Vehicle accidents claim lives and cause severe damage to property and resources. Fleet telematics systems enhance efficiency, eliminate delays, and monitor issues before they become big problems. They also allow predictive maintenance, lowering the frequency of accidents and increasing driver accountability.
Let’s explore the role of vehicle tracking systems, including how they work, benefits, and more.

What is Telematics?
Vehicle tracking is a field of technology that combines telecommunications and informatics to transmit data over long distances. In the context of vehicles, it involves using GPS technology, onboard diagnostics, and IoT sensors to collect and transmit data about a vehicle’s location, speed, engine performance, and other key metrics.
The core lies in its ability to provide real-time data, which is essential for vehicle traceability. Fleet managers use this technology to monitor vehicle locations, optimise routes, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
How Does Telematics in Fleet Management Work?
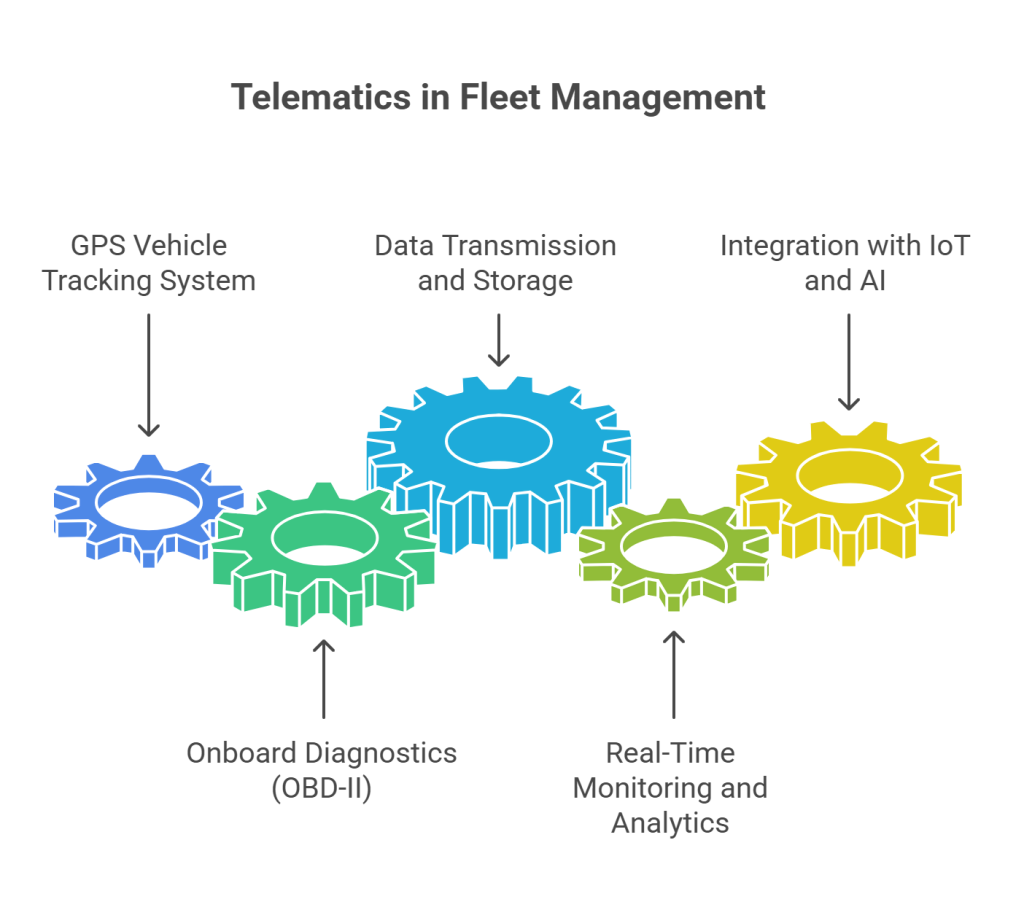
Vehicle traceability refers to the ability to track and monitor the movement and performance of vehicles in real-time. It plays a crucial role in achieving this through a combination of hardware and software.
1. GPS Vehicle Tracking System
Fleet trackers rely on GPS tracking devices installed in vehicles. These devices continuously communicate with satellites to determine the vehicle’s exact location. The data is then transmitted to a central server via cellular networks or satellite communication.
2. Onboard Diagnostics (OBD-II)
Most modern vehicles are equipped with OBD-II ports, which connect to telematics devices. These devices gather data on engine health, fuel consumption, and maintenance needs. This information is critical for tracking the vehicle’s operational status.
3. Data Transmission and Storage
These systems use cellular networks or cloud-based platforms to transmit data. The collected data is stored on secure servers, where it can be accessed and analysed by fleet managers or vehicle owners.
4. Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
The integration of fleet trackers with advanced software platforms enables real-time monitoring of vehicles. These platforms provide detailed analytics, including route optimisation, fuel efficiency, and driving behaviour.
