In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, businesses rely on data-driven decision-making to streamline operations.
Integrating Product Data Management (PDM) with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems is becoming a game-changer for companies that are aiming to enhance supply chain efficiency.

By bridging these platforms, organizations can break down data silos, improve collaboration, and optimize product lifecycle management. Through this blog, we will explore the concept of PDM integration with ERP systems, its benefits, and how it enhances supply chain management.
Let’s get started!
What is Product Data Management (PDM)?
Product Data Management (PDM) is a software solution used to manage and control product-related data, including CAD files, documents, and design specifications.
It provides a centralized platform to store, track, and manage engineering data, ensuring that stakeholders have access to accurate and up-to-date information.
To get a better understanding let’s go through some of the key functions of PDM systems which include:
- Document management and version control
- BOM (Bill of Materials) management
- Change management
- Collaboration across design and engineering teams
While PDM is often confused with Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), it’s essential to understand the difference between PLM and PDM.
PLM encompasses the entire product lifecycle from ideation to disposal, while PDM primarily focuses on managing product data during the design and development stages.
Now that we have a better understanding of PDM, let’s explore what it means to integrate it with an ERP system.
What Does Integrating PDM with ERP System Mean?
Integrating PDM and ERP systems means connecting engineering and manufacturing processes by allowing real-time data exchange.
ERP systems manage core business functions like procurement, inventory, production, and finance, while PDM systems manage product design and engineering data.
When these systems are integrated:
- Design and engineering data from the PDM system automatically updates in the ERP system.
- BOMs generated during the design phase are directly available to manufacturing teams.
- Changes made to product data are reflected across departments in real-time.
This seamless connection ensures better coordination, reduces errors, and accelerates time-to-market.
With a clear understanding of what integration involves, let’s move on to uncover the benefits of this powerful connection.
Benefits of Integrating PDM with ERP Systems
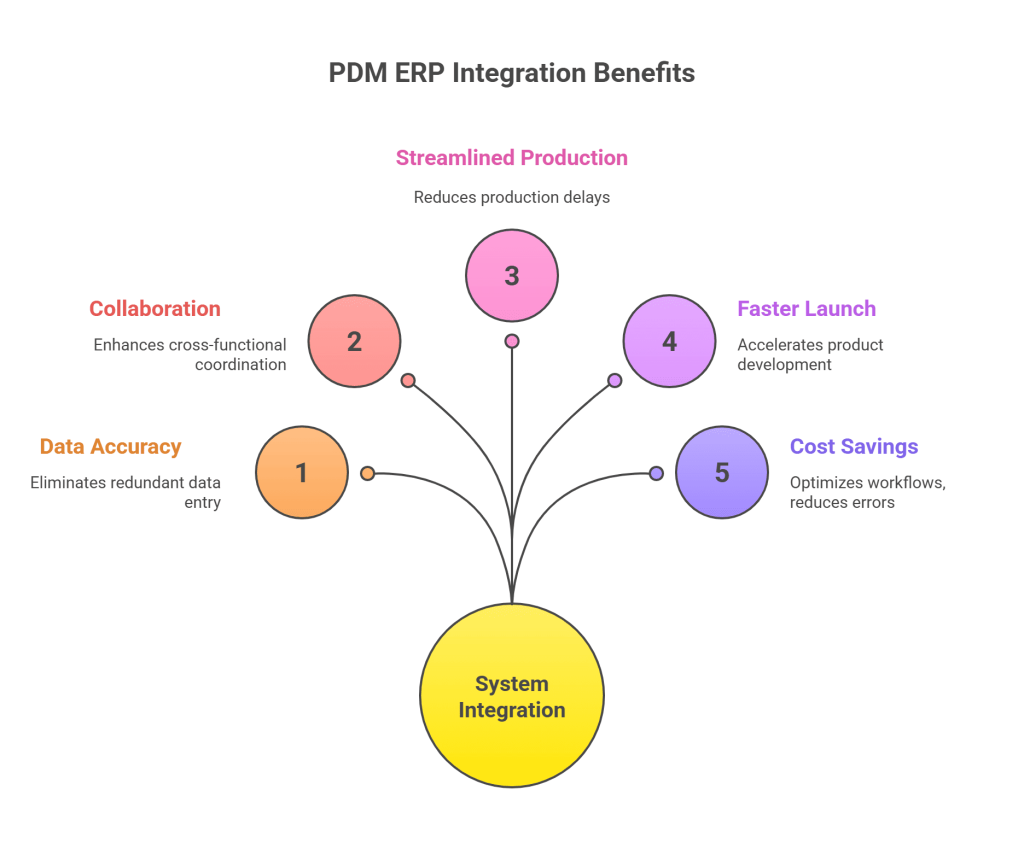
1. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Consistency
By integrating PDM PLM ERP systems, companies can eliminate redundant data entry, minimizing human errors. Data consistency across departments ensures all teams work with accurate product information.
