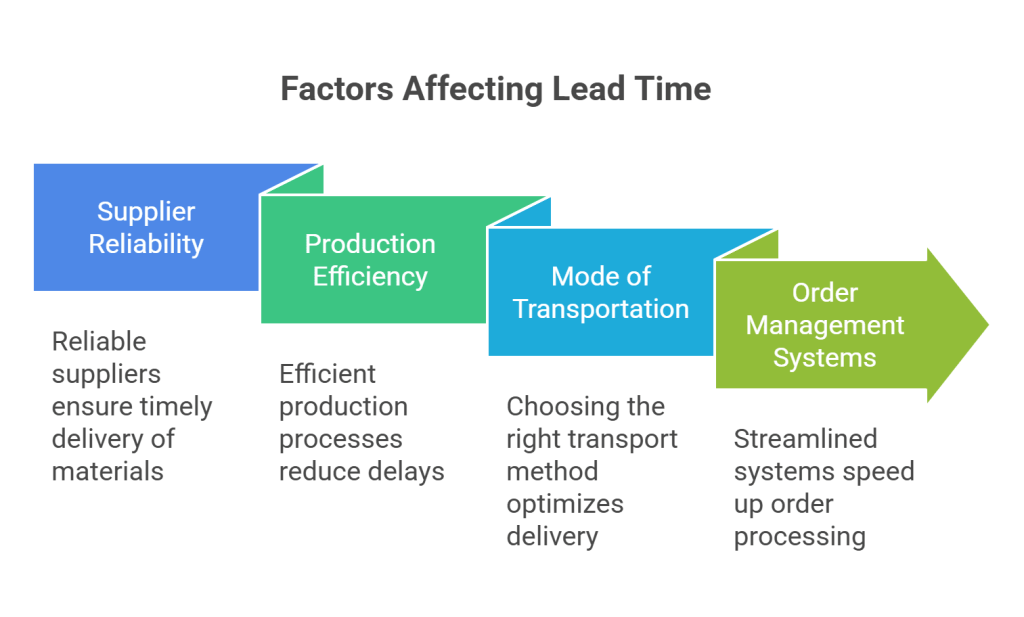
Lead time isn’t just about how fast something gets from point A to point B. It’s influenced by several moving parts in the supply chain. When any one of these parts slows down, the entire timeline can stretch—leading to delays, frustrated customers, and missed opportunities. Here are the main factors that directly impact lead time:
1. Supplier Reliability
A lot depends on your supplier. Reliable suppliers who consistently deliver raw materials or products on time help keep lead times short and predictable. But if a supplier frequently delays shipments, sends incorrect quantities, or messes up documentation, it slows down everything. Building strong, trustworthy relationships with dependable suppliers can drastically reduce these risks.
2. Production Efficiency
Once the raw materials arrive, how smoothly and quickly a business can produce the final product makes a huge difference. Efficient production lines, skilled workers, well-maintained machines, and minimal downtime all contribute to shorter lead times. On the flip side, frequent equipment breakdowns, poor scheduling, or labor shortages can extend production time unnecessarily.
3. Mode of Transportation
How goods are shipped plays a big role in determining how fast they reach their destination. Air freight is the fastest (but usually more expensive), while sea freight is slower but cost-effective for large shipments. Ground transport sits somewhere in between. Choosing the right mode based on urgency, cost, and distance is crucial for keeping lead time in check.
4. Order Management Systems
The internal systems used to process orders also affect lead time. When businesses have streamlined, automated order management systems, everything moves faster—from order confirmation to warehouse picking and packing. But if the process is manual, disorganized, or has communication gaps between departments, it leads to delays at every step.
Strategies to Reduce Lead Time:
1. Lean Manufacturing:
Implementing lean principles such as Just-In-Time (JIT) production can reduce manufacturing lead times by eliminating waste and improving process efficiency.
2. Vendor Management:
Developing strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers can help minimize procurement lead times through better communication and collaboration.
3. Transportation Optimization:
Utilizing advanced logistics technologies and optimizing transportation routes can reduce transportation lead times.
4. Process Automation:
Automating order processing and fulfillment processes can expedite delivery lead times and enhance overall efficiency.
