Supply chain bottlenecks disrupt the flow of goods and services, causing big issues in logistics operations. Even a small hiccup can delay the transportation of goods, crippling production and deliveries. It is important to maintain the delicate balance of the supply chain network.
In this article, we’ll explore the common causes of bottlenecks and ways to overcome them. Let’s go.

What is a Supply Chain Bottleneck?
A supply chain bottleneck refers to any point in the supply chain where the flow of goods, materials, or information slows down or comes to a halt. These bottlenecks limit the overall efficiency of the supply chain and can lead to delays, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
Bottlenecks can occur at various stages, such as sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, warehousing, or transportation. Even a minor disruption at one point can cascade throughout the entire supply chain, causing significant issues downstream.
Causes of Bottlenecks in Supply Chain Management
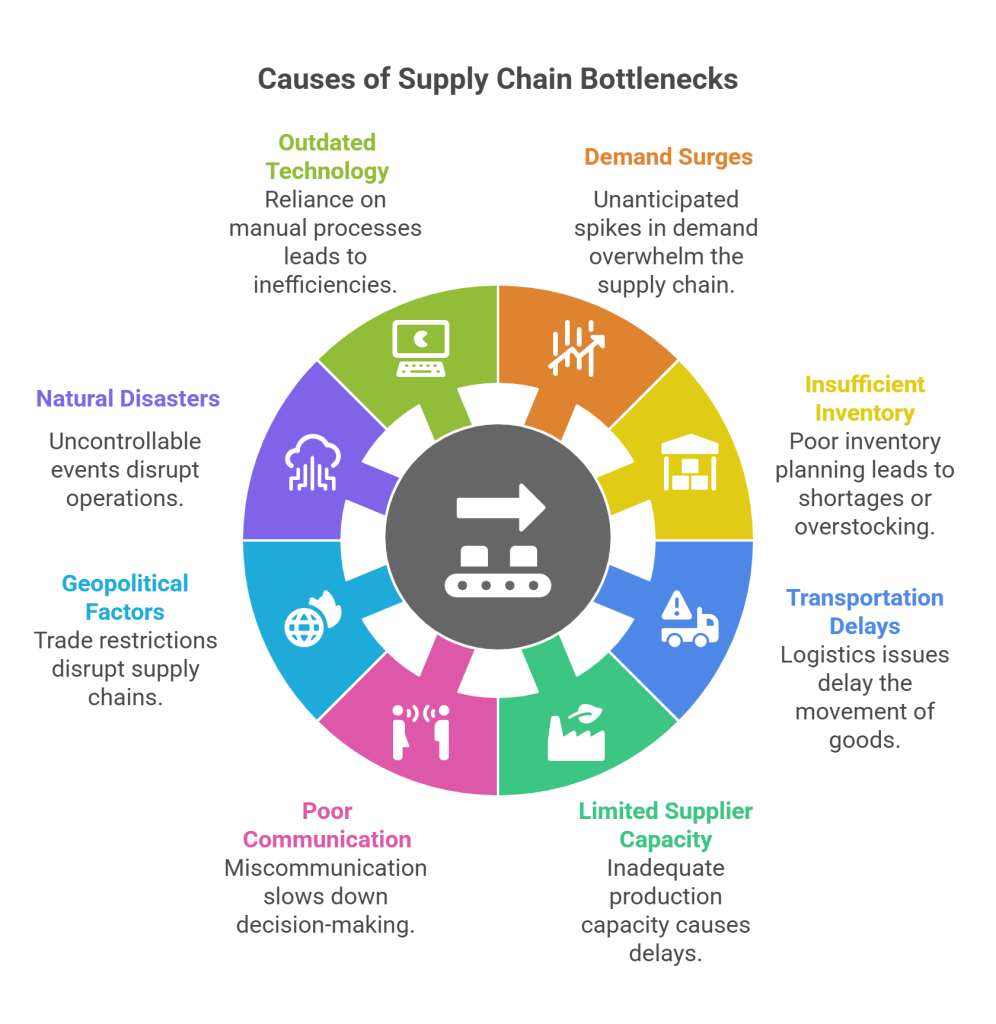
Understanding the root causes of a supply chain bottleneck is key to addressing the problem effectively. Here are some common culprits:
1. Demand Surges
Unanticipated spikes in demand can overwhelm the supply chain. Events like seasonal holidays, promotional campaigns, or market trends often cause sudden demand surges that suppliers may struggle to meet.
