Customers expect quick, dependable deliveries in today’s tech-driven, fast-paced world, and your distribution network is essential to meeting their expectations. Building a strong distribution network is essential to gaining customers’ trust, cutting expenses, and expanding operations, regardless of the size of your company.
Building a well-connected and efficient distribution network ensures that your products reach the right place at the right time—keeping your customers happy and your business growing. But how exactly do you build an effective distribution network? Don’t worry—this blog will walk you through the essentials of distribution management, from network design to choosing the right distribution channels and more.
What is a Distribution Network and Why is it Important?
A distribution network combines logistics, inventory, transportation, and channel strategy to describe the system and channels that a company uses to move goods from the point of manufacture to the end user. It involves several distribution channels, including direct-to-consumer sales and wholesalers, retailers, and distributors. A well-functioning distribution network lowers expenses, speeds up deliveries, and improves client satisfaction.
To meet your customer’s demands effectively, you need a well-designed distribution network to ensure your products are available at the appropriate time and location. Additionally, it optimizes your supply chain resiliency, lowers logistical costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
How to Build an Effective Distribution Network?
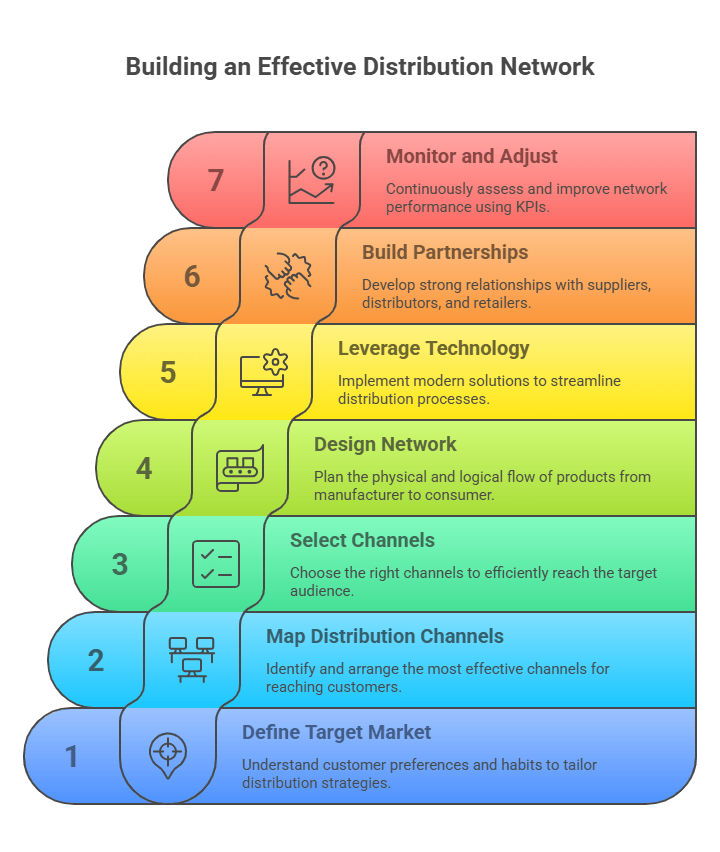
Here are important 7 steps for you to follow to build a fruitful distribution network in the supply chain:
STEP 1. Define & Understand Your Target Market
The very first thing to do to develop a distributional network for your goods and services company is to know who your target audience is. You have to be involved in complete behavioral market research where you will find your customers’ consumption habits and preferences.
To be able to segment your market, you must use demographics, geography, purchasing habits, and other criteria meaningful to your selected field. Identify what customers value most: swift delivery, low prices, or adequate product availability.
STEP 2. Map Out Your Distribution Channels
Your distribution strategy would be concerned with the arrangement of your distribution channels. There are several strategies like selling your products by yourself to the consumers at your local shops, website, or sales force (direct distribution), entering into deals with intermediaries such as wholesalers, distributors, and retailers to reach out to customers (indirect distribution) and through a combination of both ways to get an effective and productive reach (hybrid distribution).
STEP 3. Select Your Distribution Channels
Selecting the right distribution channels is a crucial step in reaching your target audience effectively. The channels you choose can directly impact your market reach, customer satisfaction, and overall business efficiency. Here are some key options to consider:
- Wholesalers: These intermediaries purchase your products in bulk and resell them to retailers or other businesses, helping you scale distribution without managing every single transaction.
- Distributors: Distributors act as a bridge between your business and multiple retail or commercial outlets. They handle logistics, warehousing, and timely delivery, easing your operational load.
- Retailers: These are the direct link to end consumers, offering your products in physical stores or through their own online platforms. Ideal for building customer relationships and brand presence.
E-commerce Platforms: Online marketplaces like Amazon or Flipkart offer a fast, direct route to customers with minimal overhead. They are perfect for businesses looking to expand their digital footprint and streamline order fulfillment.
