
With the fast-paced world today, warehouse automation is revolutionizing conventional storage and fulfillment functions. No longer only reserved for global leaders, automation has become a must for companies that want to increase efficiency, lower labor costs, and address increasing customer needs.
Through the utilization of robots, conveyance systems, artificial intelligence-powered software, and intelligent storage features, warehouses are now getting faster, safer, and more precise. Automation not only increases efficiency and accelerates processes but also provides real-time visibility and control.
As supply chains become increasingly complex, warehouse automation is becoming a prime driver of agility, scalability, and long-term success.
What Is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation is the application of technology to handle warehousing functions such as storing, picking, packaging, sorting and shipping with minimal human interference. From conveyors, sorters (which are simple automation) to robots, automated storage and retrieval solutions, AI (which is advanced automation).
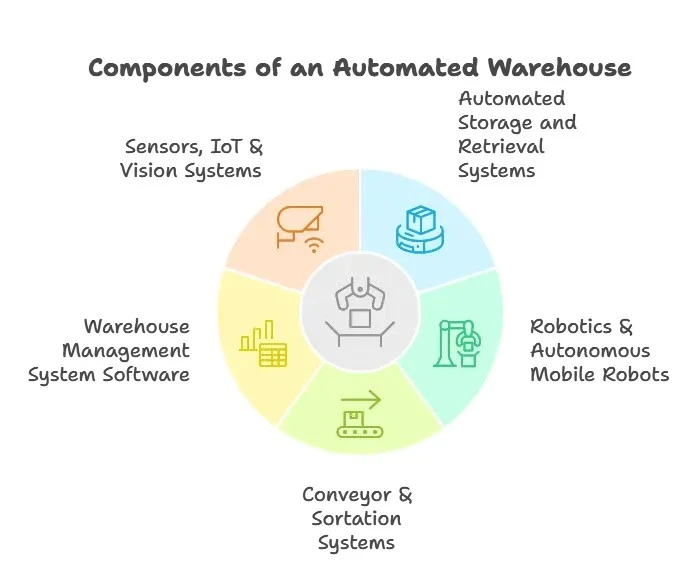
Essentials of An Automated Warehouse System
1. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) –
Systems that automatically store and retrieve items using cranes, shuttles or robotic device.
2. Robotics & Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR):
Robots that navigate through the warehouse to move goods, bring items to human operator, or perform repetitive activities.
3. Conveyor & Sortation Systems:
Mechanical systems for moving material from one place to another such as moving packages by size, weight, destination, etc. Warehouse Management
4. System (WMS) Software:
Your digital overlord that coordinates inventory, tracks operations, schedules machines and labor, and predicts demand.
5. Sensors, IoT & Vision Systems:
Machines that track surroundings, product location, packaging quality, etc. These provide inputs to the system to automate better.
Manual vs Automated Warehousing Differences
| Attribute | Manual Warehousing | Warehouse Automation |
| Labor dependency | High (many staff handling picking, carrying, counting) | Much lower; machines handle heavy loads, repetitive tasks |
| Errors and accuracy | Prone to human error | More consistent, higher accuracy |
| Speed of order fulfilment | Slower, variable | Much faster and stable throughput |
| Space usage | Often inefficient layout, wide aisles, overstocking | AS/RS and automated guided vehicles allow denser storage, optimized layout |
| Scalability | Challenging to scale without increasing labor and overheads | Easier to scale by adding machines or modules |
Why Businesses Are Investing in Warehouse Automation
Companies are investing in warehouse automation to enhance operational efficiency and remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic environment. Automation cuts reliance on manual labor, minimizes error rates, and accelerates order fulfillment, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction. Automation also maximizes warehouse space with smart storage systems, enabling companies to deal with higher volumes without physical expansion. With real-time information and AI-powered insights, companies are able to make quicker, better-informed decisions throughout their supply chain. This supports scalability, savings, and future-proofed operations in a more digitalized economy.
Top Benefits of investing in warehouse automation
1. Increased throughput & quicker order fulfillment:
Automated warehouse systems significantly cut down the period between order receipt and shipment—through streamlined picking, sorting, and packing.
2. Reduced operational expense:
Reduced reliance on manual labor, fewer mistakes, less waste, less damage, and better energy or space utilization all contribute.
3. Improved accuracy & stock visibility:
Real-time monitoring, automated stock counts, less mispicks and lost products.
4. Enhanced safety and ergonomics:
Most automation installations bring product to people instead of people walking miles and miles, less fatigue and injury.
5. Best space utilization:
Automated storage and retrieval systems in warehouses (e.g. AS/RS, shuttles) can minimize requirement for wide aisles and optimize use of vertical space.
Real‑World Example: Warehouse Automation in Action (India & Worldwide)
To see how they are working in practice, here are a few examples that illustrate how companies are using warehouse automation in India and beyond.
