In today’s fast-paced, customer-centric world, businesses are constantly searching for smarter ways to streamline services, reduce costs, and improve customer experience. One solution gaining massive popularity across industries is the kiosk system. But what is a kiosk system exactly, and why is it transforming how businesses interact with customers? Let’s dive deep into the features, benefits, and diverse applications of kiosk systems.

What is a Kiosk System?
A kiosk system is an automated machine that boosts customer interactions through intuitive displays and touchscreen terminals. From buying movie tickets to checking into hotels or printing boarding passes, kiosk systems simplify tasks that traditionally required human support.
What is a kiosk system if not a bridge between technology and convenience? By offering an interactive interface—often touch-screen enabled—these systems allow users to independently access services, get information, or complete transactions efficiently and securely.
Today, kiosk systems are found everywhere: retail stores, airports, hospitals, restaurants, and banks, each tailored to serve unique needs.
Key Features of a Kiosk System
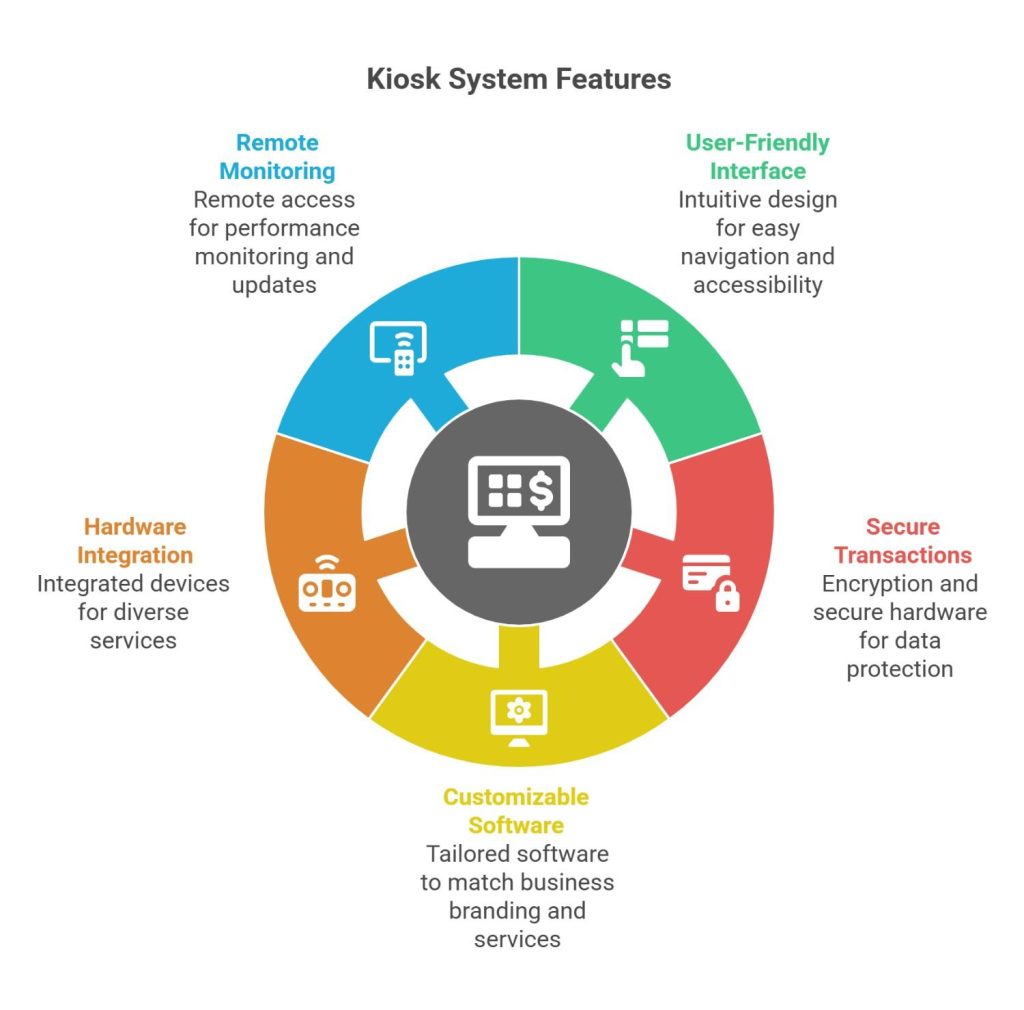
To fully understand what is a kiosk system, it’s crucial to explore the features that make them so effective:
1. User-Friendly Interface
Kiosk model systems are designed to be intuitive, with simple menus, touch-screen navigation, and clear visual cues that make them accessible to people of all ages and technical backgrounds.
