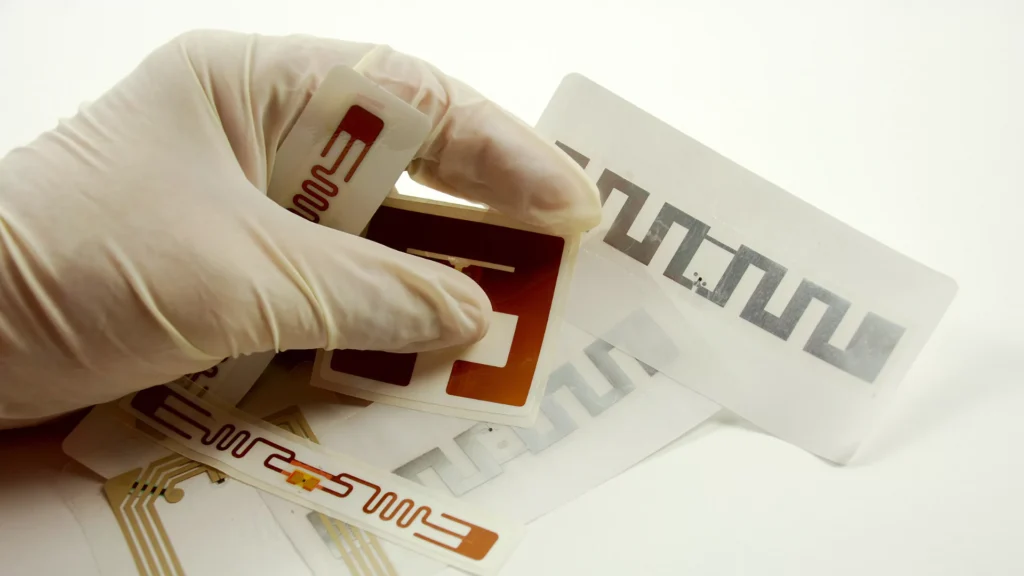
In a world moving toward automation and data-driven efficiency, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) has become a cornerstone in industries ranging from retail to logistics to healthcare. Yet, many still ask: What is RFID technology? Beyond just being a buzzword, it’s a powerful system that allows seamless identification, tracking, and data exchange without human intervention.

In this blog, we’ll explore what RFID technology is, delve deep into its components, how it works end-to-end, and how different industries are harnessing its power to revolutionize operations.
What is RFID Technology?
To put it simply, RFID is a wireless technology that uses radio waves to capture and transfer data from a tag attached to an object, using a reader, without needing direct line of sight. So, what is RFID technology in practical terms? It’s what allows supermarkets to track inventory in real time, lets logistics firms monitor shipments, and even enables pet owners to find lost pets through implanted microchips.