India Example – Prozo, Flipkart, and Others
1. Prozo:
An Indian 3PL company has implemented a mini-load AS/RS to automate storage and retrieval for part of their fulfilment operations. This minimizes human handling, speeds things up, and decreases error rates.
2. Flipkart and Amazon India:
Both have made significant investments in this field such as automated conveyor systems, pick/pack robotic arms, and AS/RS. This enables them to scale operations particularly during surge demands such as festival seasons.
3. Mahindra Logistics:
With the use of AGVs (automated guided vehicles), conveyor systems, and intelligent inventory tracking. These technologies are part of the way warehouse automation in India is improving in terms of efficiency.
Global Example – GreenBox Systems (USA)
GreenBox Systems (joint venture with SoftBank Group & Symbotic) is constructing an automated warehouse in Georgia, USA. The warehouse will employ robotics, AI, and vision‑enabled robots to manage sorting, packing, and minimize manual work. The investment is massive (approximately $144 million), which reflects how committed global players are towards warehouse automation.
Types & Roles of Warehouse Automation Systems Integrator
When organizations choose to automate, they usually seek the services of a warehouse automation systems integrator—a company that plans, installs, and supports the entire system. Here’s what integrators do and how decisions are made.
What Integrators Do
1. Assessment & design: Assess current warehouse layout, workflow, throughput, product mix, and suggest an ideal automated warehouse system.
2. Customization: No two warehouses are the same shape, loads, order profiles. Integrator creates customized conveyor routes, picking stations, robot travel routes.
3. Implementation: Hardware (robots, conveyors, racks, AS/RS) and software (WMS, monitoring dashboards) installed and integrated with ERP or other back-end systems.
4. Training & Change Management: Assisting staff to accommodate working with (and around) automated equipment; safety procedures; maintenance schedules.
5. Support & maintenance: Periodic servicing, software patches, robotics calibration, dealing with faults or breakdowns.
Which Systems to Consider
Some of the types of automated warehouse system integrators can suggest are listed below:
AS/RS units and shuttles
AMRs and AGVs (autonomous mobile robots, guided vehicles)
Pick-to-Light / Put-to-Light / Voice Picking systems
Conveyors, lifts, sorters, weigh stations
Key Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Warehouse automation is a rewarding experience, but one with challenges. Putting yourself in the shoes of a warehouse manager, managing budgets, personnel, and business demands.
Most Serious Challenges
1. Upfront capital investment (CapEx): Equipment, robots, racks, sensors are expensive. ROI sometimes means a wait.
2. Complexity of integration: Integrating the new systems with legacy warehouse management systems, ERP, workflows, human operators.
3. Change management problems: Workers might be resistant to automation; training is needed. Also safety procedures must change.
4. Scalability and flexibility: Business requirements keep changing; seasonal fluctuations; product mix variations; hence, flexibility of automation is most important.
5. Maintenance, downtime & reliability: Robots get damaged, sensors fail to read; require robust maintenance schedules and dependable suppliers.
Mitigating These Challenges
1. Pilot projects: Pilot small (a warehouse section) to test and perfect before scaling up.
2. Clear ROI modeling: Factor in labour savings, reduction in errors, improved use of space, throughput increases while developing the business case.
3. Selecting proper warehouse automation firms in India or integrators with a good reputation. Local players tend to have quicker support and more favorable cost structures.
4. Focusing on flexibility: Employ modular robotics systems, scalable warehousing storage systems, adaptable software which can be modified.
5. Organizing robust training and safety culture: Involve employees early, train for new workflows, practice safety hazards, develop SOPs.
The Indian Market: Trends, Players & Opportunities
India warehouse automation is expanding rapidly. Increasing demand in e‑commerce, tighter delivery deadlines, increasing wages, and waste reduction pressures are all driving adoption.
Where India Stands
Market growth is robust. Projections indicate high Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for India in upcoming years.
Technologies such as AS/RS, robotics, AMRs/AGVs, conveyor sorters, vision systems, IoT, and AI are being adopted.
Demand is particularly strong in regions with high manufacturing and e‑commerce concentrations: NCR, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, etc.
Who’s Doing It
A few of the warehouse automation companies in India / system integrators and solution providers making some waves:
1. Addverb Technologies – robotics, AMRs, shuttles, modular automation.
2. GreyOrange – sortation, “Butler” goods‑to‑person robots, sorter systems etc.
3. Godrej Consoveyo – AS/RS, cranes, conveyors.
4. Hitech Robotic Systemz – robots, AI for material handling.
5. Mahindra Logistics – combining logistics + automation for fulfillment centres, AGVs,
How to Plan & Implement Warehouse Automation Successfully
If you’re a business thinking: let’s do this, what’s the roadmap?