Lead time is a fundamental metric in supply chain management, influencing various aspects of operational performance and customer satisfaction. By understanding its components, importance, and factors affecting it, companies can implement strategies to reduce lead times, thereby improving agility, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business environment. Efficient management of lead time is crucial for meeting customer expectations and sustaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Lead Time Reduction

Lead time reduction is a critical objective for manufacturing companies aiming to enhance efficiency, meet customer demands swiftly, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced market. By minimizing the time it takes for a product to move from the order placement to delivery stage, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall customer satisfaction. In this article, we delve into essential strategies that manufacturing firms can adopt to achieve significant lead time reduction without compromising quality.
1. Process Optimization:
- Implement lean manufacturing principles to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities within the production process.
- Streamline workflows and eliminate bottlenecks by reorganizing workstations and optimizing resource utilization.
- Utilize advanced technologies such as automation and robotics to expedite manufacturing processes and minimize manual intervention.
2. Supply Chain Management:
- Foster closer collaborations with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of raw materials and components.
- Implement vendor-managed inventory (VMI) systems to maintain optimal stock levels and reduce dependency on lead times from suppliers.
- Explore alternative sourcing options and establish backup suppliers to mitigate the risk of disruptions in the supply chain.
3. Forecasting and Demand Planning:
- Invest in sophisticated demand forecasting tools and techniques to accurately predict future demand patterns.
- Align production schedules with demand forecasts to prevent overproduction or stockouts, thereby reducing lead times.
- Continuously monitor market trends and customer preferences to adapt production plans dynamically and proactively.
4. Inventory Management:
- Adopt just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices to minimize inventory holding costs and improve inventory turnover rates.
- Implement kanban systems to facilitate the replenishment of inventory based on actual consumption, thereby reducing excess inventory and lead times.
- Leverage inventory optimization software to analyze demand variability and establish optimal reorder points and safety stock levels.
5.Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Foster a culture of collaboration and communication among different departments, including production, procurement, logistics, and sales.
- Encourage cross-functional teams to work together towards common goals, such as lead time reduction, by sharing insights and best practices.
- Break down silos and encourage knowledge sharing to facilitate continuous improvement initiatives across the organization.
6. Continuous Improvement:
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure lead time performance regularly and identify areas for improvement.
- Conduct regular process audits and performance reviews to identify inefficiencies and implement corrective actions promptly.
- Encourage employee involvement in problem-solving and innovation through initiatives such as Kaizen events and suggestion schemes.
7.Customer Relationship Management:
- Engage closely with customers to understand their evolving needs and preferences, thereby enabling more accurate demand forecasting.
- Offer flexible delivery options and expedited services to cater to urgent customer requirements and reduce lead times.
- Solicit feedback from customers regularly to identify areas for improvement and enhance overall service levels.
Lead time reduction is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a combination of strategic planning, operational excellence, and continuous improvement efforts. By adopting the strategies outlined above and fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, manufacturing companies can effectively reduce lead times, enhance operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the market. Embracing change and leveraging technology will be key drivers in achieving sustainable lead time reduction while meeting the evolving demands of customers in today’s dynamic business environment.