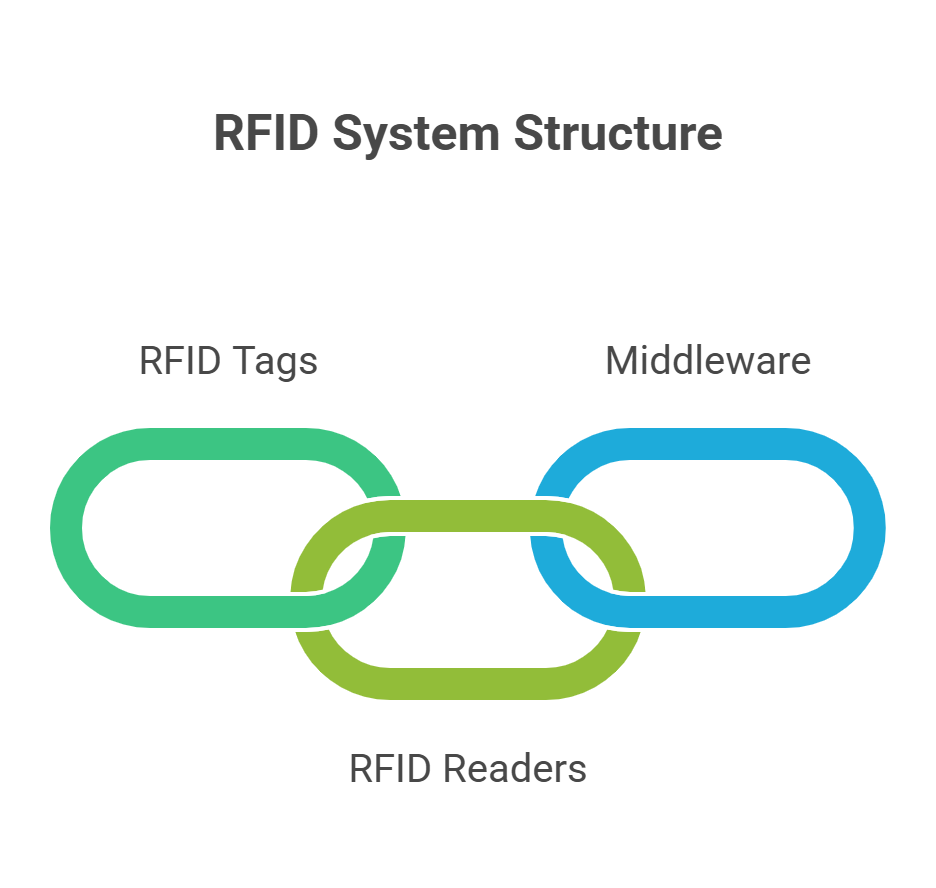
The entire workflow relies on three core components:
- RFID Tags
- RFID Readers
- Middleware/Data Management System
Let’s now break these down and examine how they work together.
Components of RFID: What Makes It Work?
1. RFID Tags
These are small devices embedded or attached to physical objects. RFID tags store data and can be:
- Passive: These tags don’t have their own power source. They rely on external readers to activate the system.
- Active: They use their batteries to charge and send back signals to the reader.
- Semi-Passive: Battery-powered but requires a reader signal to activate.
Each tag contains:
- A microchip for storing and processing data.
- An antenna – to transmit/receive signals.
- A substrate – the physical backing of the tag.
Depending on your RFID tag application—tracking cartons in a warehouse vs. tagging cattle in agriculture—you’ll choose the tag that fits the environment and range.
2. RFID Readers
RFID readers are responsible for activating the tag and receiving the information it sends back. They can be:
- Fixed – Mounted on walls, gates, or conveyors.
- Mobile – Handheld scanners or embedded in devices like smartphones.
They emit radio waves to locate tags and collect their data, which is then sent to a backend system for processing.
3. Middleware or Backend Software
This is where RFID data gets sorted, filtered, and integrated with enterprise systems like ERP or Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). It ensures clean data flows to decision-makers in real-time.
How RFID Technology Works: The Complete Workflow
To fully answer what RFID technology is, we need to understand how the system functions step by step:
- Tagging the Asset: An RFID tag is attached to or embedded in an item.
- Reader Activation: Once the reader is activated, it transfers wavy signals.
- Tag Response: If within range, the tag receives the signal, activates (if passive), and sends back its stored data.
- Data Capture: The reader collects this data and forwards it to the middleware.
- Data Processing: The middleware processes the data, removing duplicates, filtering noise, and integrates it with business applications.
- Real-time Insights: The processed data is used to automate tasks, trigger alerts, generate reports, or update databases.
This contactless process is what makes RFID ideal for high-volume, real-time environments.
Types of RFID Frequencies and Technology
What is RFID technology without understanding the frequencies it operates on? The performance of an RFID system is heavily influenced by frequency:
| Frequency | Range | Use-Cases |
| LF (125 – 134 kHz) | Up to 10 cm | Livestock tagging, key fobs |
| HF (13.56 MHz) | Up to 1 meter | Smart cards, ticketing |
| UHF (860 – 960 MHz) | Up to 12 meters | Logistics, inventory tracking |
Each frequency has its pros and cons. For instance, UHF offers a longer range but is sensitive to interference, while LF is slower but works better around metal or water.
