The European Article Numbering Code(EAN) is a series of unique numbers assigned to retail products. It is mainly used to identify objects and list down the items for retail businesses. People often ask what is the EAN 13 barcode. However, before you understand the EAN-13 barcode, let’s explore the fundamentals of a GTIN number.
We will also cover important topics related to EAN barcode scanners, applications, and more. Let’s dive deep into GTIN without wasting much time.

What is GTIN? – A General Overview
GTIN or Global Trade Item Number is a universally recognized system for product identification. The GTIN includes different formats, such as GTIN-8, GTIN-12 (UPC), GTIN-13 (EAN-13), and GTIN-14. EAN-13 is a specific type of GTIN-13 and is widely adopted in international trade and commerce.
What is the EAN 13 barcode?
EAN-13 barcodes consist of:
- Number System: The first two or three digits represent the country code or the GS1 prefix.
- Manufacturer Code: This section identifies the manufacturer.
- Product Code: A unique code assigned to each product by the manufacturer.
- Check Digit: Calculated to ensure the integrity of the barcode.
Now, that you know what is the EAN 13 barcode, let’s check out the importance of EAN 13.
Why EAN-13 Barcode is Important
The EAN-13 barcode holds immense importance in the modern business ecosystem. Its significance can be attributed to several key factors:
1) Global Standardization: EAN-13 is a globally recognized and standardized system, ensuring consistency and compatibility across diverse industries and markets.
2) Accurate Inventory Management: The unique identification provided by EAN-13 facilitates precise tracking and management of inventory, reducing errors and improving operational efficiency.
3) Efficient Retail Operations: In retail, understanding what is the EAN 13 barcode is linked to its primary function. The EAN-13 barcode streamlines checkout processes, making transactions faster and more accurate. This, in turn, enhances the overall customer experience.
4) Supply Chain Optimization: EAN-13 plays a vital role in supply chain logistics by enabling automated data capture, reducing manual errors, and enhancing the traceability of products from manufacturer to consumer.
Now, that you are aware of the importance and what is the EAN 13 barcode, let’s quickly discuss the ways through which you can generate a barcode for your business.
How to Create EAN-13 Barcode
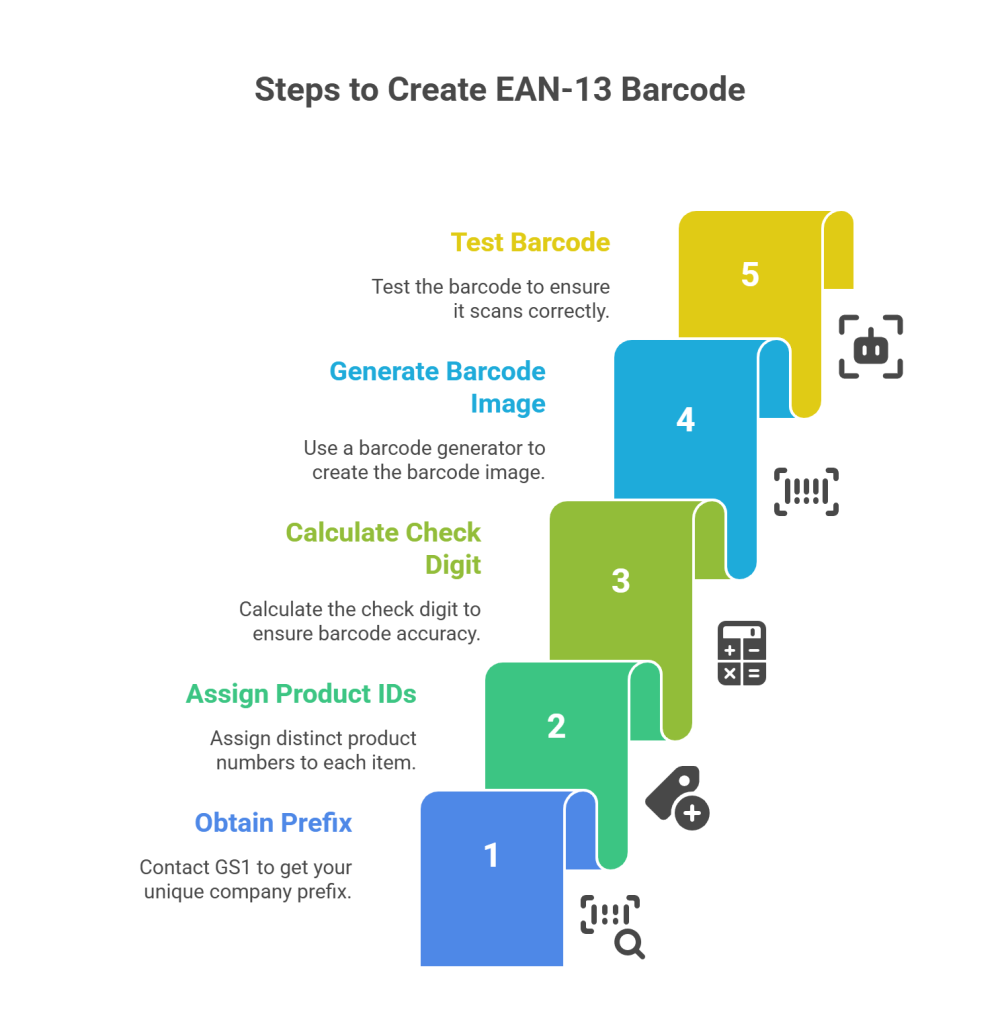
Creating an EAN-13 barcode involves a systematic process. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create an EAN-13 barcode:
Step 1: Get Your Unique Company Prefix
