Agriculture has always evolved with technology, from the plow to precision farming. But today, two innovations are rewriting the rulebook: traceability in agriculture and IoT in agriculture.
Imagine knowing exactly where your seeds came from, when they were planted, how they were irrigated, and what environmental conditions they were exposed to – all in real time.

That’s the promise of combining smart agriculture using IoT and digital seed traceability.
Let’s explore how these tools are helping farmers, governments, and agri-businesses grow smarter, greener, and more profitably.
What Is Seed Traceability and Why It’s Important
Seed traceability is the ability to track a seed’s origin, quality, and journey from production to planting. It ensures that seeds are authentic, non-contaminated, and suited for specific climates or soil conditions.
The value? Accountability, better yields, and reduced crop failures.
When integrated with IoT applications in agriculture, traceability systems can log temperature, moisture, and nutrient data linked to specific seed batches.
For instance, Bayer Crop Science uses blockchain and QR codes to tag seed packets. Farmers can scan a code and get full seed history – type, supplier, germination rate, and more.
Now that we understand what traceability is, let’s explore the Internet of Things side of the equation.
What Is IoT in Agriculture?
The Internet of Things in agriculture refers to a network of sensors, devices, and systems that collect and exchange data from the farm environment.
These tools range from soil moisture sensors and weather stations to GPS-equipped tractors and drone systems.
They provide real-time data on:
- Soil health
- Crop growth stages
- Water usage
- Pest activity
- Equipment performance
Together, these tools fuel smart agriculture using IoT, where data-driven decisions lead to better outcomes for both farmers and the planet.
Having understood how IoT works in farming, let’s now look at how it connects with seed traceability.
Combining Seed Traceability with IoT: A Perfect Match
The real magic happens when seed traceability systems are paired with sensors used in agriculture and IoT infrastructure.
