In a world where speed, accuracy, and efficiency are paramount, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has revolutionized how we track and manage objects. Whether in logistics, retail, healthcare, or manufacturing, RFID systems offer seamless identification solutions that simplify complex processes. But how RFID works often remains a mystery to many. This article will break down the science, components, and applications behind RFID and demystify its role in modern industries.

Understanding the Basics: What Is RFID?
Before diving deep into how RFID works, let’s start with the basics. RFID is a wireless communication technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags use special beams to read information from long distances.
Unlike traditional barcodes, which require manual scanning, RFID allows for automatic data capture. This greatly increases efficiency, accuracy, and speed, especially in high-volume environments.
RFID Features
To truly grasp how RFID works, it’s important to understand its three core components:
1) RFID Tag:
The tag contains a microchip and an antenna. The microchip is the storage powerhouse, while the antenna is the medium through which information is transferred to the reader.
2) RFID Reader:
The reader emits radio waves and receives signals back from the tag. It then passes the collected information to a computer system for processing.
3) Antenna:
The antenna, often integrated with the reader, creates an electromagnetic field that powers the tag (in passive systems) and facilitates communication.
Each component plays a critical role in how RFID works, enabling quick and accurate identification of tagged objects.
RFID Working Principle: Step-by-Step
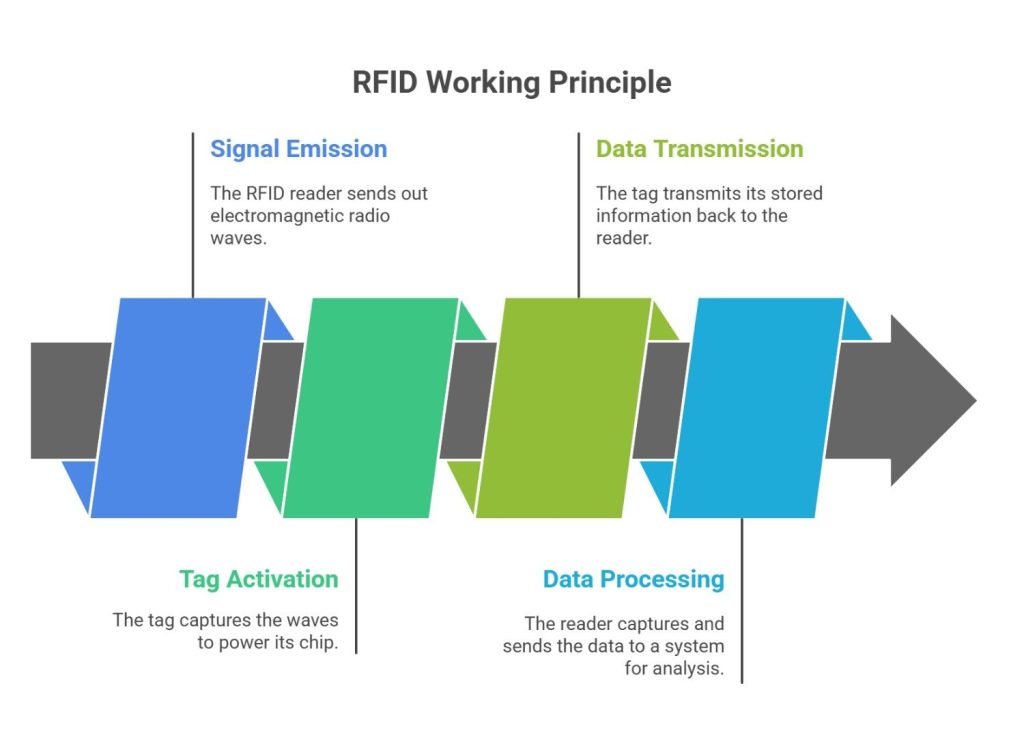
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how RFID works:
1) Signal Emission:
The RFID reader sends out electromagnetic radio waves via its antenna.
2) Tag Activation:
The reader emits RF signals via the antenna. These signals form electromagnetic waves around a particular surface. When the tag enters the field, the antenna captures the waves to power the chip present inside the tag. Once charged, the tag sends the information to the reader.
3) Data Transmission:
The powered tag transmits its stored information (like a unique serial number) back to the reader.
4) Data Processing:
The reader captures the transmitted data and sends it to a connected computer system or cloud platform, where it can be stored, analyzed, and acted upon.
This seamless process is at the heart of how RFID works, making real-time tracking and monitoring effortless.
Types of RFID Tags
When discussing how RFID works, it’s essential to know the types of tags used:
1) Passive RFID Tags:
They do not have their own power source and rely on the reader’s emitted energy. They are mostly preferred by small and medium-scale enterprises for inventory tracking.
2) Active RFID Tags:
Active tags are more powerful than passive tags as they rely on their internal battery to charge the system. They are ideal for tracking high-value assets over long ranges. The difference between active and passive tags lies in their scanning range.
