Speed, accuracy, and making decisions based on data are all important in modern manufacturing. Every minute on the shop floor is important, and every delay costs money. That’s when a manufacturing MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is very important.
It links planning, production, and performance so you can see what’s going on in real time and make decisions more quickly and wisely.
But, like any digital transformation project, putting MES into action has its own set of problems. Technology and teamwork are both important for success, whether it’s connecting old machines or helping people get used to new systems.
Let’s look at these problems and how to solve them in real life.

What Is a Manufacturing MES and Why It Matters
A manufacturing MES fills in the gaps between planning and actually making things. It links your machines, workers, and processes so you can see what’s going on in real time on the shop floor.
This is like the command centre of your factory. It keeps an eye on quality, tracks materials, measures output, and shares information right away.
One of its strongest features is MES software real time production monitoring, which allows teams to detect slowdowns or quality issues as they occur. This helps cut down on downtime, make things run more smoothly, and make sure that the quality of the products stays the same.
Common MES Implementation Challenges
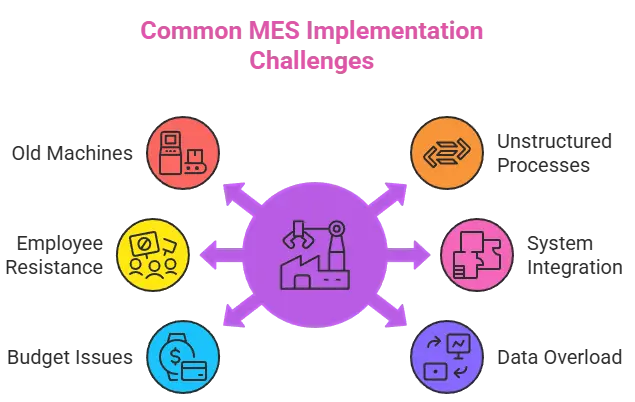
1. Old Machines and Legacy Systems
A lot of factories still use machines that don’t work well with modern software. These older machines can’t automatically share data, which makes it hard for MES to get the right information.
How to fix it:
First, find out which machines can send data electronically. For older devices, use IoT sensors or gateway devices to get basic data like speed, temperature, or downtime. Over time, upgrade important machines while keeping them connected with small digital bridges.
2. Unstructured Processes
If every line or team does things differently, MES will have a hard time getting accurate data. Your reports can be hard to understand or not trustworthy if you don’t have standard procedures
How to fix it:
Before you install the MES, make sure your workflows and key metrics are all the same. For instance, decide how you will keep track of downtime, efficiency, and defect rates. Make sure that your team knows how to report consistently so that MES data is always clean and useful.
3. Employee Resistance
Change can be hard to deal with. People who are used to keeping records by hand or in Excel sheets may not want to switch to a new digital system.
How to fix it:
Get employees involved early on. Tell them how MES makes their jobs easier and helps them solve problems. Start with small pilot runs, get feedback, and celebrate small wins to help people feel more confident and willing to accept the changes.
4. Difficult System Integration
A manufacturing MES works best when it connects smoothly with your ERP and WMS systems. This ensures production planning, material movement, and reporting all work together, but setting that up can be tricky.
How to fix it:
Before you go live, make a plan for how your MES will work with your WMS and ERP. Use open APIs or platforms that already have connectors built in. Checking the data flow early on stops reports and communication problems from happening later.
5. Budget and Timeline Issues
Setting up a MES system takes time and money for planning, customising, and training. A lot of factories don’t think about these things enough and rush the rollout.
How to fix it:
Go step by step. Begin with one line or process, test it thoroughly, and then add more lines or processes over time. Start with important features like real-time production monitoring in MES software, and add more modules later. This keeps costs down and makes sure that each step is a success.
6. Too Much Data, Too Little Insight
When MES is working, there can be a lot of data to deal with. Teams might have trouble finding what really matters if there aren’t clear dashboards or filters.
