
Conveyor belts are a boon for manufacturing assembly lines, however, different types of conveyors perform different functions. Whether it’s food and beverage, pharmaceutical, or automotive, conveyors play an important role and choosing the right belts is critical to supply chain operations.
The rise of modern technology has expanded the role of belts and they are no longer limited to material transportation.
Let’s understand conveyor application in detail.
Types of Conveyors and Their Applications – Complete Guide
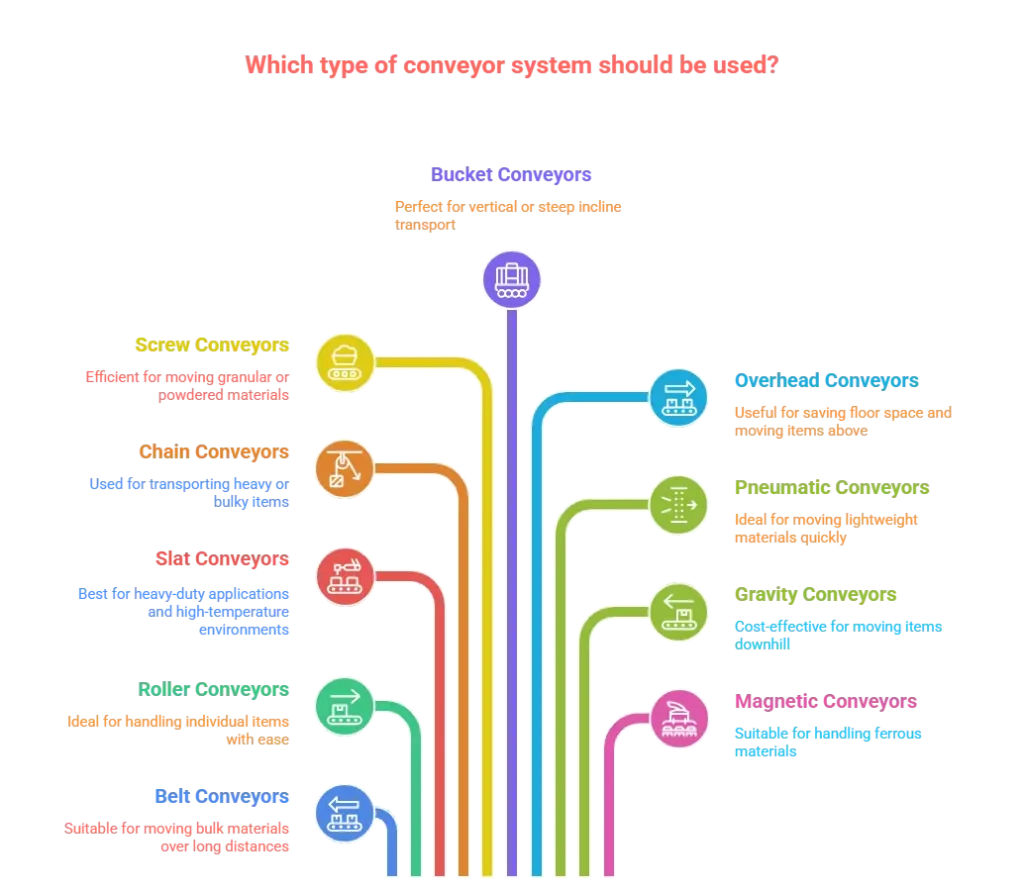
1. Belt Conveyors
One of the most common types of conveyors found in manufacturing facilities worldwide, these conveyors utilise a continuous loop of material, typically made from rubber, fabric, or plastic, to transport goods. They are versatile and suitable for conveying various products, from bulk materials to packaged goods, across various distances.
Applications of Belt Conveyors
- Agriculture – Many farming societies and companies employ conveyors for loading, unloading, and sorting crops.
- Airports – It is extensively used in airports across the globe to move luggage and cargo between terminals for faster departures and arrivals.
- eCommerce Industry – Retail operations like transportation of goods, processing in storage facilities, and bulk material handling are done by belt conveyors.
- Food Packaging – The ideal types of conveyors like belts are used for food sorting, distribution, and packaging in the F&B sector.
2. Roller Conveyors
The conveyors feature a series of rollers mounted on a frame, allowing for the smooth movement of items along a predetermined path. They are particularly effective for transporting heavy loads or items with irregular shapes.
