In the complex domain of operations management, Material Requirement Planning (MRP) stands out as a crucial component, steering the course of efficient production and resource utilization. This article delves into the intricacies of MRP, exploring how it operates and explaining the numerous advantages it provides to businesses.
What is MRP?
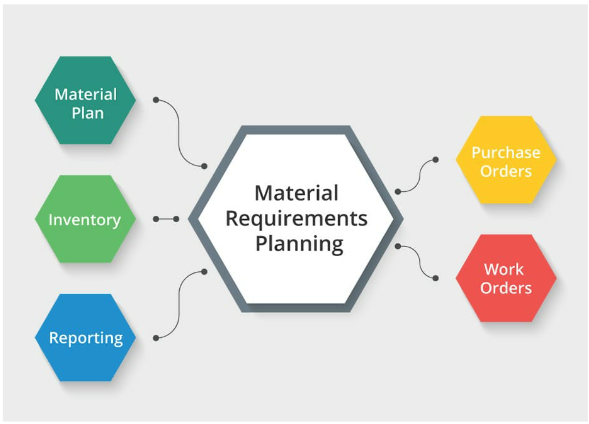
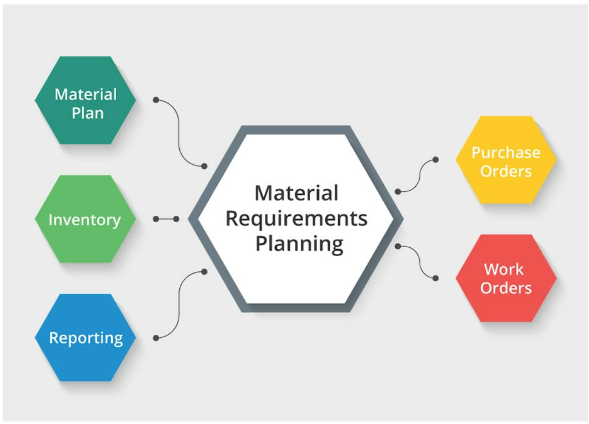
Simply put, MRP is a careful method for managing the materials needed in production. It involves planning, scheduling, and controlling inventory to ensure the right materials are on hand when needed, minimizing disruptions and optimizing production efficiency.
MRP in Operations Management
In the ever-changing field of operations management, MRP plays a crucial role in making processes more efficient. It acts as a key link connecting different production stages, starting from obtaining raw materials to assembling the final product. Companies using MRP systems experience improved coordination and smooth workflows across departments.
Advantages of Material Requirement Planning
The adoption of MRP brings forth a plethora of advantages, propelling businesses to new heights of operational excellence. Let’s delve into the key benefits that make MRP indispensable in the contemporary business landscape.
1. Streamlined Inventory Management
MRP enables businesses to maintain an optimal level of inventory by aligning it with production needs. This prevents overstocking and stockouts, ensuring that materials are available when needed. The result is a streamlined and efficient inventory management system.
2. Enhanced Production Scheduling
Using MRP, companies can create accurate production schedules using up-to-date information on customer demand and inventory levels. This improved scheduling helps to minimize delays, shorten lead times, and maintain a seamless workflow during production.
3. Cost Optimization
One of the primary objectives of MRP is to optimize costs through judicious resource allocation. By preventing excess inventory and minimizing wastage, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs, contributing to improved profitability.
4. Improved Coordination Across Departments
MRP acts as a central hub that connects various departments involved in the production process. This improved coordination ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding material requirements, production schedules, and resource utilization, fostering a collaborative and efficient working environment.
5. Timely Order Fulfillment
By aligning material availability with production schedules, MRP facilitates timely order fulfillment. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens the overall reputation of the business in the market.
6. Accurate Demand Forecasting
MRP relies on accurate demand forecasting, which is crucial for planning production activities. By analyzing historical data and market trends, businesses can make informed decisions regarding material procurement and production schedules, reducing the risk of shortages or excess inventory.
Disadvantages of Material Requirement Planning
Material Requirement Planning (MRP), while advantageous in many aspects, comes with its own set of challenges and drawbacks. Here are some of the notable disadvantages:
1. Implementation Costs
Introducing MRP systems can be a substantial financial investment for businesses. The initial costs associated with software implementation, employee training, and system integration can be a barrier, particularly for smaller enterprises.
2. Complexity and Learning Curve
MRP systems are inherently complex, and their successful utilization requires a certain level of expertise. Employees may face a steep learning curve, and the complexity of the system can lead to errors in data input or interpretation.
3. Data Accuracy Dependency
The effectiveness of MRP heavily relies on the accuracy of data input. Inaccurate or outdated data can result in flawed calculations, leading to incorrect production schedules, procurement orders, and, ultimately, disruptions in the supply chain.
4. Overemphasis on Forecasting
MRP is reliant on accurate forecasting to anticipate future demand. If market conditions change unexpectedly or if the forecasting methods are flawed, it can lead to overproduction or shortages, impacting the efficiency of the entire production process.
5. Rigidity in Handling Changes
MRP systems may struggle to adapt to sudden changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, or modifications in production processes. This lack of flexibility can result in inefficiencies and difficulties in responding promptly to evolving business conditions.
Objectives of MRP
Let’s delve into the primary objectives of material requirement planning and more granular details of the objectives that MRP seeks to achieve.
1. Optimal Resource Utilization
At the core of MRP lies the objective of optimal resource utilization. This involves not only ensuring that materials are available when needed but also minimizing waste and redundancy in the production process. By precisely aligning the procurement of materials with production schedules, MRP aims to create a lean and efficient operational ecosystem.
2. Just-in-Time Inventory Management
MRP strives for a delicate balance between having enough inventory to meet demand and avoiding excess stock. The goal is to establish a just-in-time inventory system, ensuring materials arrive precisely when required for production. This approach minimizes holding costs, mitigates the risk of obsolescence, and bolsters the overall agility of the supply chain.
