Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management
In the fast-paced world of supply chain management, reverse logistics has emerged as a critical aspect that demands attention. Understanding small aspects of reverse logistics and implementing effective strategies can significantly impact the overall efficiency of supply chain operations. This article covers the reverse logistics process, examples and much more. Let us begin with what exactly Reverse logistics is?
What is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics is the process of managing the return of goods from the final destination back to the manufacturer. Unlike traditional logistics, which focuses on the flow of products from manufacturers to consumers, reverse logistics deals with the challenges and opportunities presented by returned or end-of-life products. This process involves handling returned merchandise, refurbishing, recycling, or disposing of it in an environmentally friendly manner.
The Reverse Logistics Process
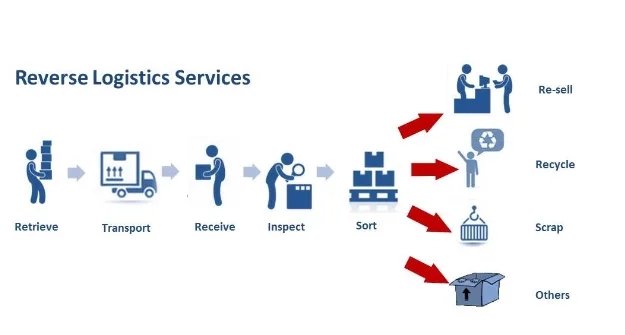
Reverse logistics is all about what happens after a product reaches the customer—whether it’s returned, reused, or responsibly discarded. It plays a crucial role in minimizing waste, recovering value, and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Let’s walk through the key stages of the reverse logistics process:
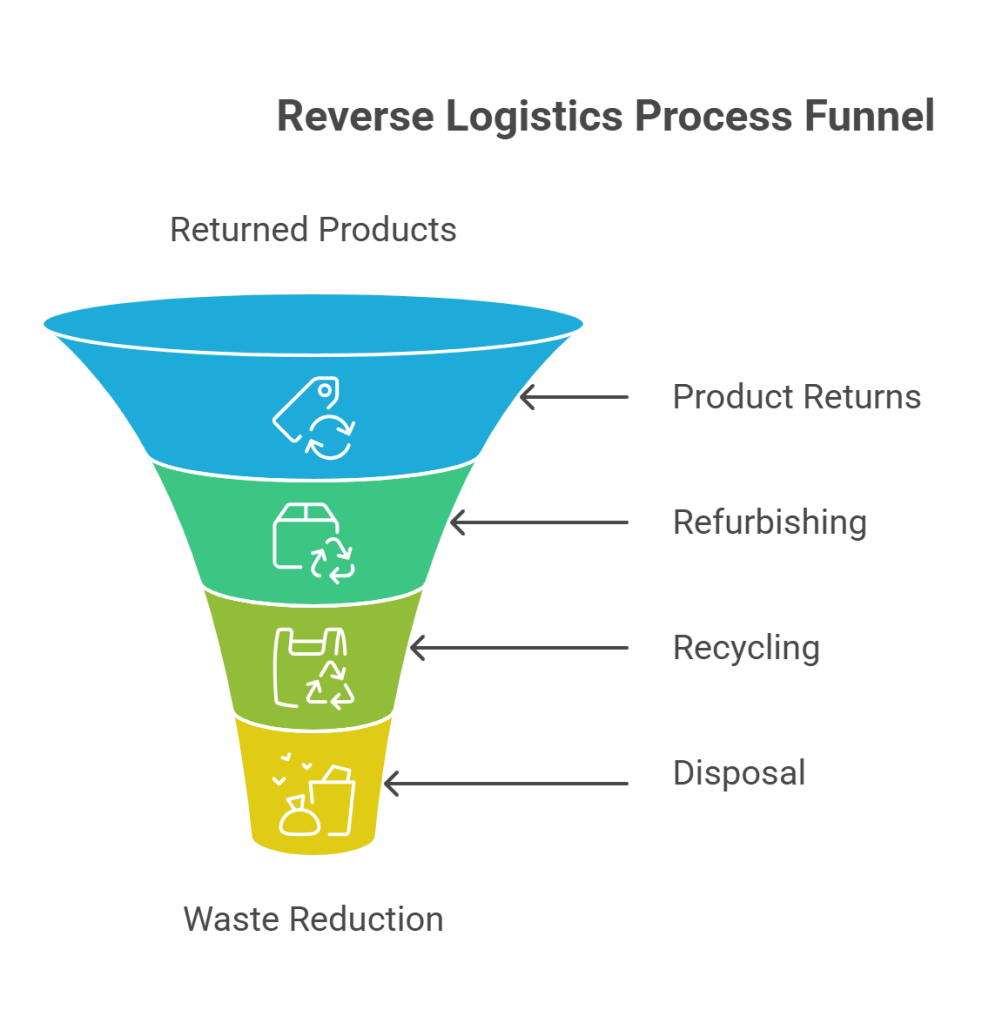
1. Product Returns
This is where the process begins. Products might be returned for various reasons—defects, wrong orders, or even a simple change of mind.