Steps to Adoption
1. Define goals clearly: Is it to reduce order processing time? Increase throughput? Reduce labour costs? Improve accuracy?
2. Audit operations as is: Layout map your warehouse, workflows, bottlenecks, order types, peak vs lull times.
3. Choose what functions to automate first: Picking? Sorting? Storage? Packaging? Or end‑to‑end in full?
4. Technology & vendor/integrator choice: Cost, support, reliability, scalability evaluate.
5. Layout & workflow design: Layout in place to accommodate new systems; robot path plan; safety zones ensure.
6. Pilot & test: Roll out small area; data collect; adjust; worker comfort ensure.
7. Roll-out full system & train staff: Roll out in stages; good change management; safety protocols.
8. Monitoring & continuous improvement: Leverage data, KPIs (throughput, error rates, downtime), evolve and improve over time.
Humanizing Automation: Impact on People & Culture
Automation usually creates anxiety: will workers lose their jobs? Will the work environment get cold and robotic? Let’s humanize the change.
What Workers Experience & What Helps
1. Role shift, not necessarily elimination:
Much manual labor is replaced but new jobs are created—robot handlers, maintenance personnel, data analysts.
2. New skills necessary: Education is important
learning to interface with automated storage, learning to follow safety procedures, watching machines.
3. Improved working environment:
Reduces repetitive heavy lifting, enhances safety, reduces fatigue. Automation can make work less physically demanding.
4. Emotional reaction:
Change is a cause of anxiety; honest communication from management avoids it. Engage employees early, explain to them how automation benefits not only the business but can enhance their working environment.
Cost vs ROI: What to Expect
Return on investment is the bottom line question for any company that invests in an automated warehouse system.
1. Elements of Cost
Capital outlays: hardware (robots, racks, conveyors), software, installation, facility changes.
Integration expenses: connecting new systems to installed ones (ERP, WMS), retrofits.
Maintenance operation: maintenance of robots, sensors; spares; software upgrades.
Training: staff instruction, change management expense.
2. ROI sources
Lower labor expense: fewer individuals to perform repetitive jobs; reduced overtime, less error.
Higher throughput: more orders per day/hour.
Improved accuracy: fewer returns; fewer errors; increased customer satisfaction.
Space conservation: utilization of vertical space; tighter storage; reduced necessity for wide aisles.
Less damage / waste: more accurate handling; less human-error.
3. Average ROI Timeline
Payback period for most implementations is 1 to 3 years based on scale, complexity, product value, labour cost.
Smaller automation (picking aids + conveyors) will realize payback quicker; completely robot / AS/RS dedicated warehouses realize longer payback but provide more scale.
Conclusion
Automating warehouses is no buzz. It’s a revolutionary approach that, if well thought out and executed, can lead to drastic improvements in speed, accuracy, cost, safety, and scalability. In India, the momentum is gathering: e-commerce, manufacturing, and logistics sectors are inducing firms to apply automated storage systems in warehouses, robotic picking, conveyors, and intelligent systems integrators.
Firms such as QodeNext are leading the way in facilitating this transition with intelligent automation solutions specific to today’s supply chain requirements. It depends not only on technology, but also on people, planning, and ongoing optimization.
If your business is considering going in this direction, start small, define your goals, select rugged partners, maintain the human touch in mind, and iterate. The warehousing future is smart, automated, efficient—and already here.
FAQs
Q1: How is an automated warehouse system different from simply using conveyor belts or sorters?
An automated warehouse system most often means a more integrated installation: powered storage and retrieval, robotics, intelligent software (WMS, AI), sensors, etc. Conveyors or sorters are part of it, but they do not constitute complete automation by themselves.
Q2: Are automated storage systems in warehouses only beneficial to large companies?
Not always. Small and medium enterprises also stand to gain — particularly where the cost of labour is high or order volumes are irregular. Modular systems ensure growth with the business. Flexible solutions for mid-sized operations are provided by some Indian vendors and solution providers.
Q3: What is the way to select a good warehouse automation systems integrator?
Seek vendors with: successful case studies; local service; good customer support; flexible, modular configurations; capability to do both hardware and software; dependable maintenance; safety certification. Warehouse visits where they’ve installed systems are helpful.
Q4: What are the risks of warehouse automation?
High initial cost and long payback period when poorly planned; failure of technology; resistance from employees; over‑automation (inflexible systems which are unable to adjust when products or order patterns change); downtime in case of non‑maintenance.
Q5: What are the differences between warehouse automation in India and developed nations?
India’s cost structures, availability of labor, infrastructure, regulatory regime vary, so systems tend to require localization (local design, local parts, local services). Further, lots of businesses here are leapfrogging phases—more manual to very advanced in a short while. Also, vendor ecosystem is increasing rapidly, which is beneficial.