Start by reaching out to GS1, the worldwide authority in barcoding. They’ll assign your business a numeric company prefix—think of this as your brand’s “digital last name.” It ensures all your products are recognized as yours, and no one else’s.
Step 2: Give Each Product Its Own ID
Once you have your company prefix, it’s time to let your creativity run—kind of like naming your products. Assign a distinct product number to each item you sell. These numbers, combined with your prefix, guarantee every product has its own unique barcode.
Step 3: Find the Check Digit
Every EAN-13 barcode ends with a check digit, which acts like a quick math safeguard. Here’s a simple way to calculate it:
- Add up all the numbers in the odd positions (first, third, fifth, etc.).
- Add together the numbers in the even positions and multiply that total by 3.
- Add those two sums together.
- Your check digit is whatever you’d add to this result to make it a multiple of 10.
Don’t sweat the math—many barcode generator tools calculate this for you, but understanding the reasoning helps you catch any mistakes.
Step 4: Create the Barcode Image
Now with your 13 digits in hand, use a reputable online barcode generator. Just enter your number, download the barcode image, and you’re ready to add it to your packaging, labels, or wherever your products need it. Make sure you use a tool you trust, since accuracy here is key!
Step 5: Put It to the Test
Before rolling out your barcodes to the world, do a quick check. Use a barcode scanner—or even your phone with a barcode app—to ensure your barcodes scan cleanly and link back to the right product info. Catching any problems now saves headaches later, both for you and your customers at checkout.
With this step-by-step approach, creating EAN-13 barcodes becomes manageable—even rewarding. It’s about giving your products a unique, recognizable identity in the marketplace, while ensuring efficiency from factory to checkout counter.
Benefits of EAN-13 Barcode
The EAN-13 barcode system has become a standard in the retail and logistics industry due to its efficiency and reliability. It plays a vital role in simplifying operations, reducing manual effort, and ensuring smooth product tracking across global markets. Let’s explore the key benefits of adopting EAN-13 barcodes:
1.Reduced Human Error
One of the biggest advantages of using EAN-13 barcodes is the significant reduction in manual data entry errors. When product information is entered manually—whether in inventory logs, point-of-sale systems, or shipping records—there is always a risk of mistakes. A simple typo can lead to wrong deliveries, stock mismatches, or customer dissatisfaction. EAN-13 barcodes eliminate this risk by automating data capture through barcode scanners, ensuring accurate and consistent product information every time.