RFID Technology Applications
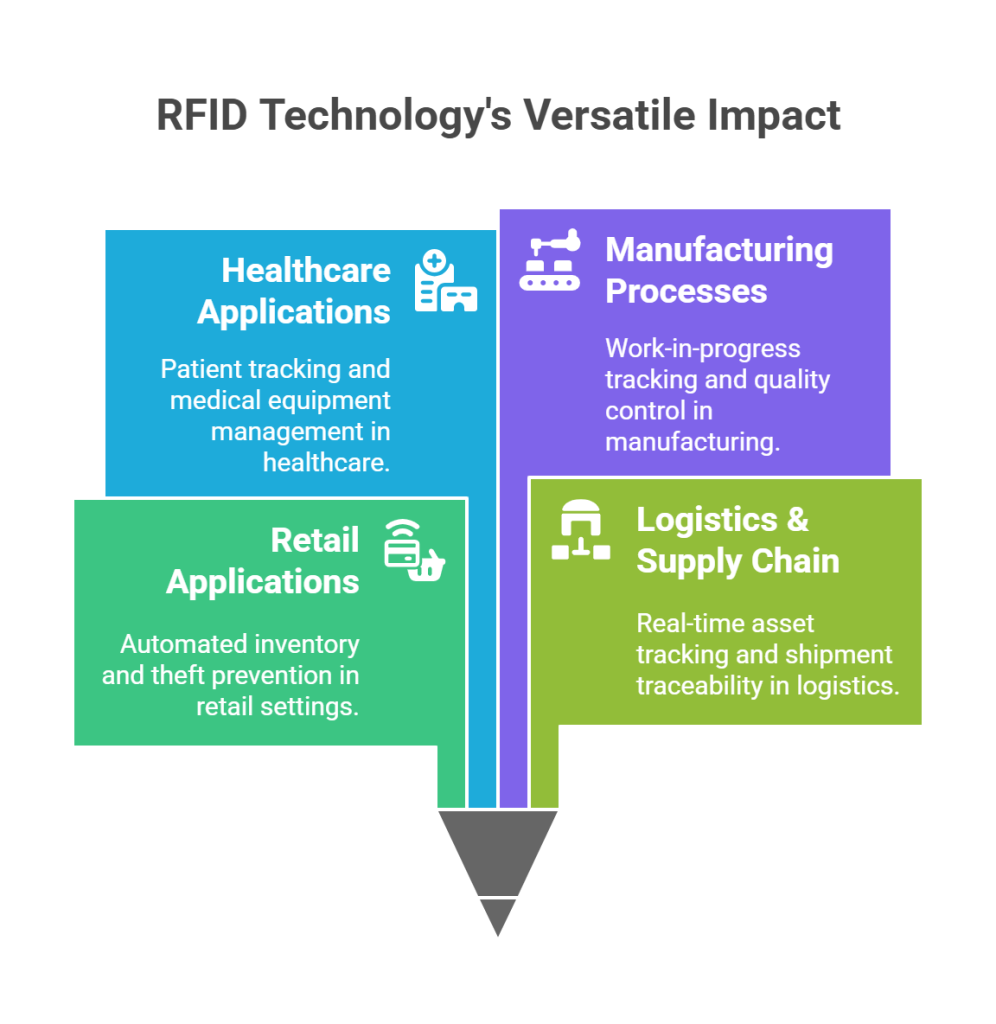
The versatility of RFID is best seen in how it adapts to industry-specific needs.