2. Secure Transactions
Whether a kiosk is used for payments, check-ins, or document printing, security is paramount. Modern kiosk systems are equipped with encryption, secure card readers, and privacy measures to protect sensitive user information.
3. Customizable Software
Understanding its standalone features will help you grasp the technology. Businesses can customize the kiosk software to reflect their branding, services, and workflows, ensuring a seamless customer experience.
4. Hardware Integration
Kiosk systems often include integrated hardware like printers, scanners, card readers, cameras, and biometric devices. These integrations enable a broad range of services, from document printing to identity verification.
5. Remote Monitoring and Updates
Many kiosks allow businesses to monitor performance, update content, and troubleshoot issues remotely. This feature reduces downtime and ensures that kiosks are always functioning optimally.
Benefits of a Kiosk System
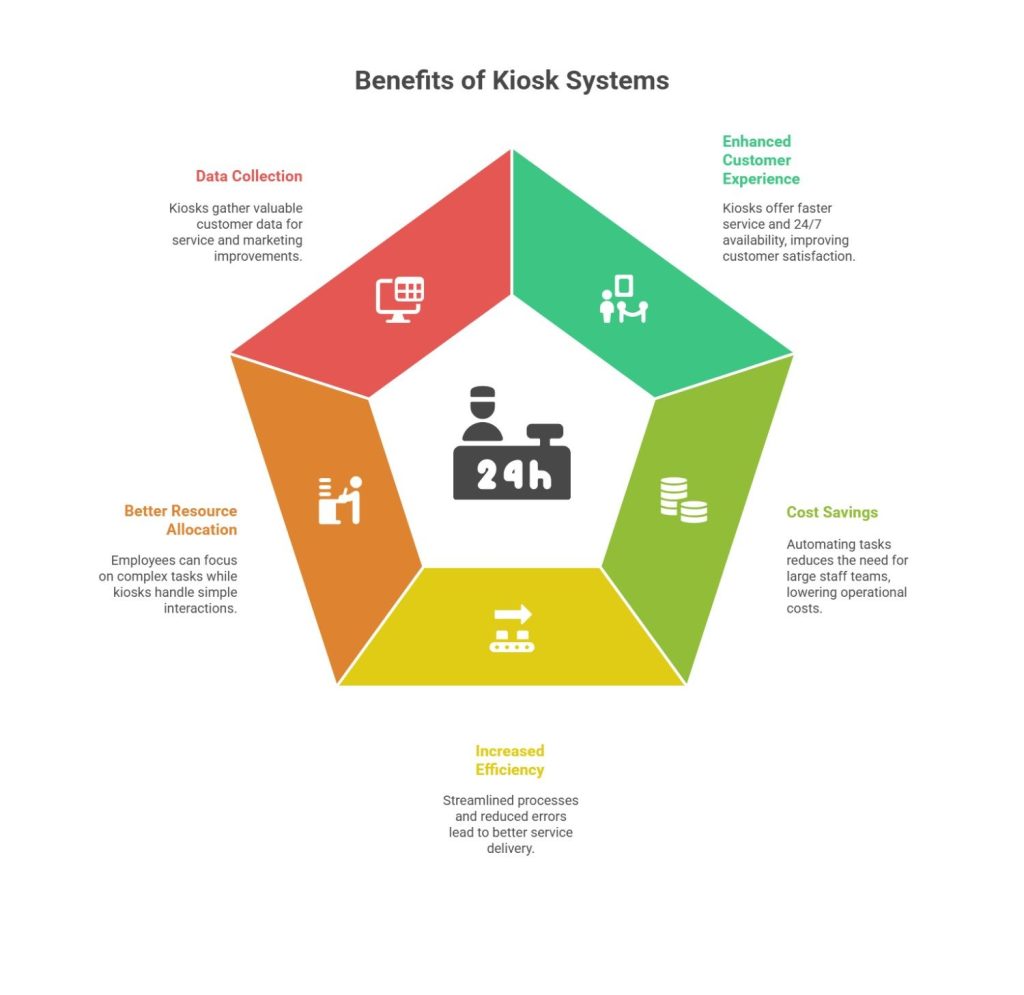
What is a kiosk system? Beyond understanding its definition, it’s important to recognise the tangible benefits it offers:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
Different types of kiosks reduce wait times, offer faster service, and provide 24/7 availability. This autonomy leads to a smoother, more satisfying experience for customers.
