Retail services today have access to more data than before. As always with businesses having metrics- they can study it, measure it and find ways to improve it. As a retailer, you are always paying attention to your inventory. You must ensure items are in stock and the ones that leave the warehouse are recorded. To measure all these you need KPI retail.
What is KPI in retail?
This is a parameter that tracks the Key Performance Indicators making your business more data-driven. It is a quantifiable metric that you can use to assess the success of a retail business.
8 Types of KPIs in Retail
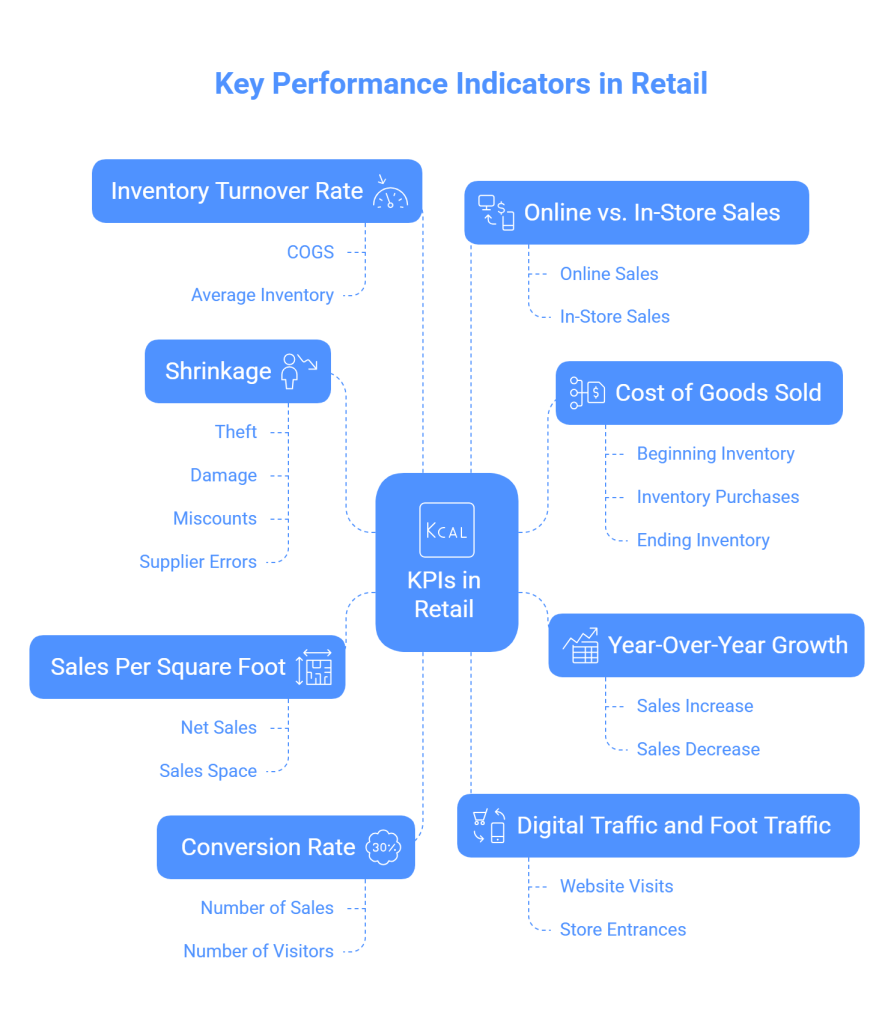
Unlocking performance potential requires a nuanced approach. Here’s a breakdown of eight types of KPI retails to gauge that success effectively.
1. Year-Over-Year Growth
This reveals how much sales have increased or decreased. It compares a company’s current sales for a specific period to its sales for the same period in the past year.