5. Integration with IoT and AI
Modern tracking systems leverage IoT sensors and AI algorithms to enhance vehicle traceability further. For instance, IoT sensors can detect temperature changes in refrigerated trucks, while AI can predict potential mechanical failures.
Benefits of Telematics in Vehicle Traceability
The adoption of vehicle tracking offers numerous advantages, particularly for industries that rely heavily on vehicle fleets.
1. Enhanced Visibility
Fleet tracking provides complete visibility into the location and movement of vehicles, which is crucial for supply chain operations, logistics, and ride-sharing services.
2. Improved Efficiency
By analysing vehicle data, fleet managers can identify inefficiencies such as unoptimised routes or excessive idling, leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
3. Increased Safety
Telematics systems monitor driving behaviour, including harsh braking, speeding, and sudden accelerations. This helps organisations identify risky drivers and implement corrective measures.
4. Regulatory Compliance
In industries like transportation and logistics, compliance with regulations is mandatory. Tracking systems ensure adherence to safety standards and provide documentation for audits.
5. Theft Prevention and Recovery
Fleet management practices aids in theft prevention by enabling real-time tracking of stolen vehicles. Geo-fencing technology can also trigger alerts when a vehicle leaves a predefined area.
Key Applications of Telematics in Vehicle Traceability
Vehicle tracking technology is versatile and finds applications in various domains, including:
1. Fleet Management
Fleet managers rely on telematic dashboards for route optimization, fuel management, and vehicle maintenance scheduling. This ensures the smooth operation of large vehicle fleets.
2. Logistics and Supply Chain
Vehicle tracking software enables end-to-end visibility in supply chain operations, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing transit-related risks.
3. Insurance
Usage-based insurance policies leverage truck data to assess driving behaviour and determine premiums. This incentivizes safer driving habits.
4. Public Transportation
Telematics systems in buses and trains provide real-time updates to passengers and improve overall transit reliability.
5. Emergency Services
Trackng vehicle information assists in dispatching emergency services to precise locations, reducing response times and saving lives.
Challenges in Implementing Telematics
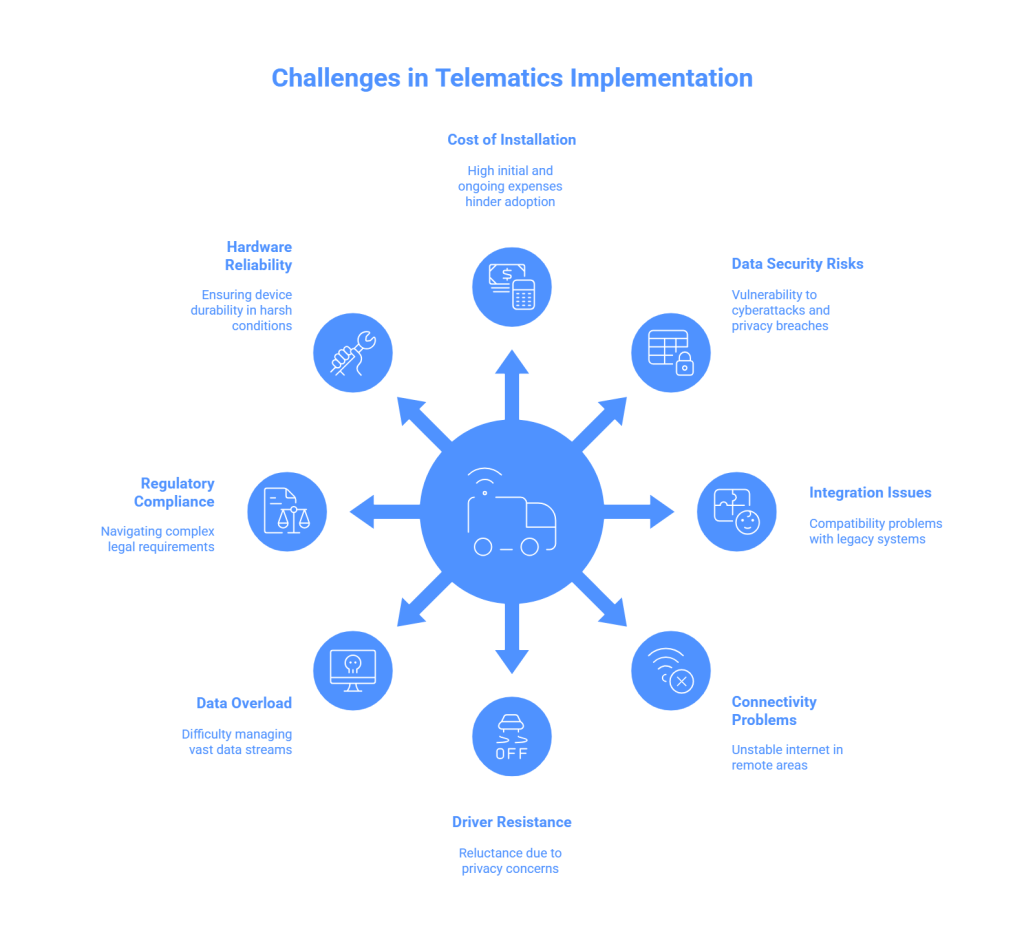
While smart transport systems offer numerous benefits, its implementation is not without challenges. These hurdles need to be addressed to leverage the full potential of vehicle tracking.