3. Accurate Demand Forecasting
Anticipating future demand is a cornerstone of effective resource planning. MRP aims to sharpen this skill by leveraging historical data, market trends, and customer insights. Accurate demand forecasting enables organizations to align their production schedules with market needs, preventing both shortages and surpluses.
4. Enhanced Production Scheduling
MRP seeks to revolutionize production scheduling by providing a dynamic and responsive framework. The objective is to create a master production schedule (MPS) that adapts to changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, and other variables. This agility in scheduling ensures that production remains efficient and responsive to the ever-changing business landscape.
5. Cost Optimization at Every Stage
Cost efficiency is not just a byproduct; it’s a deliberate objective of MRP. This encompasses cost optimization at every stage of the production process, from procurement to assembly. By minimizing carrying costs, preventing overproduction, and optimizing the use of resources, MRP contributes to a lean and financially sound operational model.
6. Timely Order Fulfillment
Ensuring timely order fulfillment is a critical objective of MRP. By synchronizing production schedules with customer demand, businesses employing MRP can meet orders promptly and maintain high levels of customer satisfaction. This objective underscores the customer-centric approach embedded in the MRP philosophy.
7. Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
MRP is not a static system; it thrives on continuous improvement and adaptability. The objective is not just to meet current operational standards but to constantly refine and optimize processes. This commitment to ongoing enhancement ensures that businesses remain competitive and resilient in a dynamic market environment.
The Material Requirement Planning (MRP) Process
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a systematic and intricate process that plays a pivotal role in optimizing resource utilization and streamlining production workflows. Let’s dissect the MRP process into its key components, unveiling the steps that businesses undertake to orchestrate a seamless and efficient production cycle.
1. Bill of Materials (BOM) Creation
The foundation of the MRP process begins with the meticulous creation of a Bill of Materials (BOM). This comprehensive document outlines the specific materials, components, and sub-assemblies required for the production of each finished product. The BOM serves as the blueprint for the entire manufacturing process, providing clarity on the elements needed for assembly.
2. Master Production Schedule (MPS) Development
With the BOM in place, the next step involves the development of a Master Production Schedule (MPS). The MPS acts as the guiding force behind the entire MRP process, dictating the production schedule based on factors such as customer demand, inventory levels, and production capacity. This master plan serves as the nucleus, aligning the entire manufacturing process with strategic business objectives.
3. Inventory Status Updates and Analysis
Real-time information is paramount in the MRP process. Regular updates on inventory status, coupled with detailed analysis, form a critical aspect of MRP implementation. This step involves monitoring stock levels, tracking usage patterns, and factoring in lead times for procurement. Accurate and up-to-date inventory data empowers businesses to make informed decisions and maintain an optimal balance between demand and supply.
4. Net Requirements Calculation
Once inventory data is examined, the MRP system calculates net requirements for each material, considering both scheduled production and existing stock levels. This calculation involves determining the net quantity of materials needed to fulfill production goals while accounting for any surplus or shortage in inventory.
5. Purchase Order Generation
Armed with net requirements, the MRP system triggers the generation of purchase orders for materials that need replenishment. These purchase orders are meticulously crafted to ensure timely procurement, preventing any disruptions in the production schedule. The precision in purchase order generation is a key factor in achieving the just-in-time inventory management objectives of MRP.
6. Work Order Creation
Simultaneously, the MRP process involves the creation of work orders for in-house production activities. These work orders outline the specific tasks and processes required for assembling products. By aligning work orders with the master production schedule, MRP ensures that the production floor operates with optimal efficiency and synchronization.
7. Monitoring and Iterative Adjustment
The MRP process doesn’t conclude with the generation of orders. Continuous monitoring is integral to its success. Businesses regularly assess the actual versus planned outcomes, allowing for iterative adjustments. This method guarantees the MRP system’s flexibility in response to shifts in demand, alterations in supply chain dynamics, and some other external factors.
Conclusion
In summary, Material Requirement Planning emerges as a linchpin for operational success, especially when guided by the expertise of Qodenext. Companies adopting their MRP experience not only heightened efficiency, substantial cost savings, and increased competitiveness but also a future-ready approach that propels them ahead in the dynamic business landscape. Embrace MRP with Qodenext– not just a choice but a strategic imperative for sustained success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.What is Material Requirement Planning (MRP)?
Material Requirement Planning (MRP)is a careful method for managing the materials needed in production. It involves planning, scheduling, and controlling inventory to ensure the right materials are on hand when needed, minimizing disruptions and optimizing production efficiency.
2.How does MRP contribute to optimal resource utilization?
MRP contributes to optimal resource utilization by aligning material procurement with production schedules. This ensures that materials are available when required, minimizing waste and redundancy in the production process.
3.What is the significance of the Bill of Materials (BOM) in the MRP process?
The Bill of Materials (BOM) is a crucial component of the MRP process as it outlines the specific materials, components, and sub-assemblies required for the production of each finished product. It serves as the blueprint for the entire manufacturing process.
4.How does MRP enhance production scheduling?
MRP enhances production scheduling by creating a Master Production Schedule (MPS) that adapts to changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, and other variables. This agility ensures that production remains efficient and responsive to the ever-changing business landscape.
5.How does MRP contribute to cost optimization?
MRP contributes to cost optimization by minimizing carrying costs, preventing overproduction, and optimizing the use of resources. This results in a lean and financially sound operational model.
6.What are the key advantages of Material Requirement Planning?
The key advantages of MRP include streamlined inventory management, enhanced production scheduling, cost optimization, and efficient resource utilization. It also facilitates timely order fulfillment and contributes to overall operational excellence.