3) Semi-Passive (Battery-Assisted Passive) RFID Tags:
These combine features of both active and passive tags, using a battery to power the chip while still relying on the reader’s signal for communication.
Understanding these variations is vital for appreciating how RFID works across different industries and use cases.
Frequency Bands in RFID Systems
How does RFID tracking work? The answer lies in the frequency bands used:
- Low Frequency (LF) (30–300 kHz): Low range scanning is ideal to track related items.
- High Frequency (HF) (3–30 MHz): Used for library systems, passports, and ticketing.
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) (300 MHz–3 GHz): Offers long read ranges and faster data transfer, common in logistics and supply chain management.
Different frequencies affect read range, data speed, and interference resistance, making frequency selection crucial for optimizing how RFID works in a given application.
Real-World Applications of RFID
Understanding how RFID works brings clarity to its widespread applications:
- Retail: RFID helps retailers track incoming and outgoing stock, prevent theft and manage daily operations.
- Healthcare: Patient tracking, equipment management, and medication authentication.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Logistics partners track shipment dispatch, delivery and location through live tags. Many RFID chips can also monitor temperature, storage, and humidity levels.
- RFID in Manufacturing: Work-in-progress tracking, quality control, and tool management.
- Access Control: Contactless entry systems for secure facilities or transportation hubs.
The more complex the environment, the more critical it is to understand how RFID works and tailor the system accordingly.
Advantages of RFID Technology
Exploring how RFID works also highlights its many advantages:
- Speed: Multiple tags can be read simultaneously, unlike barcodes.
- Accuracy: Reduces human errors in data entry and inventory checks.
- Durability: RFID tags are more resistant to dirt, moisture, and wear than traditional barcodes.
- Security: Some tags are encrypted, ensuring secure data transmission.
- Automation: Enables hands-free operations, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Each advantage ties back to how RFID works at a fundamental level: fast, reliable, and automated data capture.
Challenges in Implementing RFID
Despite its many benefits, understanding how RFID works also means recognizing its challenges:
- Cost: Active RFID systems can be expensive.
- Interference: Metals and liquids can disrupt signals, affecting read reliability.
- Privacy Concerns: Unauthorized reading of tags can lead to data breaches.
- Integration Issues: RFID systems are not easy to integrate with existing IT infrastructure. It requires careful planning to invest in a pack that matches your hardware and software models.
Proper planning and system design can overcome most of these hurdles, ensuring that RFID tags deliver maximum value.
Conclusion
Understanding how RFID works opens a gateway to countless technological possibilities. From speeding up supply chains to enhancing customer experiences, RFID technology represents the future of seamless identification and smart automation. By learning about the components, types, frequencies, and applications, you can make informed decisions about implementing RFID solutions in your business or daily life.
As industries evolve toward greater efficiency and transparency, knowing RFID technology becomes more important than ever. It’s not just about tracking objects anymore — it’s about enabling a smarter, faster, and more connected world. Want a scalable RFID solution for inventory tracking? Look no further than Qodenext to invest in a trusted brand.
FAQS – How RFID Works?
1. What is the main principle behind RFID technology?
RFID technology operates on the principle of electromagnetic field communication between a reader and a tag, enabling automatic data capture without physical contact.
2. How does RFID work compared to barcode scanning?
Unlike barcode scanning, which requires line-of-sight and manual effort, RFID involves wireless, automatic detection, allowing multiple items to be identified simultaneously and from a distance.
3. Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, many RFID tags, especially passive ones, can be reprogrammed and reused depending on the type and intended use.
4. How secure is RFID technology?
Security depends on the RFID system’s design. Encrypted RFID tags and secure communication protocols can make RFID systems highly secure.
5. Does RFID require internet connectivity to function?
No, RFID systems do not require internet connectivity for basic operations. However, for real-time global tracking and data management, integration with cloud platforms is common.
6. How do RFID tags work differently in passive and active tags?
Passive tags rely entirely on the reader’s emitted energy, whereas active tags have an internal battery, allowing them to transmit data independently over longer distances.
7. How far can RFID tags be read from?
The reading distance depends on the type of RFID tag and the frequency in use. Passive tags typically work from a few centimeters up to several meters, while active RFID tags, which have their own internal power source, can often be read from up to 100 meters or more.
8. Are RFID systems easily scalable for growing businesses?
Yes, RFID systems are highly scalable. As your business expands, you can add more tags, readers, and software modules to accommodate increased tracking needs or additional locations without major overhauls.
9. What maintenance do RFID systems typically require?
RFID systems need minimal maintenance overall. It’s advisable to periodically update the software, clean or inspect readers and antennas, and replace batteries in active or semi-passive tags to ensure the system continues to work reliably.
10. Can RFID technology be integrated with other business systems?
Absolutely. RFID is often integrated with ERP, warehouse management, asset tracking, inventory, and point-of-sale systems. This integration allows businesses to automate processes, improve data accuracy, and enable real-time tracking and analytics across operations.