2. Improved Collaboration
Engineering, manufacturing, procurement, and finance teams can collaborate effectively by accessing the same data. This enhances cross-functional coordination and reduces communication gaps.
3. Streamlined Production Processes
Manufacturing teams can retrieve BOMs, design files, and specifications directly from the ERP system. This integration reduces production delays and ensures product quality.
4. Faster Time-to-Market
With real-time data flow between systems, companies can accelerate product development and make quicker decisions, leading to faster market launches.
5. Cost Savings
Optimized workflows, reduced errors, and better resource utilization result in significant cost savings.
Now that we’ve seen the benefits, let’s dive deeper into understanding the differences between PDM, PLM, and ERP systems.
Understanding PDM, PLM, and ERP Systems
To fully grasp the advantages of integration, it’s crucial to understand the differences between PDM, PLM, and ERP systems.
| Aspect | PDM | PLM | ERP |
| Focus | Product data management | End-to-end product lifecycle management | Business operations management |
| Users | Engineers and designers | Cross-functional teams | Supply chain, finance, and operations teams |
| Data Managed | CAD files, BOMs, design data | Product lifecycle data from ideation to disposal | Inventory, production, procurement, finance data |
| Primary Function | Manage product design data | Manage complete product lifecycle | Manage business operations |
Having a solid grasp of these differences, let’s move on to the practical side of things – how to integrate these systems effectively.
How to Integrate PDM with ERP Systems
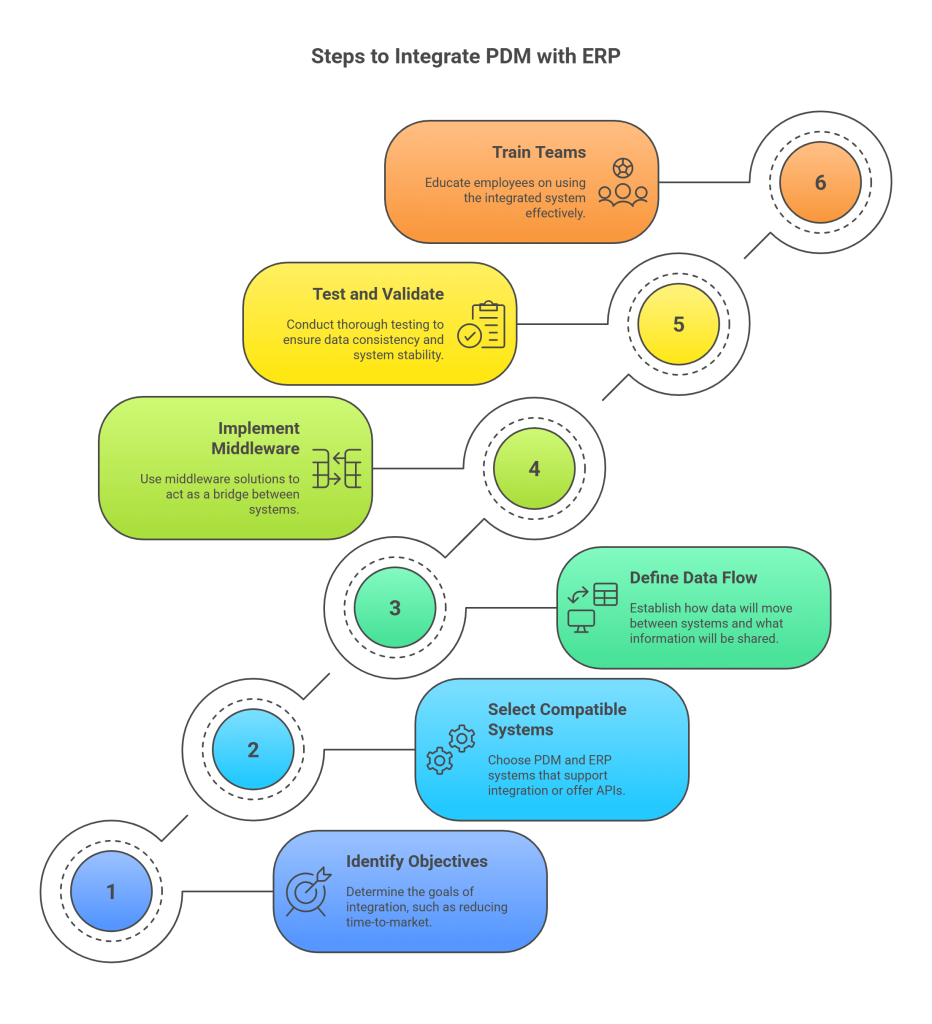
Integrating PDM PLM and ERP systems requires careful planning. Here’s a step-by-step approach to successful integration:
1. Identify Objectives
Determine what you aim to achieve, such as reducing time-to-market or enhancing data accuracy.