Production Lead Time
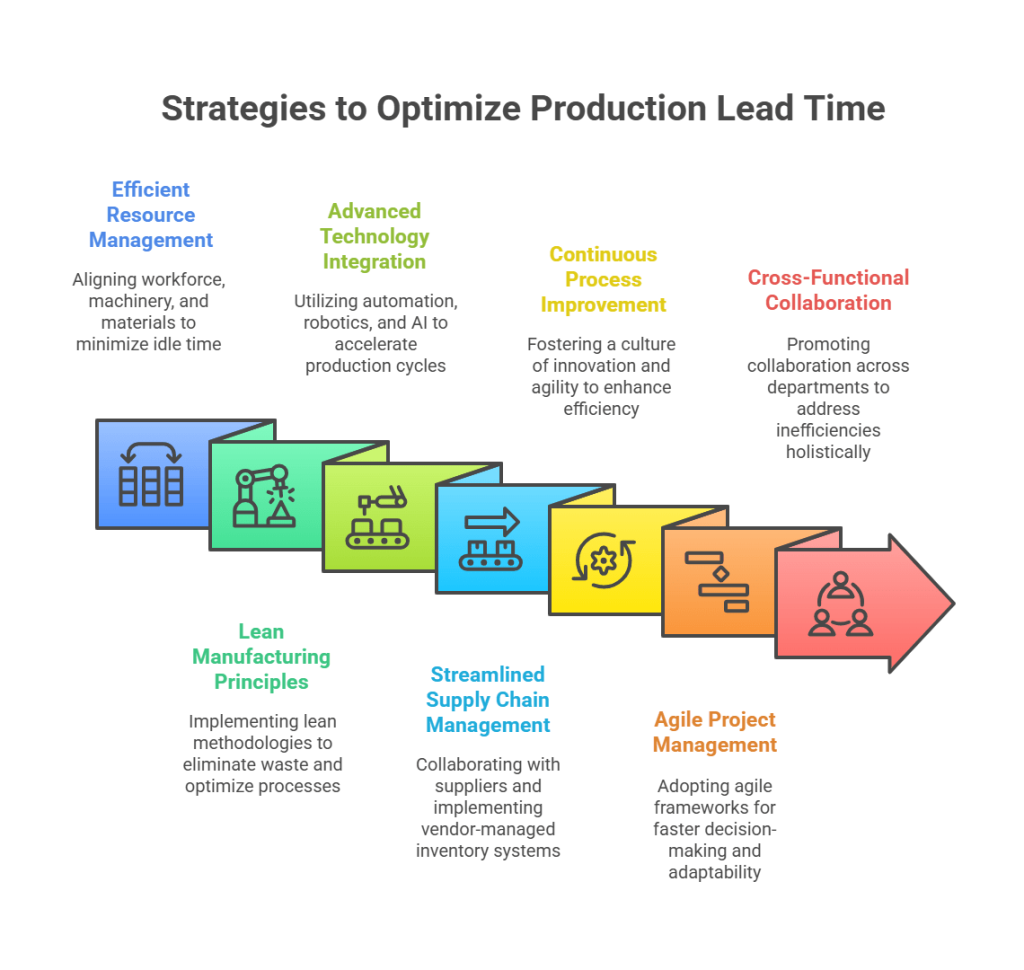
In today’s fast-paced business environment, optimizing production lead time is essential for companies striving to stay competitive. Production lead time, often referred to as manufacturing lead time, encompasses the duration from the initiation of a manufacturing process to the delivery of the final product to the customer. Shortening this time frame without compromising quality can significantly enhance a company’s efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall profitability. This article explores various strategies and techniques to streamline production lead time, ensuring smooth operations and improved outcomes.
1. Efficient Resource Management:
One of the fundamental aspects of reducing production lead time is efficient resource management. This involves aligning workforce, machinery, and materials in a manner that minimizes idle time and maximizes productivity. By maintaining a balance between supply and demand, companies can avoid delays caused by shortages or excess inventory, thus expediting the production process.
2. Lean Manufacturing Principles:
Implementing lean manufacturing principles is instrumental in minimizing waste and optimizing production lead time. By identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, such as overproduction, excess inventory, and unnecessary transportation, companies can streamline their operations and enhance efficiency. Lean methodologies, such as Just-in-Time (JIT) production and Kanban systems, enable organizations to produce goods in response to actual demand, thereby reducing lead times and enhancing responsiveness.
3. Advanced Technology Integration:
Embracing advanced technologies can revolutionize production processes and significantly reduce lead times. Automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence (AI) enable tasks to be completed faster and with greater precision, thereby accelerating production cycles. Furthermore, technologies such as predictive analytics and real-time monitoring empower companies to anticipate bottlenecks and proactively address them, minimizing disruptions and optimizing lead times.
4. Streamlined Supply Chain Management:
Effective supply chain management is crucial for minimizing production lead time, as delays in the procurement of raw materials or components can have ripple effects throughout the manufacturing process. Collaborating closely with suppliers, implementing vendor-managed inventory systems, and establishing alternative sourcing options are strategies that can mitigate supply chain risks and ensure a steady flow of materials, thereby reducing lead times and enhancing reliability.