Formula:
[(Sales of This Year- Sales of Previous Year)/ Previous Year’s Sales]x 100
Let’s say you sold INR 500,000 in Q1 of 2023 and INR 400,000 in Q1 of 2022. Your calculator for year-over-year sales will be:
YOY Sales= [(500,000-400,000)/400,00]*100= 25%
Purpose: Such retail KPI formulas show that tracking sales every quarter helps in understanding how your sales grew or declined in comparison to the previous year. It helps to put your growth in context and gives you the bigger picture of your company’s performance.
As you look at this KPI retail metric alongside other strategic changes you made, you may be able to identify what’s contributing to a decline or growth in sales. For instance, you added new products to your lineup between last year’s Q1 and this year’s. This might have affected the sales increase.
Let’s see the next KPI retail metric.
2. Sales Per Square Foot
This measures how much money you’ve earned for each square footage of the store’s floor space. Remember only the sales space is taken into account, which means fitting rooms and stockrooms are not included.
Formula:
Net sales/Amount of sales space
For instance, if your net sales were INR 40,000 for a specific time frame and you have 500 sq. ft. of space. This is how to calculate KPI in retail:
SPSF = 40,000/500 = INR 80
Simply put, you are making INR 80 in net sales for every square foot you occupy.
In other words, for every square foot of sales space you occupy, you’re making $80 in net sales.
Purpose: Most businesses that have physical stores can measure the efficiency of their store layout. This KPI retail metric allows you to get a better sense of how well a store is performing. This is important if you have multiple store locations.
By analysing these numbers you can decide whether you need to downsize or expand. You can also consider improving your store layout, optimising pricing strategy to get people to stay longer or offering creative promotions.
3. Conversion Rate
This KPI retail factor allows you to measure the percentage of visitors to your store or website who bought products, generating revenue.
Formula:
(Number of Sales/ Number of store visitors) x 100
For example, if you had 5,00 visitors in a month and 2500 of them converted (bought products), your calculation would be:
Conversion Rate: (2000/5000) x100 =40%
Purpose:How to achieve KPI retail? Well, you can measure the conversion rate to see if you’ve convinced customers to make a purchase. Traffic is not the only factor contributing to your revenue. Make sure there are conversions as well.
A low conversion rate would suggest that you must adjust your retail sales process. For instance, you can consider revamping your store or website, using more compelling promotional tactics.
4. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
This measures what it costs for you to acquire or produce the inventory.
Formula:
Beginning inventory + Inventory purchases – Ending inventory
Let’s see one of the retail store KPI examples.
A store starts with 20,000 INR worth of inventory then purchasing more of 70,000 INR. The year ends with a 10,000 INR inventory then the cost of goods sold will be:
Cost of Goods Sold: 20,000+70,000-10,000= 80,000 INR
Purpose: You must measure COGS to assess profitability. Knowing how much you spent to have the products, you can set up the selling prices accordingly. Additionally, this KPI retail factor is important in your accounting records where you need to measure metrics like gross profits.
Want to know how to increase KPI in retail? Check out the next factors that are quite crisp.
5. Digital Traffic and Foot Traffic
This KPI measures how many people interact with your brand both online and in-store. It provides insight into how well your marketing efforts are driving traffic and awareness.
Formula (Digital Traffic):
Total number of website visits during a specific time period
Formula (Foot Traffic):
(People entering the store / People passing by) × 100
Example:
If 10,000 people passed by and 1,000 entered the store:
Foot Traffic = (1,000 / 10,000) × 100 = 10%
Purpose: Tracking this KPI helps you understand your brand’s reach, customer interest, and store attractiveness. It supports decisions on advertising placement, store layout improvements, or online promotions.
6. Inventory Turnover Rate
This KPI reveals how quickly inventory is sold and replenished over a given period. It helps determine whether your stock levels match your sales velocity.
Formula:
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Average Inventory
Example:
If the COGS is ₹500,000 and average inventory is ₹100,000:
Inventory Turnover Rate = 500,000 / 100,000 = 5
Purpose: A high turnover rate indicates strong sales and good inventory control. A low rate may suggest excess inventory or weak product demand, requiring pricing adjustments or promotions.
