Where there is connectivity, there’s vulnerability.
Today’s supply chains aren’t just about moving goods. They’re powered by cloud systems, IoT sensors, third-party platforms, and real-time data. This digital fabric brings speed and visibility, but also opens the door to cyber threats.

Every connected partner, platform, or device becomes a potential entry point for attackers. And in such a tightly linked system, one weak node can compromise the whole network.
That’s why cyber security in supply chain operations is no longer optional, it’s mission-critical.
In this blog, we’ll explore the rising risk of cyber supply chain attacks, how they impact real businesses, and what you can do to stay ahead.
Why Cybersecurity is Now a Supply Chain Essential
It’s not just your own company that you have to protect.
A modern supply chain might include dozens of software vendors, transport providers, IoT devices, cloud platforms, and third-party suppliers. If even one of those links is weak, the whole chain is at risk.
This creates what we call the cybersecurity value chain which is an extended network where each node represents a potential entry point for attackers. You could have the best firewall in the business, but if your logistics partner gets hacked, your data could be compromised.
Now that we understand how interconnected the risk is, let’s dive into how these attacks actually happen.
What Are Cyber Supply Chain Attacks?
Cyber supply chain attacks happen when hackers infiltrate a system not by targeting you directly, but by exploiting a weaker third party that has access to your systems.
A few examples:
- Malware hidden in a software update from a trusted vendor
- Compromised login credentials shared with supply partners
- A vulnerability in an IoT device used in warehouse automation
One of the most notorious examples is the 2020 SolarWinds attack.
Hackers planted malicious code in a routine software update, affecting thousands of organizations, including government agencies. It was a wake-up call for the industry.
Understanding how these attacks work gives us a better sense of what’s at stake. Let’s talk about the real-world impact.
The Business Impact of Cyber Supply Chain Attacks
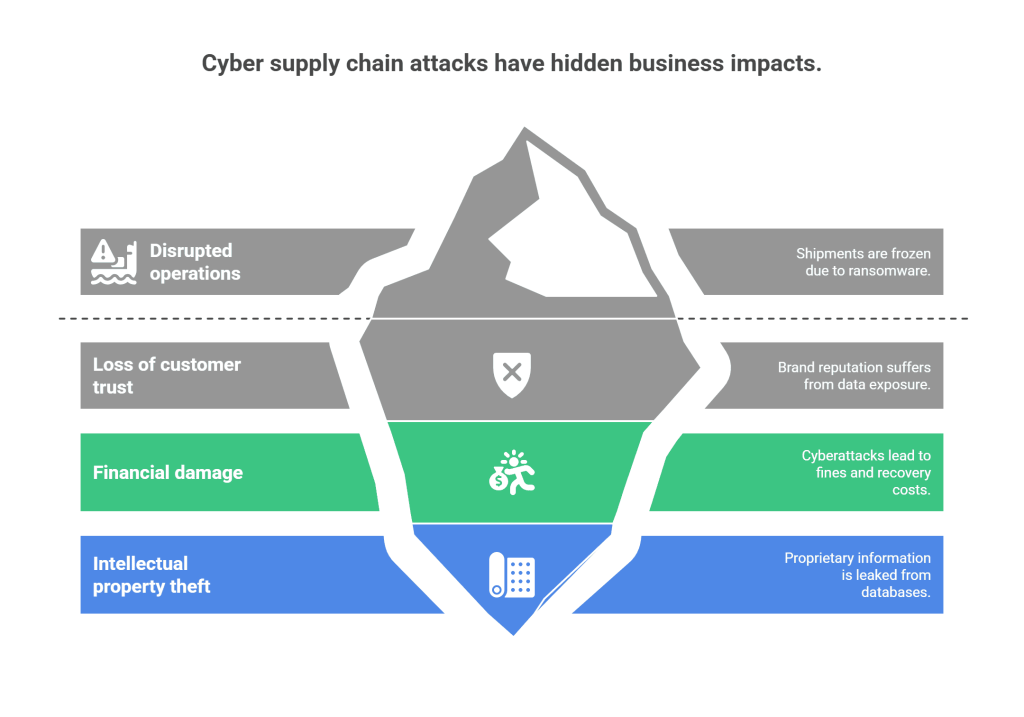
When a cyber supply chain breach occurs, the ripple effect can be devastating:
- Disrupted operations: A ransomware attack on a logistics provider can freeze your shipments.
- Loss of customer trust: If customer data is exposed via a third-party breach, your brand takes the hit.
- Financial damage: From fines to lawsuits to recovery costs, cyberattacks can drain your budget fast.
- Intellectual property theft: A breach in your design or supplier database could leak proprietary product information.
A single weak link can drag down the entire chain. Now that we know what can go wrong, let’s focus on how to make it right.