How to fix it:
Set up dashboards for each role that show the most important metrics for that role. For instance, operators get alerts when there is downtime, and managers see trends in efficiency. Make it easy to see, understand, and act on.
Why Real-Time Monitoring Matters
With real-time monitoring, manufacturers gain these crucial advantages:
- More Clarity: A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) lets you see what’s going on in the shop floor in real time, including how well machines are working, how fast production is going, and how good the quality is.
- Instant Awareness: You don’t have to wait for reports at the end of the shift. You can see problems as soon as they happen.
- Quick Action: The MES sends an alert to the right team right away if a machine slows down, stops, or makes mistakes. This helps you fix problems before they cause downtime or losses.
- Continuous Improvement: Real-time data helps find problems that keep coming up, keep an eye on efficiency, and improve processes for better results.
- Better Choices: You can better plan production, allocate resources, and improve operations with real-time, accurate information.
MES Integration with ERP and WMS
An MES doesn’t work alone; it needs to connect with your existing systems to deliver full value.
- ERP manages planning, resources, and order tracking.
- WMS manages material flow and inventory control.
- MES executes production activities and ensures they match the plan.
When these systems work together, you get a connected ecosystem. Knowing exactly how MES integrates with WMS and ERP helps avoid delays, improve scheduling accuracy, and provide complete visibility from order to delivery.
For even tighter synchronization, MES can also connect with a Warehouse Inventory Management System (IMS) to ensure material availability aligns with production schedules.
MES for Discrete Manufacturing
A MES system for discrete manufacturing is very helpful for factories that make things like cars, electronics, or machinery one at a time.
It keeps track of each part at every stage of production to make sure it can be traced and is of high quality. It also helps keep track of complicated assembly lines, making sure that each step is done in the right order and to the right standard.
Low-Code MES for Small Factories
Many small and mid-size manufacturers avoid MES because they think it’s expensive or too complex. That’s changing fast with the rise of low code MES platform for small factories.
These platforms let you:
- Customize workflows with simple drag-and-drop tools
- Integrate systems faster without major IT setup
- Scale easily as your operations grow
This makes MES adoption accessible, affordable, and flexible — even for small operations.
Best Practices for a Smooth Implementation
- Start small, scale later – Begin with one line or one function.
- Standardize processes – Keep data entry consistent across teams.
- Communicate clearly – Explain how MES will make everyone’s job easier.
- Train continuously – Offer refresher sessions and on-floor support.
- Measure success early – Use key metrics like OEE and defect rate improvements to prove ROI.
Future of MES: Smarter, Simpler, Connected
The future of MES is in being smart and easy to use. AI-driven and cloud-based MES tools will speed up decision-making, work well with IoT, and help you see problems before they happen. Low-code platforms will keep making it easier for smaller manufacturers to use smart manufacturing systems at lower costs.
Conclusion
It takes work to set up a manufacturing MES, but the benefits are worth it. MES helps your factory work faster, safer, and more efficiently by giving you real-time visibility, better process control, and smarter decision-making.
The most important thing is to start small, tackle your biggest problems first, and include your employees in every step. Your MES journey can lead to long-term manufacturing excellence if you have the right plan and attitude.
FAQs(Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the first steps in planning a manufacturing MES project?
To begin, figure out what problems you have with production and what data you don’t have. Then, set clear goals, like lowering downtime, raising quality, or making it easier to find things.
2. How long does a typical MES implementation take?
It depends on the size of the factory and the scope of the project. A basic system can be up and running in a few weeks, but full integration with ERP and WMS could take a few months.
3. How do I measure MES success after launch?
Track things like equipment uptime, defect reduction, and production throughput. Signs of success include faster response times and smoother operations.
4. Is MES suitable for all types of manufacturing?
Yes. MES is most useful in discrete manufacturing, but it also helps process industries by making sure that everything is done the same way and that rules are followed.
5. How can small factories afford MES?
A low-code MES platform for small factories has modular pricing and is easy to set up. You only pay for what you use and can add more as you need them.