Applications of Types of Conveyors – Roller
- Warehouse & Distribution – They are used to make boxes, cartons, and materials within the production facilities.
- Postal Services – Rollers are the lifeline of the postal industry. They enhance the efficiency of sorting and distribution for courier companies, and packaging hubs.
- Automotive Industry – It is used to transfer auto parts and heavy machinery along the assembly line. Rollers facilitate the seamless flow of goods across multiple logistical channels.
- Airport terminals – These types of conveyors are commonly used in cargo facilities to handle heavy items.
3. Slat Conveyors
These conveyors utilize slats or plates made from steel, wood, or plastic, which are linked together to form a continuous surface for conveying goods. They are well-suited to carry heavy or bulky items that may not be suitable for other types of conveyors. Slat conveyors are widely used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and material recycling.
Applications of Slat Conveyors
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used to move heavy engine blocks, chassis parts, and other bulky components through assembly lines due to their sturdy, flat surfaces.
- Construction Materials: Ideal for transporting bricks, tiles, and other building supplies without risk of jamming or spillage.
- Material Recycling: Efficient for moving large, irregularly shaped recyclable items, helping to automate sorting and processing.
4. Chain Conveyors
Chain conveyors employ chains or chains with attachments to move materials along a predefined path. They are robust and capable of handling heavy loads, making them ideal for applications involving supply chain management or high-throughput operations. Industries such as mining, cement production, and industrial manufacturing rely on chain conveyors for efficient material handling.
Applications of Chain Conveyors
- Mining Industry: Used for handling minerals, ores, and other bulk materials, thanks to their strength and ability to carry heavy loads over long distances.
- Cement Production: Essential for moving clinkers, cement bags, and raw materials between processing stations securely.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Transporting heavy pallets, containers, or steel products along fixed routes through factories.
5. Screw Conveyors
Screw conveyors consist of a rotating screw or auger enclosed within a trough, used to move granular or powdered materials horizontally or at a slight incline. These conveyors are highly versatile and can handle various types of materials, including grains, powders, and chemicals. Common applications include agriculture, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment plants.
Applications of Screw Conveyors
- Agriculture: Moving grains, animal feed, fertilizers, and other bulk powders between silos or into trucks for distribution.
- Chemical Processing: Handling powdered chemicals and granules in a safe, enclosed environment to prevent contamination or spillage.
- Wastewater Treatment: Used to convey sludge, grit, or dewatered waste from collection points to disposal or treatment facilities
6. Bucket Conveyors
Bucket conveyors feature buckets or containers attached to a rotating chain or belt, used to scoop up and transport bulk materials vertically or horizontally. They are particularly suitable for handling abrasive or fragile materials, as well as those with high temperatures. Industries such as mining, agriculture, and construction utilize bucket conveyors for efficient material handling and transportation.
Applications of Bucket Conveyors
- Mining: Lifting and moving coal, gravel, or ore vertically from underground mines to surface processing plants.
- Agriculture: Elevating grain, seeds, or fertilizer to storage bins or silos, reducing manual labor.
- Construction: Transporting sand, cement, or other aggregates to high elevations at building sites.
7. Overhead Conveyors
Overhead conveyors are mounted above the production floor, allowing for the efficient movement of goods in a vertical or horizontal direction. They are space-saving and suitable for transporting items through various stages of the production process, such as painting, curing, and assembly. Overhead conveyors find applications in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and garment production.
Applications of Overhead Conveyors
- Automotive Manufacturing: Moving car bodies or parts through painting and drying stages while freeing up floor space below.
- Aerospace: Transporting aircraft components across assembly lines without interfering with ground operations.
- Garment Production: Efficiently moving clothing and textiles through various finishing, packaging, and quality control stages.
8. Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic conveyors use air pressure or vacuum to transport materials through a pipeline, eliminating the need for mechanical components like belts or chains. They are ideal for handling fine powders, granules, and other lightweight materials, offering flexibility and efficiency in material handling processes. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing benefit from the clean and hygienic operation of pneumatic conveyors.
Applications of Pneumatic Conveyors
- Pharmaceuticals: Transferring powders, tablets, or capsules in clean, contamination-free pipelines between production stages.
- Food Processing: Moving flour, sugar, grains, and spices efficiently through enclosed systems that meet hygiene standards.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Handling lightweight powders or hazardous materials where dust control and explosion prevention are critical.