2. Cost Savings
Companies use kiosks to automate redundant activities. Kiosks handle multiple customer interactions simultaneously, lowering the need for large frontline staff teams. This reduces costs in the long run.
3. Increased Efficiency
Self-service kiosks streamline operations by eliminating bottlenecks, speeding up processes, and reducing human error, all of which contribute to better service delivery.
4. Better Resource Allocation
Understanding what is a kiosk system highlights how businesses can reassign employees to more complex, value-driven tasks while kiosks manage simple interactions.
5. Data Collection
Kiosk systems can gather customer data such as preferences, behaviours, and feedback. This data is valuable for businesses aiming to improve their services and marketing strategies.
Popular Use Cases of Kiosk Systems – Examples
What is a kiosk system? It’s fascinating to see how they are revolutionising multiple industries:
1. Retail
Self-service checkout kiosks are now a staple in supermarkets and stores. They allow customers to scan, pay for, and bag their purchases without waiting in long lines.
2. Hospitality
Hotels use kiosks for self-check-in and check-out, enabling guests to skip front-desk queues. In some resorts, kiosks help guests book activities, order room service, or print boarding passes.
3. Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics utilise kiosks for patient check-ins, appointment scheduling, payment processing, and even telemedicine consultations, offering greater convenience and efficiency.
4. Transportation
Understanding what is a kiosk system explains why airports worldwide have installed kiosks for self-check-ins, baggage tagging, and ticket printing, making air travel more streamlined.
5. Restaurants
Quick-service restaurants deploy kiosks to let customers place orders and pay without waiting for a server. This boosts order accuracy and reduces service time.
6. Banking
ATM machines are one of the earliest examples of kiosk systems. Today, advanced banking kiosks offer services like cash deposits, account openings, and loan applications without visiting a bank branch.
The Future of Kiosk Systems
As businesses seek new ways to improve customer engagement and operational efficiency, the future trends of interactive kiosk technology look even more promising. With AI, facial recognition, voice commands, and Iot integration, the next generation of kiosks will deliver smarter, more personalised experiences.
If you’re asking, what is a kiosk system in tomorrow’s world, the answer is simple: an intelligent, interactive platform bridging businesses and customers with unparalleled speed, accuracy, and convenience.
Conclusion
What is a kiosk system? In a world where speed, convenience, and accuracy are paramount, understanding it opens the door to new possibilities for businesses. From enhancing customer satisfaction to boosting operational efficiency, kiosk systems offer an innovative, future-ready solution for diverse industries. As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities of kiosks, making them an even more indispensable part of modern business operations.
If you’re considering investing in a kiosk system, contact Qodenext today for a hassle-free investment.
FAQS – What is a Kiosk System?
1. What is a kiosk system in simple terms?
A kiosk system is a device that interacts with customers on behalf of brands. It’s designed to offer fast, easy, and independent service. It is based on programmable and intuitive features that allow quick decision-making and brand deals.
2. Where are kiosk systems commonly used?
Kiosk systems are commonly used in retail stores, airports, hospitals, banks, hotels, and restaurants to simplify customer service and automate processes.
3. What are the core components of a kiosk system?
The core components include a user interface (usually touch-screen), a central processing unit (CPU), payment systems, printers, scanners, and software integrated with business operations.
4. How do kiosk systems benefit businesses?
They enhance customer satisfaction, reduce operational costs, streamline processes, improve data collection, and free up human resources for more complex tasks.
5. Are kiosk systems secure?
Yes, modern kiosk systems are highly secure, featuring encryption protocols, secure hardware components, and privacy-focused software design.
6. Can kiosk systems be customized for specific industries?
Absolutely. Kiosk systems are highly flexible and can be customized to meet the specific needs of industries such as healthcare, hospitality, retail, and banking.
7. What types of payments can kiosk systems accept?
Kiosk systems can handle various payment methods including cash, debit and credit cards, contactless payments, mobile wallets, and even QR codes. The exact payment options depend on the hardware and software integrated into the kiosk.
8. Are kiosk systems accessible for people with disabilities?
Absolutely. Many kiosk systems are built with accessibility in mind. You’ll find options like screen readers, braille keypads, adjustable height screens, and audio output, making it easier for users with visual, hearing, or mobility challenges to use the kiosk independently.
9. How do businesses keep kiosk systems secure?
Security is crucial in kiosk deployment. Businesses use encrypted communications, secure login credentials, firewalls, regular software updates, physical locks, and real-time monitoring to prevent both data breaches and tampering.