Let’s say a farmer plants a seed batch tagged with traceable data. As that crop grows, in-ground sensors measure moisture and nutrients while aerial drones assess plant health. This data gets recorded and tied back to that specific seed lot.
This means that if a problem arises – a disease outbreak or poor yield – farmers can trace it to a specific seed supplier, field, or environmental factor. That’s traceability in agriculture powered by real-time insights.
Now that we’ve explored the power of combining the two, let’s see how these systems actually work on the ground.
Technologies Making It Happen
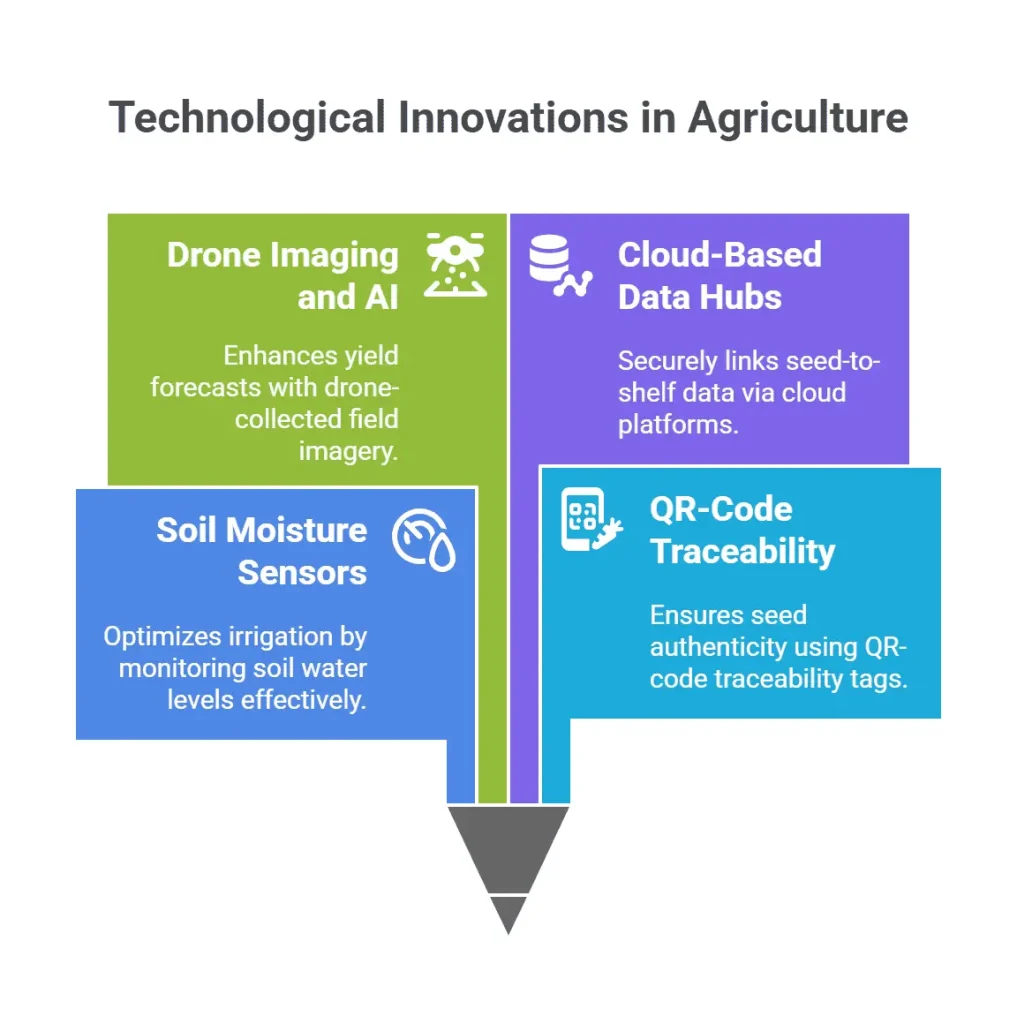
Here are some of the IoT applications in agriculture and traceability tools making a real-world impact:
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Companies like CropX and Arable use these to monitor soil water levels, helping optimize irrigation.
- QR-Code Traceability Tags: Used by Bayer and Syngenta for seed authentication.
- Drone Imaging and AI: John Deere integrates drone-collected field imagery with yield forecasts.
- Cloud-Based Data Hubs: Platforms like IBM Food Trust help link seed-to-shelf data securely.
These technologies aren’t just theoretical. Big players are already using them to boost productivity and compliance.
For example, Cargill integrates IoT and blockchain to ensure traceable sourcing from seed to shipping.
Key Sensors Used in Agriculture
Let’s now take a closer look at what sensors actually do the heavy lifting in this ecosystem.
Understanding the different types of sensors in IoT is essential to seeing how this tech works:
- Soil Sensors: Monitor pH, moisture, and temperature.
- Weather Sensors: Measure rainfall, humidity, solar radiation.
- Crop Sensors: Use infrared imaging to monitor plant stress.
- Location Trackers (GPS): Used in equipment and livestock management.
- RFID Tags: Attached to seed packets for scanning and data access.
These industrial IoT sensors deliver the real-time data that powers both automation and traceability efforts.
So how do these innovations translate into actual benefits?