2. Select Compatible Systems
Ensure the PDM and ERP systems you choose support integration or offer APIs.
3. Define Data Flow
Establish how data will move between systems and what information will be shared.
4. Implement Middleware or Connectors
Middleware solutions act as a bridge between systems, enabling seamless data exchange.
5. Test and Validate
Conduct thorough testing to ensure data consistency and system stability.
6. Train Teams
Educate employees on using the integrated system effectively.
With these steps in mind, let’s explore some real-world examples of successful PDM and ERP integration.
Examples of PDM and ERP Integration
Example 1:
A manufacturing company designing complex machinery integrates its PDM and ERP systems. Engineers create a BOM in the PDM system, which is automatically transferred to the ERP for procurement and production planning.
Example 2:
An automotive company uses PDM PLM software to manage product designs and integrates it with its ERP system. Changes made by design teams are reflected in inventory management and production processes in real time.
FAQs: Integrating PDM with ERP Systems: Achieve a Seamless Supply Chain
1. Can small businesses benefit from PDM and ERP integration?
Yes, even small businesses can benefit from streamlined operations, improved collaboration, and reduced data entry errors.
2. What challenges can arise during integration?
Common challenges include data inconsistency, system compatibility, and user adoption. These can be mitigated with proper planning and training.
3. How long does it take to integrate PDM with ERP systems?
The timeline depends on the complexity of the systems and the scope of the integration, typically ranging from a few months to a year.
4. What types of data are typically shared between PDM and ERP systems during integration?
Data most commonly exchanged includes Bill of Materials (BOMs), design specifications, engineering change orders, part numbers, and product documentation. This seamless data flow ensures manufacturing and procurement teams always have access to up-to-date information.
5. Is it possible to integrate PDM with cloud-based ERP systems?
Yes, many modern PDM platforms offer connectors or APIs to facilitate integration with cloud-based ERP solutions. This enables organizations to leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud platforms while maintaining synchronized product and business data.
6. How does integrating PDM with ERP systems impact compliance and traceability?
Integration greatly improves compliance and traceability by ensuring all product data and changes are accurately recorded and connected across the product lifecycle. This helps companies meet industry regulations and simplifies audit processes.
7. What strategies can help ensure a smooth PDM-ERP integration process?
Best practices for successful integration include thorough requirements analysis, selecting compatible platforms, involving cross-functional teams in planning, utilizing experienced integration partners, prioritizing data quality, and providing ongoing staff training.
Conclusion
Integrating PDM and ERP systems is a strategic move for companies looking to enhance their supply chain efficiency. It bridges the gap between engineering and business operations, ensuring data consistency, improving collaboration, and accelerating time-to-market.
While selecting the right systems, understanding the difference between PLM and PDM and the role of PDM PLM ERP integration is essential. By embracing this integration, companies can unlock new levels of productivity and competitiveness in the market.
If you are ready to optimize your supply chain, start by evaluating your existing systems and exploring how seamless integration can transform your operations.