2. Insufficient Inventory Management
Poor inventory planning, whether due to overstocking or understocking, creates inefficiencies. For instance, understocking leads to shortages, while overstocking ties up capital and space, hampering the smooth flow of goods.
3. Transportation Delays
Logistics issues, such as vehicle breakdowns, traffic congestion, or port congestion, can delay the movement of goods, causing a supply chain bottleneck in distribution.
4. Limited Supplier Capacity
Relying on a single supplier or one with inadequate production capacity often leads to delays. If a supplier cannot meet growing demands or faces disruptions, it directly affects the entire chain.
5. Poor Communication and Data Flow
Supply chains involve multiple stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors. Miscommunication, delayed information, or outdated systems can slow down decision-making and cause bottlenecks.
6. Geopolitical Factors
Trade restrictions, tariffs, or political unrest in certain regions can disrupt supply chains. These factors often lead to material shortages or extended delivery times.
7. Natural Disasters and Pandemics
Uncontrollable events such as floods, earthquakes, or pandemics disrupt operations and create supply chain challenges, contributing to bottlenecks.
8. Outdated Technology
Organizations still relying on manual processes or outdated software struggle to adapt to modern supply chain management risks and challenges. Lack of automation and real-time data leads to inefficiencies.
Top Challenges in Supply Chain – Impact
A supply chain bottleneck can have a wide range of consequences, not just for businesses but also for their customers and partners. When the smooth flow of goods and services is disrupted, the entire supply chain experiences a domino effect, leading to significant operational and financial repercussions. Here’s a detailed look at how it affects different business aspects:
1. Production Delays
When raw materials or components don’t arrive on time, manufacturing processes are disrupted. This forces production lines to either halt operations or run below capacity, leading to unmet deadlines. For industries like automotive or electronics, where production schedules are tightly synchronized, even a small delay can cause ripple effects across multiple stages of production.
2. Increased Operational Costs
A supply chain bottleneck often leads to unforeseen expenses. Companies might need to pay for expedited shipping, alternative suppliers, or additional labour to resolve issues. These costs can accumulate quickly, eating into profit margins. Additionally, holding inventory for longer than expected or dealing with penalties for late deliveries can further strain financial resources.
3. Customer Dissatisfaction
Late deliveries, stockouts, or product shortages can frustrate customers and damage a company’s reputation. If a business repeatedly fails to meet those expectations due to bottlenecks, it risks losing customers to competitors who can deliver on time. This is especially critical in industries like e-commerce, where customer loyalty is fragile.
4. Loss of Revenue
Delays in the supply chain can directly result in lost sales opportunities. For instance, if a retailer is unable to stock popular items during peak seasons, such as holidays or sales events, they miss out on potential revenue. Similarly, manufacturers may face penalties for not delivering goods to distributors or clients on time.
5. Reduced Productivity
Employees and teams across the organization may become less productive when bottlenecks occur. For example, warehouse staff might be left idle due to delayed shipments, or customer service teams might spend extra time handling complaints and managing expectations. This not only impacts operational efficiency but also lowers morale.