2. Enhanced Supply Chain Traceability
Traceability is critical for today’s fast-moving supply chains. EAN-13 barcodes make it easy to track a product’s journey from manufacturing to final sale. By scanning the barcode at various touchpoints—like warehouses, trucks, and retail counters—businesses gain complete visibility into where a product has been and where it’s going. This is especially important in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, where quick identification and recall of defective or expired items can prevent major losses and regulatory issues.
3. Operational Efficiency and Time Savings
The use of EAN-13 barcodes significantly streamlines retail and warehouse operations. Scanning barcodes is not only faster than manual entry but also reduces the time spent searching for product details. Inventory management becomes more accurate, billing is processed more quickly, and labor costs are reduced due to increased automation. These small efficiency gains add up to big savings, especially in high-volume environments like supermarkets, ecommerce fulfillment centers, and logistics hubs.
4. Seamless Global Compatibility
Because EAN-13 is an internationally standardized barcode format, it allows products to move across countries and continents without compatibility issues. Whether you’re shipping goods to Europe, Asia, or the Americas, EAN-13 ensures that your product data can be read and understood by retailers and supply chain partners worldwide. This global compatibility simplifies international trade, improves shelf visibility in overseas markets, and enhances collaboration with global retailers and distributors.
Future Trends
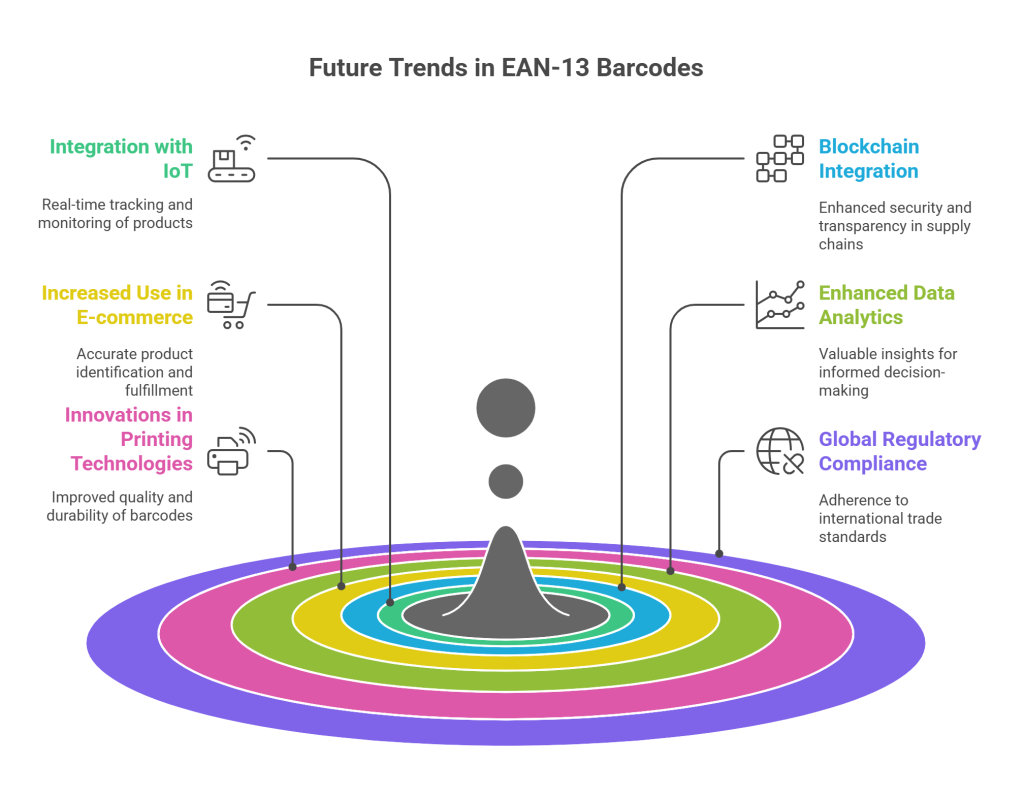
As technology continues to advance, the future of barcode systems, including EAN-13, is likely to witness several trends:
1. Integration with IoT:
EAN-13 barcodes may be integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time tracking and monitoring of products. This integration could enable real-time tracking and monitoring of products throughout the supply chain.