9. Gravity Conveyors
Gravity conveyors rely on the force of gravity to move items along a downward slope or decline. They are simple in design and require no external power source, making them cost-effective and easy to maintain. Gravity conveyors are commonly used in warehousing, distribution centers, and order fulfillment operations for transporting goods over short distances with minimal effort.
Applications of Gravity Conveyors
- Order Fulfillment Centers: Using gravity-fed chutes and rollers to move boxes or packages from picking areas to shipping docks with minimal power use.
- Warehousing: Providing flexible, low-cost movement of pallets, totes, or cartons between workstations or down packing lines.
- Distribution Centers: Temporarily storing or accumulating products before they are manually loaded onto transport vehicles.
10. Magnetic Conveyors
Magnetic conveyors utilise magnetic fields to transport ferrous materials such as steel or iron. They offer precise control over the movement of materials and are suitable for applications where traditional conveyors may not be feasible, such as handling hot or sharp-edged objects. Magnetic conveyors are utilised in industries such as metal fabrication, recycling, and mining for efficient material handling and separation.
Finally, let’s address the commonly asked queries of conveyors to gain a complete understanding of the subject.
Applications of Magnetic Conveyors
- Metal Fabrication: Transferring sharp or hot steel scrap, stamping slugs, or metal shavings safely between machines and recycling bins.
- Recycling: Separating and moving ferrous metals from non-metallic waste streams for efficient sorting and recovery.
- Mining: Handling iron ore, steel parts, or metal powders in a controlled, dust-free way.
Conclusion
Many different types of conveyors have various applications in multiple industries and help cut labour costs, speed up production and maintain order and hygiene. They significantly improve efficiency in manufacturing and enhance worker safety. In addition to conveyor belts, there are many solutions to tackle the challenges of supply chain operations. Get in touch with Qodenext to drive expert-led solutions for your logistical problems.
FAQs – Types of Conveyors and Their Applications in Manufacturing
1.What are the basics of a conveyor?
It is a machine strapped across pulleys to form a closed loop for consistent rotation. The drive pulley tows the belt to move items from one place to another.
2.What are the common maintenance requirements for conveyor systems?
The maintenance depends on different types of conveyors and their operating conditions. However, routine tasks typically include cleaning and lubricating moving parts, inspecting belts and chains for wear, checking for loose or damaged components, and addressing any issues promptly to prevent downtime and ensure reliability.
3.Are there any environmental considerations associated with conveyors?
Yes, it is increasingly important in modern manufacturing. Conveyor systems can impact energy consumption, emissions, and waste generation. Choosing energy-efficient components, implementing recycling and waste reduction measures, and optimizing material flow can help minimize the environmental footprint of conveyor systems.
4.What are some emerging trends in conveyor technology?
Advancements in different types of conveyors continue to drive innovation in manufacturing. Some emerging trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) sensors for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, the adoption of robotics and automation for enhanced flexibility and efficiency, and the development of eco-friendly conveyor materials and energy-saving technologies.
5.How can I ensure compliance with industry regulations when implementing conveyor systems?
Compliance is a must for installing different types of conveyors and their applications. Working with reputable suppliers and manufacturers who adhere to relevant regulations, conducting thorough risk assessments, and staying updated on industry best guidelines can help ensure compliance and mitigate potential risks.
6. How do I choose the right type of conveyor for my manufacturing application?
Selecting the right conveyor depends on the nature of the products (size, weight, shape), the required speed, production volume, the distance to be covered, environmental factors (temperature, humidity), and specific industry requirements. Consulting with conveyor system specialists and analyzing your workflow help ensure the best fit.
7. Can conveyor systems be customized for unique manufacturing processes?
Yes, modern conveyor systems are highly customizable. Manufacturers often tailor systems with specialized belts, rollers, controls, or layouts to accommodate unique products, challenging spatial constraints, or specific integration needs within an assembly line.
8. Are conveyors suitable for cleanroom or sanitary manufacturing environments?
Absolutely. Many conveyor types, such as modular belt, wire mesh, or sanitary plastic chain conveyors, are designed for hygienic applications. They use easy-to-clean materials and construction methods ideal for pharmaceuticals, electronics, or food and beverage sectors.
9. What safety features should be included in conveyor systems?
Key safety features include emergency stop buttons, safety guards, start-up alarms, anti-jamming devices, and regular safety audits. Advanced systems may offer sensor-based worker protection and automatic shutoff in case of an emergency.






