Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are at the forefront of innovation, transforming industries and redefining automation. In this comprehensive blog, we will explore the captivating world of AMRs and unveil their remarkable potential. Delving into the core concepts that drive these intelligent robotic systems, we shall navigate through their diverse applications across sectors.
From cutting-edge technology empowering their navigation and perception capabilities to their profound impact on logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, and beyond, we shall unravel the intricate details of this rapidly evolving field. Join us on this enlightening journey as we unlock the wonders of autonomous mobile robots and their role in shaping the future.

What Are Autonomous Mobile Robots?
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are advanced robotic systems designed to navigate and operate in various environments without constant human intervention. These robots are equipped with sophisticated sensors, processors, and algorithms that enable them to perceive their surroundings, make intelligent decisions, and execute tasks autonomously.
AMRs have become increasingly popular in industrial, commercial, and even domestic settings due to their ability to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and improve safety. They offer a wide range of applications, from material handling and logistics in warehouses to security patrols and healthcare assistance.
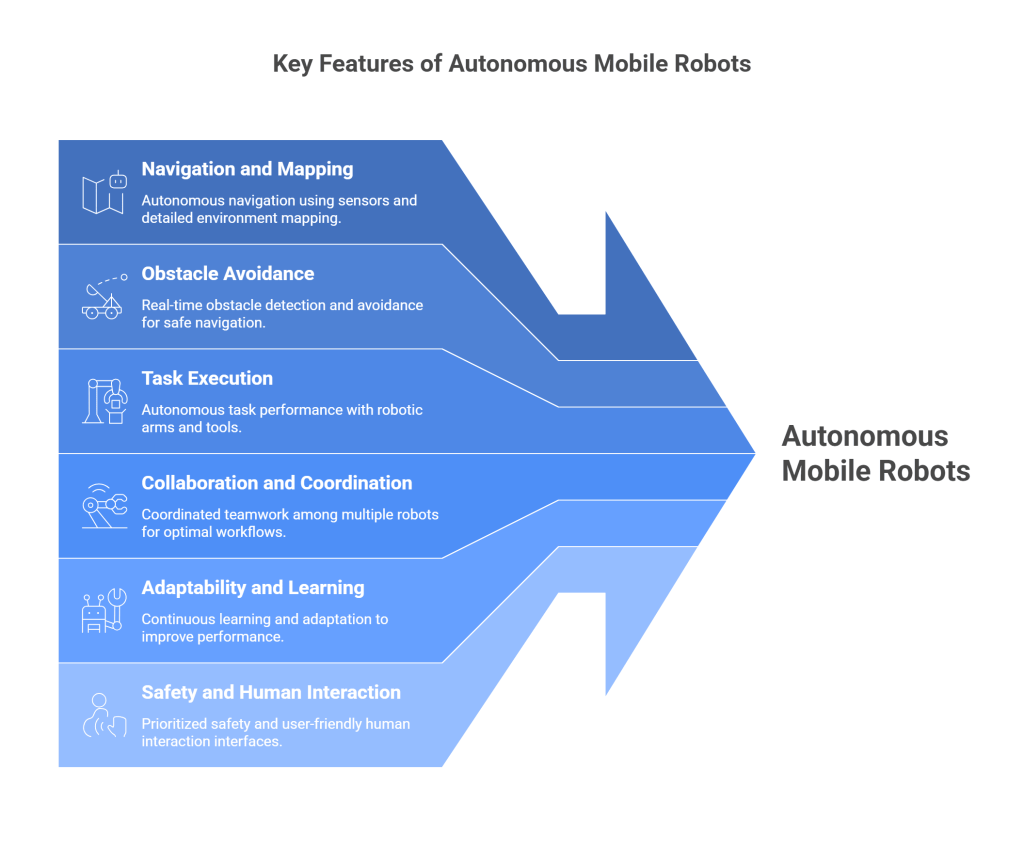
Some of the key features of Autonomous Mobile Robots are listed below :
- Navigation and Mapping: AMR utilizes sensors such as cameras, LIDAR, and ultrasonic devices to perceive their environment, create detailed maps, and navigate autonomously. They can identify obstacles, plan optimal paths, and adapt to dynamic surroundings.