How to Build a Resilient Cyber Security Supply Chain
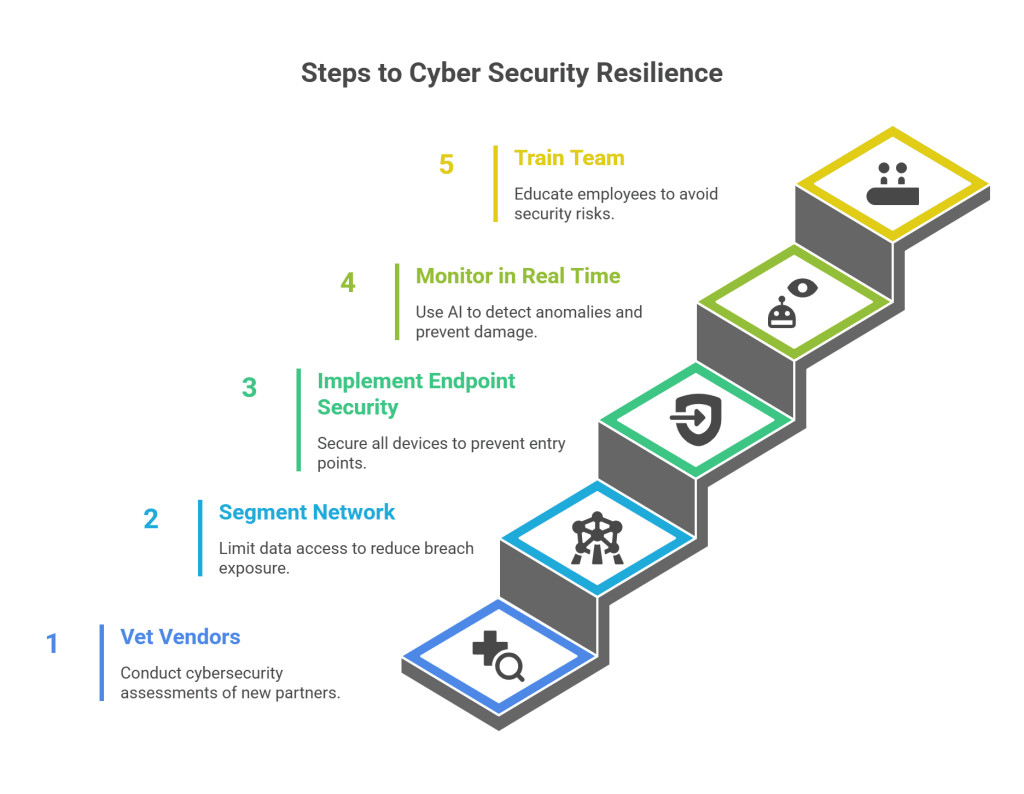
Here’s where the rubber meets the road. Let’s break down practical steps you can take to boost your cyber security in supply chain management:
1. Vet Your Vendors
Conduct cybersecurity assessments of every new tech or logistics partner. Ask about their security certifications and incident response plans.
2. Segment Your Network
Limit what data partners can access. Use separate environments or permissions to reduce exposure in case of a breach.
3. Implement Endpoint Security
Secure every device – from handheld scanners to shipping terminals. These devices are common entry points in supply chain cyber security.
4. Monitor in Real Time
Use AI or analytics to detect anomalies in your digital operations. Early detection can prevent major damage.
5. Train Your Team
Even one employee clicking a phishing link can expose the entire chain. Security training should be part of every role.
These are the first steps, but cybersecurity is an ongoing process. Let’s look at the evolving threat landscape.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Supply Chain Technologies
As supply chains go digital, threats get smarter. Here’s what to watch for in the next few years:
- AI-powered attacks that mimic legitimate supplier behavior
- Deepfake scams targeting procurement or vendor relations teams
- IoT-focused breaches as more warehouses adopt smart sensors
- Cloud infrastructure attacks targeting shared platforms
Your cyber security in supply chain strategy should evolve alongside these threats. Static defenses won’t work in a dynamic digital environment.
Next, let’s look at what frameworks and standards can guide your strategy.
Standards and Best Practices to Follow
There are globally recognized standards for managing cyber security supply chain risk:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Offers a step-by-step model to identify and reduce cyber risks.
- ISO/IEC 27001: A certification standard for information security management.
- Zero Trust Architecture: A strategy that assumes no device or user is safe by default.
Adopting these frameworks helps ensure your organization’s approach is proactive and consistent.
Let’s talk about companies that have done it right.
- Maersk-The global shipping giant suffered a NotPetya ransomware attack that shut down operations across 600 locations. They rebuilt their systems from scratch and invested heavily in supply chain cybersecurity.
- Cisco– Cisco requires cybersecurity audits for all vendors and implements secure software development practices throughout its global supply chain.
- Johnson & Johnson – The pharma giant integrates cyber risk management into every step of product development and supplier onboarding.
These examples show that investing in cyber security in supply chain is not just smart – it’s essential.
FAQs: Why Supply Chains Need Stronger Cybersecurity Now
1. What is the biggest cyber threat to supply chains today?
Third-party software vulnerabilities and phishing attacks targeting logistics or procurement teams.
2. Are small businesses at risk of cyber supply chain attacks?
Yes, they are often targeted because they lack robust defenses but still have valuable access to larger networks.
3. How often should vendor cybersecurity audits be done?
At least annually, or whenever a major system change or breach occurs.
4. Can automation help with supply chain cybersecurity?
Absolutely. Automation helps monitor systems in real-time, flag anomalies, and enforce access controls.
5. What industries are most affected by cyber supply chain threats?
Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and technology are particularly vulnerable due to high levels of connectivity.
Conclusion
In today’s connected world, your supply chain is only as secure as the least protected partner in your network. That’s why cyber security in supply chain management can’t be an afterthought.
From preventing cyber supply chain attacks to building long-term resilience, the steps you take today will define your ability to operate tomorrow.
Don’t wait for a breach to act. Strengthen your supply chain cyber security now, because once the damage is done, recovery is costly and trust is even harder to regain.