IoT devices, such as sensors and RFID tags, can communicate with EAN-13 barcodes, providing businesses with valuable insights into the location, condition, and movement of products.
2. Blockchain Integration:
Blockchain technology could enhance the security and transparency of supply chain processes associated with EAN-13 barcodes. Integrating EAN-13 barcodes with blockchain can create an immutable and tamper-proof record of the product’s journey from manufacturer to consumer.
This can be particularly beneficial in industries where traceability and authenticity are critical, such as pharmaceuticals and high-value goods.
3. Increased Use in E-commerce:
With the growing prominence of e-commerce, EAN-13 barcodes will likely play a crucial role in ensuring accurate product identification and fulfillment. The barcode’s ability to streamline logistics and inventory management aligns with the demands of the e-commerce industry, where rapid and error-free order fulfillment is essential for customer satisfaction.
4. Enhanced Data Analytics:
EAN-13 barcodes generate a wealth of data that, when leveraged effectively, can provide valuable insights for businesses. Future trends may see advancements in data analytics tools that can process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by EAN-13 barcodes.
This, in turn, can lead to more informed decision-making, improved inventory forecasting, and better supply chain optimization.
5. Innovations in Printing Technologies:
As printing technologies advance, the quality and durability of printed barcodes are likely to improve. This is crucial for industries where products may be exposed to harsh environmental conditions during their lifecycle.
Innovations in printing technologies can ensure that EAN-13 barcodes remain scannable and reliable throughout the entire supply chain.
6. Global Regulatory Compliance:
The global nature of trade requires adherence to various regulatory standards. Future trends may involve updates and adaptations to EAN-13 barcodes to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
This could include changes in the structure of the barcode or the incorporation of additional information to comply with specific industry or regional regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what is the EAN-13 barcode stands as a cornerstone in the world of product identification, offering a standardized and efficient solution for businesses across diverse sectors. Identifying its creation process, benefits, and potential future trends is essential for companies seeking to optimize their operations and embrace the evolving landscape of commerce.
Do you to integrate a robust barcode system into your business, look no further than Qodenext to optimize your supply chain operations. The EAN-13 barcode will continue to play a vital role in the ever-expanding realm of global trade and commerce.
Also read: Unveiling the Types of Barcode Labels and How to Generate Them.
Finally, let’s delve into the commonly asked questions on what is the EAN 13 barcode.
FAQs – What is the EAN 13 Barcode
1. What is the purpose of the check digit in the EAN-13 barcode?
The check digit is calculated to ensure the accuracy of the entire 13-digit code. It acts as a form of error detection, reducing the likelihood of scanning errors.
2. Can I generate EAN-13 barcodes without a GS1 prefix?
No, a GS1 prefix is essential for creating legitimate EAN-13 barcodes. It ensures global uniqueness and compliance with standards.
3. Is the EAN-13 barcode only used in retail?
While EAN-13 is widely used in retail, its applications extend to various industries, including logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing, for efficient product identification.
4. How do I get an EAN 13 barcode?
You have to self-register with GS1. You can then buy your first EAN codes and identify products, locations, or shipping items across the globe. The EAN codes are internationally available and can be converted into EAN -13 using the specific product label.
5. What is the difference between EAN 13 and EAN 14?
Both EAN 13 and EAN 14 are used for inventory control management. While EAN 13 is used for tracking individual objects, EAN 14 is used for identifying a group of consumer items across the logistics and distribution process.
6. What is an example of an EAN 13 code?
EAN 13 contains a total of 13 digits. The first two digits represent the country code, the next five are the manufacturer code and the subsequent five digits represent the product code. The last digit maintains the accuracy of the product code. For example: the EAN barcode format number can be 0123456789123.
7. Is the EAN code mandatory in India?
Every online retailer needs to insert these codes while selling their goods online. However, it is not mandatory to produce these codes. Virtual marketplaces like Amazon and Flipkart request sellers to enter the EAN codes during the listing of products.