- Obstacle Avoidance: These robots are equipped with intelligent algorithms that allow them to detect and avoid obstacles in real time. By analyzing sensor data and making rapid decisions, AMRs can navigate complex environments safely and efficiently.
- Task Execution: AMRs are designed to perform specific tasks autonomously. They can interact with objects, manipulate tools, and carry out operations such as picking, placing, and transporting items. They are often integrated with robotic arms, grippers, or conveyors to accomplish various tasks.
- Collaboration and Coordination: In environments with multiple AMRs, coordination, and collaboration are crucial. These robots can communicate and share information to optimize workflows, avoid collisions, and work together to achieve common goals.
- Adaptability and Learning: AMRs possess learning capabilities that allow them to adapt to changing environments and improve their performance over time. They can learn from their experiences, optimize their paths, and adjust their behavior based on feedback from their interactions.
- Safety and Human Interaction: Autonomous mobile robots prioritize safety and are designed to operate alongside humans. They are equipped with sensors that detect human presence and can slow down or stop to prevent accidents. They also have user-friendly interfaces for human interaction, enabling operators to monitor their status, set tasks, and intervene when necessary.
These key features make autonomous mobile robots versatile and valuable assets in a wide range of industries, enabling efficient and flexible automation in various applications.
How Does Autonomous Mobile Robots Work?
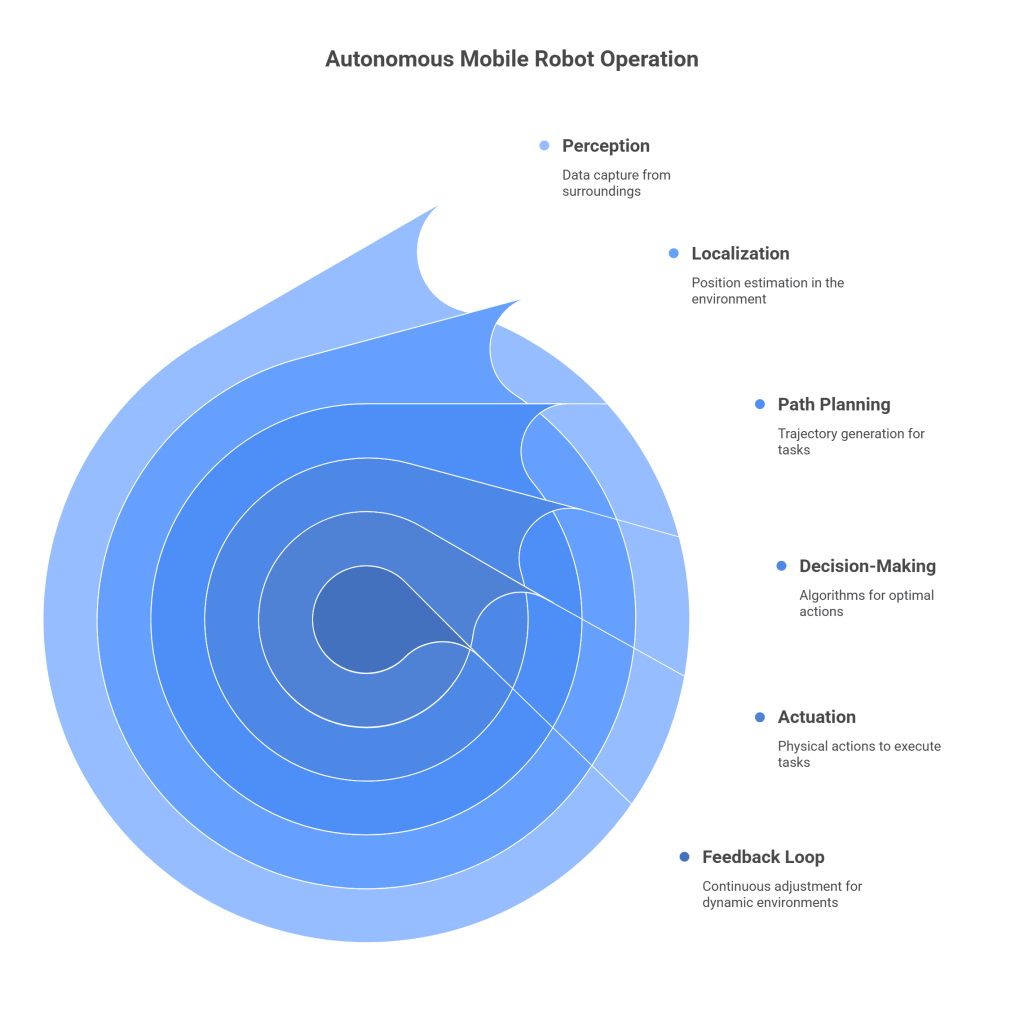
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are advanced machines designed to perform tasks or navigate in various environments without human intervention. These robots incorporate a combination of sensors, algorithms, and actuators to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and execute actions. To understand how AMRs work, let’s break it down into several steps:
- Perception: AMRs are equipped with a range of sensors, including cameras, lidar (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and ultrasonic sensors. These sensors capture data about the robot’s surroundings, such as the presence of objects, obstacles, or landmarks. The sensor data is processed to create a detailed representation of the environment.
- Localization: Once the robot has perceived its environment, it needs to determine its position within it. This is achieved through localization techniques such as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). By comparing sensor data with pre-existing maps or creating new maps as they navigate, AMRs can estimate their position accurately.