How to Overcome Supply Chain Bottlenecks
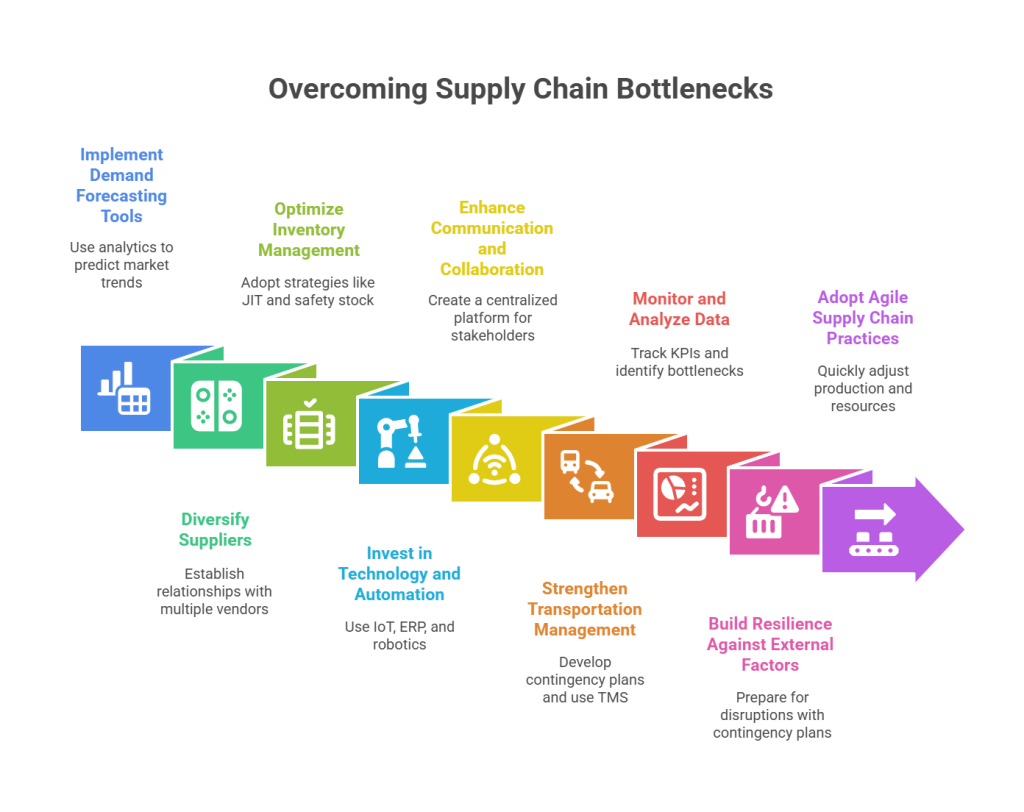
Solving a bottleneck requires a mix of strategic planning, technology, and process optimization. Here’s how to address them effectively:
1. Implement Demand Forecasting Tools
Invest in advanced analytics and demand forecasting tools to predict market trends and prepare for production and logistics visibility. Using historical data and AI-driven algorithms, businesses can better align inventory levels with expected demand.
2. Diversify Suppliers
Avoid over-reliance on a single supplier. Establish relationships with multiple vendors across regions to ensure a steady supply of materials, even during disruptions.
3. Optimise Inventory Management
Adopt inventory optimization strategies like Just-In-Time (JIT), safety stock, or buffer inventory. Inventory management software can help monitor stock levels and automate replenishment.
4. Invest in Technology and Automation
Use technologies such as:
- IoT: Real-time tracking of shipments and inventory.
- ERP Systems: Integrating data from various supply chain stages for better visibility.
- Robotics: Automating warehouse operations for improved efficiency.
5. Enhance Communication and Collaboration
Create a centralized platform where all supply chain stakeholders can share information in real-time. This reduces delays caused by miscommunication and ensures alignment across the chain.
6. Strengthen Transportation Management
Develop contingency plans for transportation delays, such as alternative routes or backup carriers. Investing in Transportation Management Systems (TMS) can improve logistics planning and execution.