5. Continuous Process Improvement:
Continuous improvement is essential for optimizing production lead time in the long term. By fostering a culture of innovation and agility within the organization, companies can continually identify opportunities for enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Encouraging employee involvement, implementing regular performance evaluations, and embracing feedback-driven initiatives enable organizations to adapt quickly to changing market dynamics and continuously refine their processes to achieve shorter lead times.
6. Agile Project Management:
Adopting agile project management methodologies can facilitate faster decision-making and greater adaptability, leading to shorter production lead times. Agile frameworks, such as Scrum and Kanban, emphasize iterative development, frequent communication, and rapid problem-solving, enabling teams to respond swiftly to changes and deliver high-quality products within compressed time frames.
7. Cross-Functional Collaboration:
Promoting collaboration across different departments and functions is essential for streamlining production lead time. By breaking down silos and fostering interdisciplinary communication, companies can identify and address inefficiencies holistically. Cross-functional teams can collaborate to optimize processes, troubleshoot issues, and implement innovative solutions, resulting in reduced lead times and improved overall performance.
Optimising production lead time is critical for enhancing competitiveness and meeting customer expectations in today’s dynamic business landscape. By implementing strategies such as efficient resource management, lean manufacturing principles, advanced technology integration, streamlined supply chain management, continuous process improvement, agile project management, and cross-functional collaboration, companies can shorten lead times, improve operational efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth. By prioritizing efficiency and innovation, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and thrive in an increasingly demanding market environment.
What Is Lead Time In Inventory
Lead time in inventory management refers to the duration between placing an order for goods or materials and receiving them. It is a critical metric for businesses as it directly impacts their ability to meet customer demand, maintain optimal inventory levels, and effectively manage supply chain operations. Understanding lead time is essential for businesses to streamline their procurement processes, minimize stockouts, and improve overall operational efficiency.
1. Definition of Lead Time in Inventory:
Businesses can employ several strategies to effectively manage lead times, including establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers, implementing just-in-time inventory practices, utilizing technology such as inventory management software and demand forecasting tools, and diversifying sourcing options to mitigate risks.
2. Impact on Supply Chain Performance:
Lead time directly affects supply chain performance metrics such as order fulfillment rates, inventory turnover, and on-time delivery. By reducing lead times, businesses can enhance supply chain agility, responsiveness, and competitiveness in the market.
3. Continuous Improvement:
Lead time management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, analysis, and improvement. Businesses should regularly review their processes, identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and implement corrective actions to optimize lead times and enhance overall operational performance.
4. Customer Expectations:
In today’s competitive business landscape, customers expect fast and reliable delivery of products. Lead time directly influences customer satisfaction and loyalty, making it essential for businesses to prioritize lead time management to meet evolving customer expectations.
5. Risk Mitigation:
Long lead times can increase the risk of supply chain disruptions due to factors such as natural disasters, geopolitical events, or unexpected changes in demand. Businesses should implement risk mitigation strategies such as safety stock, alternative sourcing options, and supply chain diversification to minimize the impact of unforeseen disruptions on lead times.
In conclusion, lead time is a critical component of inventory management that significantly impacts supply chain performance, customer satisfaction, and overall business success. By understanding the key concepts and best practices associated with lead time management, businesses can optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and enhance their competitive advantage in the market.
Lead Time In Operations Management
Lead time plays a crucial role in operations management, serving as a vital metric for assessing efficiency, managing inventory, and meeting customer expectations. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the concept of lead time, its significance, calculation methods, and practical implications in various industries.
1. Definition and Significance:
Lead time refers to the total duration required to fulfill a customer order from the moment it is placed to the moment it is delivered. It encompasses various stages such as order processing, production, transportation, and delivery. Understanding lead time is essential as it directly impacts customer satisfaction, inventory levels, and operational costs.