STEP 4. Design Your Distribution Network
Such design encompasses the physical and logical flow of your products as they move from the manufacturer to the consumer. Some of the components include-
Installation of warehouses near your suppliers, customers, transportation facilities, and delivery areas to reduce time and cost, choosing fast transportation means for timely delivery, and balancing your inventory levels by avoiding overstocking and preventing understocking.
STEP 5. Leverage Technology
In the current era of technology, distribution networks can be easily implemented using more modern solutions. Incorporate WMS into your warehouse to streamline production and reduce processing time efficiently and easily. By leveraging a transportation management system (TMS), you can strategize, execute, and facilitate the distribution of your goods. The use of Inventory automation software will also help you yield real-time tracking and inventory level management without delays.
STEP 6. Build Strong Partnerships
Your distribution network will only become strong when you keep good relationships with your partners. So, it is essential to develop consistent partnerships with suppliers & distributors, and retailers for effective networking. Maintaining transparent communication and mutual trust leads to better operations and a steady flow of products.
STEP 7. Monitor and Adjust the Optimization of Your Network
Ensuring constant performance monitoring of your distribution network and identifying potential for improvement using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as delivery times, order accuracy, and inventory levels. You should also use data analytics to understand the strength of your network and maintain feedback loops to bridge the gaps in your distribution processes, if any.
Upcoming Developments in Distribution Network
Distribution networks also keep changing along with the technology change. Have a look at the following trends to get a vivid idea!
1. AI and automation
Distribution networks are being completely transformed by automation and artificial intelligence (AI). Autonomous delivery trucks, AI-powered demand forecasting, and automated warehouses are becoming more prevalent.
2. Ecological Viability
Designing distribution networks is becoming more and more dependent on sustainable practices. Businesses are concentrating on employing green technologies and effective logistics to lower their carbon footprints.
3. Distribution Through Multiple Channels
Omnichannel distribution networks, which include online and physical channels, are becoming more and more important as e-commerce grows. By doing this, a smooth consumer experience is guaranteed at every touchpoint.
4. Technology of Blockchain
Blockchain is an important technology for distribution networks because it provides security and transparency in supply chains. It can support product tracking, authenticity verification, and compliance.
When you design or reconfigure your network, factor in modularity for future adoption of these trends (e.g. built-in capacity for automation, flexibility for adding micro-nodes).
Conclusion
Building a strong distribution network is no longer optional—it’s a critical driver of business success in today’s fast-paced, customer-centric market. From identifying your target audience and selecting the right distribution channels to leveraging cutting-edge technology and nurturing partnerships, every step plays a vital role in ensuring products reach the right place, at the right time, and in the most efficient manner.
As supply chain dynamics continue to evolve, staying agile and embracing emerging trends like AI, automation, sustainability, and omnichannel strategies will help future-proof your distribution model.
Remember, a robust distribution network not only streamlines operations—it creates value, enhances customer satisfaction, and lays the foundation for long-term business growth.
FAQs: 7 Steps to Develop a Robust Distribution Network in 2024
1. What are the usual problems encountered in the channel network?
Some common challenges namely, costly shipments, merchandise control, ensuring swift delivery service, and the process of the tried and tested regulations. These plights may be appropriated by introducing route optimization, demand forecasting (advanced), strategic transportation methods, and compliance systems (management).
2. What strategy can small businesses adopt to compete for distribution channels without ample resources?
Small businesses may benefit from the utilization of third-party logistics (3PL) suppliers, cloud-based inventories, concentrating on certain market segments for complex distribution, and teaming up by sharing warehouses with local distributors to control costs.
3. Can you share one example of a successful distribution network?
The Network of Amazon, for instance, is something praiseworthy. From advanced technology and vast transportation to sophisticated warehousing and order fulfillment systems and a data-driven decision-making mindset to optimize operations and guarantee fast, reliable deliveries at every location, their infrastructure is designed to provide you with the best shopping experience.
4. How often should a business review its distribution network?
Businesses should assess their distribution network at least annually or whenever significant changes in demand, technology, or market conditions occur to stay agile and competitive.
5. What KPIs should I track to measure distribution efficiency?
Track metrics like order accuracy, delivery lead times, fill rate, inventory turnover, cost per order, and customer satisfaction scores.
6. How can technology help reduce distribution costs?
Tools like WMS, TMS, and AI-driven demand forecasting help streamline operations, reduce manual errors, optimize delivery routes, and improve inventory control.
7. What’s the difference between direct and indirect distribution?
Direct distribution involves selling directly to the customer, while indirect distribution uses intermediaries like wholesalers or retailers to reach the end user.
8. Why is warehouse location important in a distribution network?
Strategically placed warehouses reduce delivery time and transportation costs, improving service levels and overall customer satisfaction.