- Path Planning: Based on the robot’s perception and localization, algorithms analyze the collected data to generate a path or trajectory to reach the desired destination or complete a given task. Path planning algorithms take into account factors like obstacle avoidance, efficiency, and safety.
- Decision-Making: AMRs employ intelligent algorithms and decision-making systems to interpret the collected data and make real-time decisions. These algorithms analyze the information from the sensors, consider the robot’s current state, and determine the best course of action to accomplish the assigned task or navigate the environment.
- Actuation: Once a path and decision are determined, the robot’s actuators, such as motors or wheels, are activated to move the robot accordingly. The actuators translate the decisions into physical actions, allowing the robot to navigate, pick up objects, or perform other tasks.
- Feedback Loop: Throughout the entire process, the AMR continually receives feedback from its sensors to verify the success of its actions and adjust its behavior if necessary. This feedback loop enables the robot to adapt to dynamic environments and handle unexpected situations.
By integrating perception, localization, path planning, decision-making, actuation, and feedback mechanisms, autonomous mobile robots can operate independently and perform tasks efficiently and safely in a wide range of environments. Their capabilities make them valuable in various industries, including manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and agriculture, among others.
Examples of Autonomous Mobile Robots
Autonomous mobile robots have revolutionized various industries by performing tasks without human intervention, increasing efficiency and productivity. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors, artificial intelligence algorithms, and mobility capabilities, enabling them to navigate and operate in dynamic environments. Here are six notable examples of autonomous mobile robots:
- Amazon Robotics: Amazon utilizes a fleet of autonomous mobile robots in its fulfillment centers. These robots autonomously navigate the warehouses, retrieve shelving units, and transport them to human workers for order picking. This automation streamlines the order fulfillment process and increases operational efficiency.
- Boston Dynamics’ Spot: Spot is a quadruped robot developed by Boston Dynamics. With its advanced mobility and perception capabilities, Spot can autonomously traverse various terrains, perform inspection tasks, and carry payloads. It finds applications in industries such as construction, mining, and public safety.
- Aethon TUG: The Aethon TUG is a versatile autonomous robot used in healthcare facilities and warehouses. It can transport goods, medical supplies, and waste autonomously, reducing the need for human labor and ensuring timely delivery.