2. Types of Lead Time:
When we talk about “lead time,” we’re not just referring to one single clock ticking. Lead time is actually a combination of different time frames that cover various parts of the supply chain. Understanding the types of lead time helps businesses identify where delays may happen and where they can improve. Let’s break it down:
a) Manufacturing Lead Time
This refers to the time it takes to turn raw materials into a finished product. It starts the moment production begins and ends when the product is ready to be shipped. If there are delays in any part of the production process—like machine breakdowns, labor shortages, or quality issues—this lead time gets longer.
b) Procurement Lead Time
Procurement lead time covers the duration between placing an order for raw materials or components and actually receiving them. This depends a lot on supplier efficiency, order processing speed, and shipping time. The more reliable your supplier, the shorter and more predictable this lead time becomes.
c) Delivery Lead Time
Once a product is manufactured, it still has to reach the customer. Delivery lead time refers to how long it takes to transport goods from the production site or warehouse to the customer’s doorstep. Factors like distance, shipping method (air, sea, road), and even customs clearance can influence this.
d) Total Lead Time
Think of this as the grand total. Total lead time is the sum of all the lead times mentioned above—procurement, manufacturing, and delivery. It represents the entire journey from ordering raw materials to the moment the final product reaches the end customer. This is the key metric businesses monitor to ensure timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
3. Calculating Lead Time:
Lead time calculation varies depending on the specific stage of the operation. For manufacturing lead time, it involves summing up processing time, queue time, setup time, and waiting time. Procurement lead time includes order processing time, supplier lead time, and transit time. Delivery lead time considers transportation time and order processing time.
4. Importance in Inventory Management:
Lead time directly influences inventory management practices such as safety stock levels and reorder points. Longer lead times necessitate higher safety stock levels to prevent stockouts and meet customer demand during delays. By accurately estimating lead time, organizations can optimize inventory levels and minimize carrying costs.
5. Impact on Customer Satisfaction:
Lead time significantly impacts customer satisfaction levels. Shorter lead times enhance customer experience by reducing waiting times and increasing responsiveness. Meeting or exceeding lead time expectations can lead to repeat business, positive reviews, and enhanced brand reputation.
6. Continuous Improvement:
Lead time reduction should be viewed as an ongoing process rather than a one-time initiative. Continuous monitoring, analysis of performance metrics, and feedback mechanisms are essential for identifying areas of improvement and implementing corrective actions.
Lead time is a critical metric in operations management, influencing various aspects of supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. By understanding lead time dynamics, implementing effective strategies, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can enhance operational performance and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business environment.
Conclusion:
In a competitive marketplace, mastering lead time management is paramount for businesses to thrive. By implementing robust strategies and embracing technological advancements, organizations can minimize delays, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. At Qodenext, we specialize in providing innovative solutions to optimize supply chain performance and drive business success.
FAQs: Understanding Lead Time In Supply Chain: Strategies To Minimize Delays
1. What is lead time in supply chain management?
Lead time is the total time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered to the customer. It includes procurement of materials, manufacturing, transportation, and delivery stages.
2. Why is managing lead time important for businesses?
Managing lead time well improves customer satisfaction through faster deliveries, helps optimize inventory to avoid stockouts or excess, and enhances overall operational efficiency and competitiveness.
3. What are the main components of lead time?
Lead time is made up of procurement lead time (ordering materials), manufacturing lead time (producing the goods), transportation lead time (shipping products), and delivery lead time (final delivery to the customer).
4. How does supplier reliability affect lead time?
Reliable suppliers who deliver quality materials on time help keep lead times consistent and short. Unreliable suppliers can cause delays that ripple through the entire supply chain.
5. What strategies can reduce lead time in manufacturing?
Manufacturers can use lean principles like Just-In-Time production, optimize workflows, automate processes, and invest in employee training and equipment maintenance to speed up production.
6. How can transportation be optimized to shorten lead time?
Choosing the right shipping mode (air, sea, road), optimizing routes using technology, and partnering with dependable carriers all help reduce transportation delays.
7. What role does technology play in lead time management?
Automation, order management software, real-time tracking, and data analytics provide better visibility and speed across the supply chain, allowing businesses to anticipate issues and act swiftly.
8. How does lead time impact inventory management?
Longer lead times require holding more safety stock to avoid running out, which increases costs. Shorter, more predictable lead times allow businesses to maintain leaner inventories and reduce costs.
9. What is production lead time and why is it critical?
Production lead time is the time from starting manufacturing to finishing the product. Shortening this improves responsiveness to customer demand and reduces costly delays in the supply chain.
10. How can continuous improvement help with lead time reduction?
Regularly reviewing processes, measuring lead time performance, involving employees in problem-solving, and adopting best practices enable ongoing reductions in lead time and improved supply chain agility.