Key Benefits for Farmers and the Supply Chain
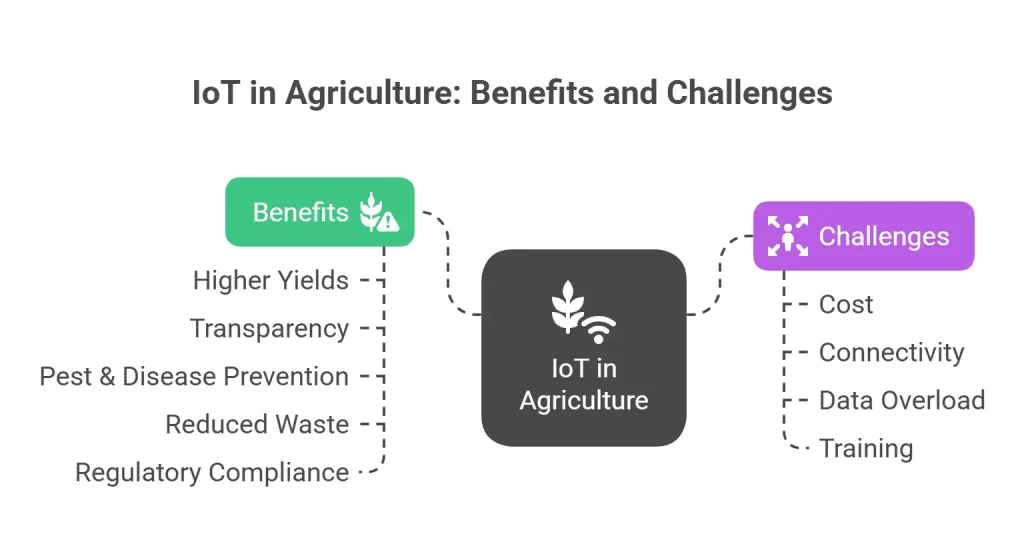
Combining IoT in agriculture with seed traceability brings tangible advantages:
- Higher Yields: Real-time monitoring leads to faster interventions and healthier crops.
- Transparency: Every step – from seed origin to harvest data – can be verified.
- Pest & Disease Prevention: Sensors can detect early signs of outbreaks.
- Reduced Waste: Better forecasting and traceability reduce over-fertilizing or over-watering.
- Regulatory Compliance: Digital trails make audits and certifications easier.
We’ve covered the tech, but what about challenges? Let’s read about some of them.
Challenges to Widespread Adoption
Despite its promise, implementing smart agriculture using IoT and traceability faces hurdles:
- Cost: High upfront investment for small farmers.
- Connectivity: Remote areas often lack internet access.
- Data Overload: Too much unstructured data can be hard to manage.
- Training: Farmers need support to use these systems effectively.
However, many agri-tech startups are now offering affordable, modular solutions – making it easier for even small-scale farmers to adopt these tools.
Still curious about the broader implications? Let’s take a peek at what the future holds.
The Road Ahead – A Fully Transparent Food System
As global food demand rises, the need for efficient, transparent farming systems becomes urgent. By combining traceability in agriculture with IoT in agriculture, we move closer to farms that are not just productive, but also sustainable and trustworthy.
In the near future, consumers could scan a QR code on a tomato and see:
- The seed batch it came from
- The field it was grown in
- Water and nutrient usage
- Harvest and transport dates
Companies like Two Brothers Organic Farms and SAP are already piloting this kind of full transparency with big agribusiness clients. That’s the kind of end-to-end visibility these technologies promise.
FAQs: IoT & Seed Data: A New Era for Agriculture
1. Can IoT help reduce water usage in farming?
Yes. IoT sensors can monitor soil moisture and weather to deliver just the right amount of water, reducing waste.
2. How is seed traceability useful for organic farming?
It ensures that seeds meet certification standards and provides proof of compliance through digital records.
3. Are there cybersecurity risks in using IoT in agriculture?
Like all connected tech, IoT devices can be vulnerable. Encryption, firewalls, and regular updates are essential.
4. Is this tech useful only for large farms?
Not at all. Many startups offer scaled-down, affordable versions for small and mid-sized farms.
5. What kind of data can farmers get from sensors?
Data ranges from soil and weather conditions to plant health, equipment usage, and pest activity.
Conclusion
Farming is no longer about guesswork. It’s about data, precision, and trust.
With IoT in agriculture and robust traceability in agriculture systems, we can grow more with less while building confidence in our food systems.
From the seed to the supermarket, this transformation is paving the way for smarter, safer, and more sustainable agriculture.






