India, a land of diverse cultures and traditions, is also emerging as one of the fastest-growing retail markets globally. According to recent statistics, the Indian retail market is projected to reach a value of 1.75 trillion U.S. dollars by 2026. With the ever-expanding retail industry and the increasing need for efficient inventory management, accurate product tracking has become crucial. This is where barcodes step in as a game-changer. Barcodes have revolutionised the way businesses operate by providing a standardised method of encoding data for various purposes. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of barcodes, exploring the different barcode types, different formats, examples, types of barcode readers, and how you can create a barcode for your product.

Barcode Types: A Brief Overview
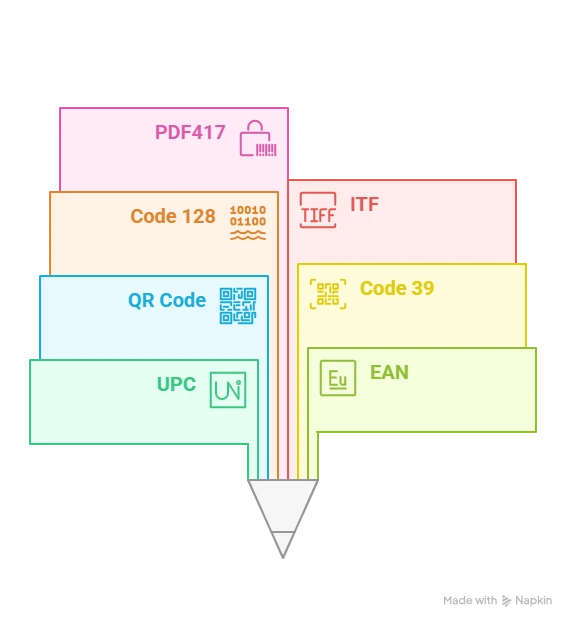
Barcodes, a familiar sight in our daily lives, are graphical representations of data that can be read by machines, making data capture quick and error-free. They come in various types, each serving specific purposes. The most common barcode types include:
1. UPC (Universal Product Code)
Widely used in the retail industry, UPC barcodes are found on most consumer products, such as groceries, electronics, and clothing. The UPC-A format consists of 12 numerical digits.
2. EAN (European Article Numbering)
Similar to UPC, EAN barcodes are prevalent globally and are used to identify products, especially in the European market. EAN-13 is the most commonly used format with 13 numerical digits.
3. QR Code (Quick Response Code)
QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes capable of storing more data than traditional 1D barcodes. They appear as square patterns with black modules arranged in a grid. QR codes can store URLs, contact information, product details, and much more.
4. Code 39
This alphanumeric code barcode is commonly used in industrial and military applications. It can encode letters, numbers, and a few special characters.
5. Code 128
A high-density code barcode is used for shipping labels and packaging. It can encode a large amount of data, making it suitable for complex applications.
6. ITF (Interleaved 2 of 5)
Suitable for numeric-only data, ITF barcodes are primarily used in logistics and transportation for package tracking.
7. PDF417
Another two-dimensional barcode often used in identification cards and government documents. It can store large amounts of data and is highly secure.
Each barcode type serves a unique purpose, and understanding the appropriate format is crucial for successful implementation in various industries.
Barcode Formats: Unravelling the Designs
Barcodes come in various formats, dictating their appearance and structure. The most popular formats are:
- 1D (One-Dimensional) Barcodes
These are linear barcodes, represented by varying widths and spacings of parallel lines. They can hold limited data and are widely used for simple identification purposes. Some of the common 1D barcode formats include UPC, EAN, Code 39, and Code 128.
- 2D (Two-Dimensional) Barcodes
Unlike 1D barcodes, 2D barcodes can store data both horizontally and vertically. They appear as squares or rectangles filled with small dots, squares, or hexagons. QR codes and PDF417 are examples of 2D barcodes. The advantage of 2D barcodes is their ability to store much more data, making them ideal for applications requiring extensive information storage.
Each format has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application. The choice between 1D and 2D barcodes depends on the amount of data to be stored and the purpose of barcode implementation.
Barcode Examples: Visualising the Versatility
Barcodes have become an integral part of our lives, with applications spanning across various industries. Let’s take a look at a few real-world examples of barcodes:
Example 1
Imagine you’re buying groceries at a supermarket. The cashier scans the barcode on each item, and the product information, along with the price, is automatically added to your bill. UPC and EAN barcodes are commonly used in retail environments, ensuring a smooth and efficient checkout process.
Example 2
You receive a business card with a QR code. When you scan it with your smartphone, it instantly adds the person’s contact information to your address book. QR codes have found widespread use in digital marketing, enabling businesses to provide interactive content to potential customers.