7. Online vs. In-Store Sales
This KPI compares the revenue contribution from digital platforms and physical stores. It is especially valuable for hybrid retail models.
Formula:
(Sales from Channel / Total Sales) × 100
Example:
If your online sales are ₹300,000 and in-store sales are ₹700,000 out of ₹1,000,000 total sales:
Online Sales = (300,000 / 1,000,000) × 100 = 30%
In-Store Sales = (700,000 / 1,000,000) × 100 = 70%
Purpose: This metric helps identify the stronger sales channel and can guide decisions on marketing budgets, staffing, and inventory distribution.
8. Shrinkage
Shrinkage measures inventory loss not caused by sales. It includes losses from theft, damage, miscounts, or supplier errors.
Formula:
Recorded Inventory Value – Actual Inventory Value
Example:
If the recorded inventory is ₹250,000 and actual inventory is ₹240,000:
Shrinkage = 250,000 – 240,000 = ₹10,000
Purpose: High shrinkage negatively impacts profits. This KPI helps in identifying areas of concern, such as weak internal controls, poor security, or vendor fraud.
With these eight KPIs, your retail business will be a roaring success.
Conclusion
Unleash peak performance with data-driven KPI retail insights. These eight KPIs empower you to optimise inventory, sales and customer experience. Carefully navigate the complexities.
That is where, Qodenext, your supply chain experts are here to help. We streamline operations, boost inventory management, elevating customer satisfaction. Get an inquiry today!
FAQs: What is KPI Retail: Measuring 8 Metrics for Success
1. What exactly is a KPI in retail?
A KPI (Key Performance Indicator) in retail is a measurable value that helps you track how well your business is doing in specific areas like sales, inventory, customer experience, or store performance. It gives you clarity on what’s working — and what’s not.
2. Why should I care about retail KPIs?
Because numbers don’t lie. KPIs show you where your business stands and help you make smarter decisions — whether it’s stocking more of a popular product, improving store layout, or adjusting prices to boost profit.
3. How do I know which KPIs matter for my business?
Start by identifying your goals. Want to grow revenue? Focus on sales growth and conversion rates. Struggling with inventory issues? Look at turnover rates and shrinkage. The right KPIs depend on your business type and priorities.
4. Can one KPI tell me everything?
Not really. One metric can give you a clue, but it’s only part of the story. For example, high foot traffic is great, but if your conversion rate is low, something’s going wrong inside the store. KPIs work best when analyzed together.
5. How often should I review my KPIs?
It depends on the metric and your business. Some KPIs like foot traffic or sales might be reviewed weekly, while others like year-over-year growth are better suited to monthly or quarterly analysis. The key is to stay consistent.
6. What’s the difference between online and in-store KPIs?
Online KPIs focus on metrics like website visits, bounce rate, or average order value. In-store KPIs are more about foot traffic, sales per square foot, and conversion rate. While both aim for better customer experience, the tracking methods differ.
7. I run a small store. Are KPIs still relevant for me?
Absolutely! Even small businesses benefit from tracking performance. Simple KPIs like daily sales, best-selling products, or customer feedback can help you make impactful improvements without needing complex tools.
8. How can KPIs help improve my inventory management?
KPIs like Inventory Turnover Rate or Shrinkage help you see if you’re overstocking, understocking, or losing inventory to theft or damage. With this insight, you can plan smarter, save costs, and avoid stockouts.
9. What should I do if my KPIs are showing poor performance?
Don’t panic — see it as an opportunity. Use the data to pinpoint what’s going wrong. Maybe your pricing strategy needs tweaking, or your store layout needs improvement. KPIs help you fix problems early before they snowball.
10. Do I need expensive software to track KPIs?
Not at all. While there are great tools out there, many KPIs can be tracked using simple spreadsheets, POS data, or Google Analytics for online sales. What matters is understanding the numbers and using them to guide your actions.