7. Monitor and Analyse Data
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like order accuracy, lead times, and on-time deliveries. Regular data analysis helps identify recurring bottlenecks and allows for proactive measures.
8. Build Resilience Against External Factors
Prepare for geopolitical or natural disruptions by developing contingency plans. Stockpile critical materials in strategic locations to mitigate the impact of unexpected events.
9. Adopt Agile Supply Chain Practices
Flexibility is key in handling bottlenecks. An agile supply chain can quickly adjust production schedules, reallocate resources, or switch suppliers when disruptions occur.
Examples of Supply Chain Bottlenecks in Real Life
1. The Global Chip Shortage
The semiconductor industry faced significant bottlenecks due to pandemic-induced disruptions and soaring demand. This delayed the production of electronics and automobiles globally.
2. Port Congestion During COVID-19
Global ports experienced severe congestion as container shortages and labour constraints hampered shipping operations. This caused massive delays in the delivery of goods.
Conclusion
Understanding supply chain bottlenecks is key to maximising profitability. It’s impossible to avoid disruptions but planning the possible outcomes will help you overcome challenges. For further assistance in supply chain management, contact Qodenext today.
FAQs – Supply Chain Bottlenecks
1. What is the most common cause of a supply chain bottleneck?
The most common cause is a mismatch between supply and demand, often driven by poor forecasting, supplier constraints, or unexpected demand spikes.
2. How can technology help in addressing supply chain bottlenecks?
Technology like IoT, AI, and TMS enables real-time tracking, better demand forecasting, and streamlined communication, reducing inefficiencies.
3. How do bottlenecks affect customer satisfaction?
Bottlenecks can lead to delayed deliveries and stockouts, creating a poor customer experience and potentially damaging brand loyalty.
4. Can supply chain bottlenecks be completely eliminated?
While it’s impossible to eliminate all bottlenecks, proactive planning, diversification, and technology adoption can significantly minimize their impact.
5. What industries are most affected by supply chain bottlenecks?
Industries like manufacturing, retail, automotive, healthcare, and electronics are highly susceptible to supply chain disruptions.
6. What is the difference between a temporary and a chronic supply chain bottleneck?
A temporary bottleneck is usually caused by short-term disruptions—such as a sudden surge in demand, weather-related transport delays, or a one-off supplier issue. Once the disruption is addressed, the bottleneck resolves. Chronic bottlenecks, however, are ongoing issues resulting from systemic problems like inadequate supplier capacity, outdated technology, or ineffective processes. These require a fundamental change in strategy or infrastructure to fix.
7. How can companies measure and identify bottlenecks in their supply chain?
Companies can spot bottlenecks by monitoring key performance indicators such as order cycle time, fill rates, production lead times, and on-time delivery rates. Data analysis can reveal consistent slow points or recurring issues in the process. Mapping the entire supply chain and analyzing where delays or inventories build up is also helpful for pinpointing bottleneck locations.
8. What role does supplier collaboration play in preventing bottlenecks?
Strong supplier collaboration means regular communication, shared data, and joint planning for production and delivery schedules. When suppliers and buyers work closely and transparently, they can anticipate changes in demand, address capacity constraints proactively, and resolve disruptions faster—minimizing the risk of bottlenecks.
9. Are there early warning signs of an emerging supply chain bottleneck?
Yes, signs include frequent inventory shortages or surpluses, increased lead times, spikes in expedited freight costs, declining on-time delivery, and an uptick in customer complaints about late orders. Keeping an eye on these indicators allows companies to act quickly before a minor issue becomes a major bottleneck.
10. How often should businesses review their supply chain to prevent bottlenecks?
Regular supply chain reviews—quarterly or even monthly in fast-moving industries—are essential. In volatile markets or complex supply networks, more frequent monitoring is advisable. Scheduled reviews, combined with real-time data dashboards, help businesses adapt to emerging risks and continuously improve processes to stay resilient against new bottlenecks.