1. Cost of Installation and Maintenance
The upfront cost of installing tracking systems can be prohibitive, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. Expenses include hardware, software subscriptions, and training personnel to use the systems effectively. Additionally, ongoing maintenance costs, such as software updates and device repairs, can add to the financial burden.
2. Data Security and Privacy Risks
Telematics systems collect vast amounts of sensitive data, such as vehicle locations, driver behaviour, and engine diagnostics. This makes them prime targets for cyberattacks. Unauthorized access to this data can lead to significant privacy breaches, potentially damaging a company’s reputation and violating data protection regulations.
3. Integration with Legacy Systems
Organizations with existing legacy systems often face compatibility issues when integrating IoT vehicle technology. Retrofitting older vehicles with tracking devices or ensuring seamless data transfer between new and existing systems can be both complex and time-consuming.
4. Connectivity Issues
Mobility systems rely heavily on stable internet connections for real-time data transmission. However, vehicles operating in remote or rural areas often face connectivity challenges, leading to delays or gaps in data transmission. This can compromise the effectiveness of vehicle tracking.
5. Driver Resistance and Training
Some drivers may resist the implementation of fleet trackers, viewing it as an invasion of privacy or an additional layer of scrutiny. Organisations must invest in driver education to highlight the benefits such as improved safety and reduced workloads. Building trust with drivers is crucial for successful adoption.
6. Data Overload and Analysis Complexity
Telematics systems generate vast amounts of data. Managing and analysing this data to derive actionable insights can be overwhelming, especially for organisations without robust data analytics capabilities. This can result in underutilisation of the technology’s potential.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Legal Issues
Different regions have varying regulations regarding data collection, storage, and usage. Ensuring compliance with these laws requires companies to invest in legal expertise and adapt their systems accordingly, which can add to the complexity and cost of implementation.
8. Hardware Reliability and Durability
Telematics devices installed in vehicles must endure harsh environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, vibrations, and humidity. Ensuring the reliability and durability of this hardware is critical, as frequent device failures can disrupt operations and increase maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Vehicle telematics plays a crucial role in tracking driver behaviour and vehicle condition. It gives you actionable insights into fuel consumption, engine condition, and operating efficiency. It will streamline the fleet management industry in the coming years. For further assistance in asset tracking and traceability, contact Qodenext today.
FAQs – Telematics
1. How to track a vehicle?
Connected vehicle systems is a technology that combines telecommunications and informatics to track and monitor vehicles in real time. It collects data on location, speed, engine health, and more.
2. How to track a GPS-enabled vehicle?
Install a GPS tracking device which connects to the vehicle’s power supply. Activate the tracker and use a software/app to connect the link. Once connected, open the app to review the vehicle data, location, speed, and other information.
3. Is fleet tracking only for commercial vehicles?
No, it is not limited to commercial vehicles. Vehicle tracking is also used in personal vehicles, public transportation, and emergency services.
4. What are the key components of a wireless tracking system?
A wireless system typically includes GPS trackers, onboard diagnostics (OBD-II), IoT sensors, and software platforms for data analysis.
5. Are there any privacy concerns with telematics?
Yes, privacy concerns can arise due to the transmission and storage of sensitive data. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to address these concerns.
6. How do telematics systems handle data privacy concerns?
Telematics systems collect sensitive information, so data privacy is crucial. Reputable providers use strong encryption, secure servers, and strict access controls to protect data. Companies must also inform drivers about data collection policies and comply with relevant privacy laws like GDPR or CCPA to ensure transparency and legal compliance.
7. What types of vehicles can benefit from telematics systems?
Telematics is applicable not only to commercial fleets but also to personal vehicles, public transportation, emergency services, and rental companies. Any operation requiring real-time vehicle tracking, maintenance monitoring, or driver behavior analysis can gain from telematics technology.
8. Can telematics improve driver behavior and safety?
Yes, telematics systems monitor driving habits such as speeding, hard braking, and idling. With this data, fleet managers can provide feedback and training to encourage safer driving. Some systems include real-time alerts for risky behavior, helping reduce accidents, improve compliance, and lower insurance costs.
9. What challenges do companies face when implementing telematics?
Common challenges include the initial investment costs, integrating telematics with existing IT infrastructure, data overload requiring advanced analytics capabilities, and resistance from drivers concerned about privacy or monitoring. Successful adoption often depends on clear communication, choosing the right technology, and providing ongoing training.
10. How does telematics support regulatory compliance?
Telematics helps fleets meet regulatory requirements such as hours-of-service for drivers, vehicle inspection records, and environmental standards. By automatically logging data and generating compliance reports, it simplifies audits and reduces the risk of violations and penalties.