1) Retail
- Automated inventory counts
- Theft prevention
- Smart fitting rooms
- E-Commerce Store Tracking
2) Logistics & Supply Chain
- Real-time asset tracking
- Proof of delivery
- Shipment traceability
3) Healthcare
- Patient ID tracking
- Medical equipment location
- Drug authentication
4) RFID Technology in the Manufacturing Process
- Work-in-progress tracking
- Quality control checkpoints
- Tool/equipment usage logs
Each application streamlines operations, reduces errors, and enhances visibility. Still wondering what RFID technology is doing in daily life? Think of Amazon Go stores, airport baggage checks, or livestock tagging—it’s everywhere.
Benefits of RFID Technology
Understanding what RFID wireless technology is also means appreciating the value it brings:
- Speed: Scan hundreds of tags in seconds.
- Accuracy: Reduce human errors.
- Visibility: Real-time data means better decision-making.
- Security: Unique IDS make duplication hard.
- Automation: Triggers workflows without manual intervention.
Challenges & Considerations
Of course, RFID isn’t without challenges:
- High initial costs (especially active RFID)
- Interference from metals/liquids
- Privacy concerns in personal tracking
- Data overload if the middleware isn’t configured properly
Yet, with proper planning, the ROI often outweighs the costs, especially in large-scale operations.
Future of RFID: Where It’s Headed
RFID is evolving rapidly. The rise of Iot, blockchain integration, and AI-powered analytics means RFID will play a bigger role in smart factories, cold chain logistics, and even food safety.
What is RFID technology in the near future? A gateway to more intelligent, connected, and automated systems.
Conclusion
So, what is RFID technology? It’s more than just wireless tracking—it’s an enabler of efficiency, accuracy, and automation. From simplifying inventory management to enhancing supply chain visibility, RFID plays a silent yet powerful role in modern business ecosystems.
As adoption grows and tech becomes more affordable, RFID will move from niche to necessity across industries. The sooner businesses understand their workflow, the faster they can turn this silent signal into a competitive edge. Need help with tailored supply chain strategies? Get in touch with Qodenext today.
FAQS: What is RFID Technology?
1. What is RFID technology, and how is it different from barcodes?
RFID uses radio waves to read data wirelessly and doesn’t need a line of sight, while barcodes require a scanner to visually read the code. RFID reads at a much faster rate than barcodes.
2. Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, many RFID tags (especially passive ones) can be reprogrammed and reused, depending on the tag type and application.
3. Is RFID safe for human health?
Yes, RFID uses low-frequency radio waves that are non-ionizing and safe for both humans and animals.
4. What is RFID technology’s biggest advantage?
Its ability to automate tracking and data collection at scale, enabling real-time decision-making and reducing human error.
5. Can RFID be used outdoors or in harsh environments?
Absolutely. Many RFID tags are designed to withstand heat, cold, water, and chemical exposure.
6. How secure is RFID?
While secure by design, RFID systems should still be encrypted and integrated with secure middleware to prevent unauthorized access or spoofing.
7. What is RFID technology, and how is it different from barcodes?
RFID technology uses radio waves to read data wirelessly and doesn’t require a direct line of sight, while barcodes need to be scanned visually with a line of sight. RFID can scan multiple tags simultaneously and at a much faster rate than barcode scanning.
8. Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, many RFID tags, especially passive ones, can be reprogrammed and reused. The ability to reuse depends on the tag type and how it has been applied within the system.
9. Is RFID safe for human health?
Yes, RFID systems use low-frequency, non-ionizing radio waves, which are safe for humans and animals. The technology poses no known health risks at the frequencies and power levels used.
10. What is RFID technology’s biggest advantage?
The biggest advantage of RFID is its ability to automate tracking and data collection at scale, enabling real-time visibility, reducing human errors, and improving operational efficiency across various industries.
11. Can RFID be used outdoors or in harsh environments?
Absolutely. Many RFID tags are engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, and physical wear, making RFID suitable for outdoor and industrial use.