- Starship Technologies’ Delivery Robots: Starship Technologies’ autonomous delivery robots are designed to transport goods and groceries over short distances. These robots navigate sidewalks and use advanced sensors to avoid obstacles, ensuring safe and efficient deliveries in urban environments.
- KUKA AG’s Mobile Robots: KUKA AG develops autonomous mobile robots for industrial applications. Their robots are capable of navigating factory floors, collaborating with human workers, and performing tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality control.
- BlueBotics’ Autonomous Forklifts: BlueBotics specializes in autonomous navigation technology for forklifts. Their solutions enable forklifts to operate without human intervention in warehouses and logistics centers, optimizing material handling operations and reducing the risk of accidents.
These examples showcase the versatility and potential of autonomous mobile robots in transforming various industries. With ongoing advancements in robotics and AI, we can expect further innovations in this field, leading to increased automation and improved efficiency across different sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that autonomous mobile robots are revolutionizing various industries with their ability to operate independently and efficiently perform a wide range of tasks. From manufacturing and warehousing to healthcare and logistics, these robots are increasing productivity, reducing costs, and improving safety.
With their advanced sensors, navigation systems, and AI capabilities, autonomous mobile robots are poised to reshape the future of automation. If you’re interested in incorporating autonomous mobile robots into your operations, Qodenext can help.
Contact Qodenext today to explore how our expertise and solutions can optimize your business processes and propel you into the era of robotics automation. Take the next step with Qodenext and unlock the full potential of autonomous mobile robots.
FAQ’s : Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
1. What are Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)?
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are intelligent robotic systems designed to move and perform tasks without constant human control. They use advanced sensors, mapping technology, and AI algorithms to navigate complex environments, detect obstacles, and make real-time decisions.
2. How do AMRs differ from traditional automated guided vehicles (AGVs)?
Unlike AGVs that follow fixed paths or magnetic strips, AMRs navigate dynamically using sensors and onboard mapping systems. AMRs can reroute in real-time, making them more flexible and adaptable to changing environments than AGVs.
3. What are the main components that enable AMRs to function autonomously?
Key components include:
- Sensors (e.g., LIDAR, cameras) for perception
- SLAM algorithms for localization and mapping
- AI-based decision-making systems
- Actuators for movement
- Feedback loops to adapt and improve operations
4. In which industries are AMRs commonly used?
AMRs are widely used in:
- Logistics and Warehousing for material transport
- Manufacturing for assembly line assistance
- Healthcare for delivery of medical supplies
- Retail for shelf scanning and restocking
- Agriculture for precision farming tasks
5. What tasks can AMRs perform in a warehouse?
In warehouse environments, AMRs handle tasks such as:
- Picking and placing items
- Transporting goods between zones
- Sorting packages
- Inventory management
- Assisting in loading and unloading
6. Are AMRs safe to operate around human workers?
Yes, AMRs are designed with safety in mind. They use real-time obstacle detection, speed control, and human presence sensors to operate safely in environments shared with people. Many also include emergency stop mechanisms and audible/visual alerts.
7. How does an AMR navigate and avoid obstacles?
AMRs use sensor data (LIDAR, ultrasonic, infrared) to build a map of their surroundings. With this map and path-planning algorithms, they can autonomously detect and avoid obstacles by dynamically adjusting their route.
8. Can multiple AMRs work together in the same facility?
Yes, AMRs can communicate and collaborate through a centralized fleet management system. This allows them to coordinate tasks, avoid collisions, and optimize workflow efficiency across the facility.
9. What are the benefits of using AMRs in business operations?
AMRs offer several advantages:
- Increased operational efficiency
- Reduced labor costs
- Enhanced workplace safety
- Real-time data collection and analytics
- Scalability and easy integration with existing systems
10. How can Qodenext help implement AMR solutions?
Qodenext provides expert consulting and tailored solutions for businesses seeking to adopt autonomous mobile robots. From hardware selection to systems integration, Qodenext ensures seamless deployment of AMRs to optimize your workflow and drive automation forward.