What matters most is handling these returns quickly and smoothly, both for the customer and the company.
The returned items are inspected to assess:
- Their physical condition
- Whether they can be resold as-is
- If they need repairs or repackaging
- Or if they must be scrapped altogether
A clear and efficient return policy helps businesses build customer trust and retain loyalty—even after a sale.
2. Refurbishing and Repackaging
Not all returned products are waste. Many can be brought back to life through minor repairs or updates.
This stage involves:
- Refurbishing: Repairing or restoring products to working condition
- Repackaging: Giving products a fresh look so they’re ready to be resold
This process reduces waste, saves costs, and supports sustainability. It’s especially useful in electronics, appliances, and fashion where product lifespan can be extended.
3. Recycling
For items that can’t be resold but still contain valuable materials, recycling is the best option.
At this stage, businesses:
- Identify reusable parts or materials (like metal, plastic, or glass)
- Send them to certified recycling facilities
- Ensure environmentally safe practices
Recycling helps companies meet sustainability goals and reduce their carbon footprint, while recovering some material value.
4. Disposal
When a product can’t be refurbished or recycled, proper disposal becomes necessary.
This step must be handled responsibly to avoid environmental harm. It often involves:
- Following local and international regulations
- Disposing of hazardous or electronic waste safely
- Keeping detailed records to show regulatory compliance
Proper disposal is not just about getting rid of waste—it’s about doing so in a way that’s ethical, legal, and environmentally sound.
Supply Chain Management and Reverse Logistics
Incorporating reverse logistics into supply chain management is critical for a comprehensive and sustainable approach. It adds an extra layer of complexity to the traditional supply chain, requiring businesses to adapt and optimize their processes for both forward and reverse flows of goods.
Reverse Logistics Examples
To better understand the concept, let’s look at some reverse logistics examples:
- Product Recalls: When a product is recalled due to defects, reverse logistics ensures the safe return and disposal of the faulty items.
- Seasonal Returns: Retailers often experience an influx of returns after holiday seasons or sales events. Effective reverse logistics helps manage this surge efficiently.
- End-of-Life Products: Electronics and other goods reaching the end of their life cycle require responsible disposal. Reverse logistics handles the proper recycling or disposal of such items.
How to Improve Reverse Logistics
Now, let’s explore actionable strategies to improve reverse logistics:
1. Advanced Technology Integration
Investing in cutting-edge technology, such as RFID tracking and advanced analytics, enhances visibility throughout the reverse logistics process. This enables real-time monitoring, reduces errors, and streamlines operations.
2. Collaboration with Partners
Building strong partnerships with suppliers, retailers, and third-party logistics providers is crucial. Effective communication and collaboration facilitate smoother reverse logistics operations, from returns processing to final disposition.
3. Data Analytics for Decision Making
Utilizing data analytics allows businesses to gain insights into return patterns, identify recurring issues, and make informed decisions. This proactive approach minimizes future return issues and optimizes reverse logistics processes.
4. Efficient Returns Management System
Implementing a robust returns management system ensures prompt processing of returns, reducing the time products spend in the reverse logistics pipeline. This enhances customer satisfaction and reduces overall costs.
5. Environmental Sustainability
Prioritizing environmental sustainability is not only a corporate responsibility but also a market differentiator. Implementing eco-friendly practices in reverse logistics, such as recycling and responsible disposal, contributes to a positive brand image.
Conclusion
In summary, grasping the intricacies of reverse logistics is imperative for contemporary businesses committed to establishing streamlined and eco-friendly supply chain operations. By embracing the complexities and possibilities inherent in handling returned products, Qodenext can not only minimize expenses but also elevate customer satisfaction, positioning ourselves as champions of a greener and more sustainable future.
FAQs
1. What is reverse logistics?
Reverse logistics is the process of managing the return of goods from the final destination back to the manufacturer. It involves handling returned merchandise, refurbishing, recycling, or disposing of it in an environmentally friendly manner.
2. How does reverse logistics differ from traditional logistics?
Traditional logistics focuses on the flow of products from manufacturers to consumers. In contrast, reverse logistics deals with the challenges and opportunities presented by returned or end-of-life products, involving processes like product returns, refurbishing, recycling, and disposal.
3. Why is reverse logistics important in supply chain management?
Integrating reverse logistics into supply chain management is crucial for a comprehensive and sustainable approach. It adds complexity by addressing the return flow of goods, requiring businesses to adapt and optimize processes for both forward and reverse logistics.
4. Can you provide examples of reverse logistics?
Certainly! Examples include product recalls due to defects, seasonal returns after holidays or sales events, and the responsible disposal or recycling of end-of-life products like electronics.
5. How can businesses improve their reverse logistics processes?
Businesses can improve reverse logistics by integrating advanced technology, collaborating with partners for efficient communication, using data analytics for decision-making, implementing an efficient returns management system, and prioritizing environmental sustainability through eco-friendly practices.