Example 3
A courier service uses barcodes on packages to track them throughout the delivery process, ensuring accurate and timely shipments. The use of barcodes in logistics has significantly improved inventory management and reduced errors in the shipping process.
Barcodes streamline processes and enhance efficiency in various industries, simplifying tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Types of Barcode Readers: Decoding the Technology
Barcode readers, also known as scanners, are devices used to read and decode barcodes. Different types of barcode readers include:
- Pen-type Scanners: These handheld devices must physically touch the barcode to read it. They are suitable for low-volume scanning applications and are commonly used in retail environments.
- Laser Scanners: These scanners use laser beams to read barcodes from a distance, making them ideal for high-volume scanning at retail checkout counters and warehouses
- CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) Scanners: CCD readers use an array of tiny light sensors to capture barcode data. They offer better accuracy and can read damaged barcodes more effectively than pen-type scanners.
- Image Scanners: These advanced scanners use cameras or imaging technology to capture 2D barcodes like QR codes. They are versatile and can read both 1D and 2D barcodes, making them suitable for various applications.
The type of barcode reader you choose depends on the barcode format and your specific application requirements. For retail environments, laser scanners are commonly used due to their speed and accuracy.
How to Create a Barcode for a Product: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a barcode for your product is a straightforward process. To do so, follow these steps:
- Choose a Barcode Type
Decide which barcode type is suitable for your product and application. UPC or EAN codes are commonly used for retail products, while QR codes work well for marketing and promotions.
- Generate the Barcode
You can use various online barcode generators to create your barcode. Input the relevant product information, and the generator will create the barcode image. Many generators also allow you to customise the appearance of the barcode, such as adjusting the size and adding text.
- Review and Test
Once the barcode is generated, review it for accuracy and test it with different barcode readers to ensure it can be easily scanned. This step is crucial to avoid any issues during product scanning at retail points or other application areas.
- Incorporate the Barcode
Place the barcode on your product’s packaging or label, ensuring it is clear and easily accessible for scanning. The barcode should be printed at a size that allows easy scanning without compromising on clarity.
- Integrate with Inventory Systems
If you are using barcodes for inventory management, ensure that your barcode system is integrated with your inventory management software. This allows seamless tracking of stock levels and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
By following these steps, you can quickly implement barcodes for your products, improving inventory management and customer experience.
FAQs: Barcode Types
1. Are barcodes only used in the retail industry?
No, barcodes are used in various industries, including healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and more. They offer benefits in streamlining processes and data management across diverse sectors.
2. Can I create my own barcode for personal use?
Yes, you can create custom barcodes for personal use, such as generating QR codes for sharing contact information or URLs.
3. Are barcode scanners compatible with all types of barcodes?
Barcode scanners are designed to read specific barcode types. Ensure you choose a scanner that matches the format of the barcode you intend to use.
4. Do I need special software to create barcodes?
Many online barcode generators offer free services to create standard barcodes. However, for advanced applications, specialised software may be required.
5. Can barcodes be used for marketing purposes?
Absolutely! QR codes, in particular, are widely used in marketing campaigns for promoting products, services, and providing interactive content to customers.
6. How do I choose the right barcode type for my business?
The choice depends on your industry, the amount of data you need to encode, and how the barcode will be used. For retail products, UPC or EAN codes are standard, while logistics and warehousing often use Code 128 or ITF. If you need to store web links, contact information, or other complex data, QR codes or PDF417 barcodes are more suitable.
7. Are all barcode types globally accepted?
Not all barcode types are universally accepted; for example, UPC is primarily used in North America, while EAN is the standard in Europe and many other regions. Some industries also have specific barcode standards, such as Code 39 in defense or healthcare. Always check the requirements of your target market or industry before selecting a barcode type.
Wrapping Up
Barcodes have become an indispensable part of modern businesses, revolutionising inventory management, product tracking, and data capture. With various barcode types and formats available, you can choose the most suitable option for your specific needs. The advancements in barcode readers further enhance their utility, providing quick and accurate data retrieval.
Whether you are a retailer looking to streamline checkout processes, a manufacturer aiming to track inventory efficiently, or a marketer seeking to engage customers with QR codes, barcodes have a solution for you. Understanding the different types and formats of barcodes empowers businesses to make informed decisions and optimise their operations.
If you are looking for cutting-edge barcode solutions tailored to your business needs, Qodenext is the absolute choice. With our innovative barcode technology and expert guidance, we at Qodnext can help you harness the full potential of barcodes and take your business to the next level.







