A warehouse inspection is a crucial process that ensures efficiency, accuracy, and compliance within a warehouse facility. By regularly conducting a warehouse audit, businesses can minimize operational risks, optimize inventory management, and enhance overall productivity. Whether you operate a small distribution center or a large logistics hub, a well-structured audit helps identify inefficiencies, reduce costs, and improve service levels.
This guide will walk you through the key aspects of a warehouse inspection, including its importance, types, step-by-step execution, and best practices. By following this structured approach, you can conduct a comprehensive review that drives long-term improvements.
What is a Warehouse Audit?
A warehouse audit is a systematic evaluation of warehouse operations, inventory management, safety measures, and compliance with industry regulations. It helps businesses identify inefficiencies, ensure inventory accuracy, improve warehouse workflows, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Types of Warehouse Audits
- Inventory Audit – Assesses stock levels, discrepancies, and accuracy of inventory records.
- Process Audit – Evaluates warehouse operations such as receiving, storage, picking, and shipping.
- Safety and Compliance Audit – Ensures adherence to OSHA and industry safety standards.
- Financial Audit – Reviews costs, budget allocations, and cost-effectiveness of operations.
- Technology Audit – Examines the efficiency of warehouse management systems (WMS) and automation tools.
Why is a Warehouse Quality Audit Checklist Important?
A warehouse audit offers several advantages, making it an essential practice for businesses:
- Enhances Inventory Accuracy – Reduces stock discrepancies and prevents overstocking or stockouts.
- Boosts Operational Efficiency – Identifies inefficiencies and improves workflow optimization.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance – Meets safety and legal standards to avoid penalties.
- Reduces Costs – Identifies wasteful expenses and improves budget control.
- Improves Customer Satisfaction – An internal audit of warehouses ensures timely and accurate order fulfillment.
- Enhances Warehouse Safety – Identifies hazards and ensures compliance with health and safety regulations to prevent workplace accidents.
- Optimizes Warehouse Operations – Helps in organizing inventory better, leading to efficient space management and streamlined operations.
- Improves Supplier and Vendor Relations – Ensures proper handling of incoming and outgoing shipments, reducing disputes and errors.
- Supports Data-Driven Decision Making – Provides valuable insights through audit reports that help businesses make strategic decisions to enhance productivity and growth.
Step-by-Step Guide to Warehouse Audit Procedures
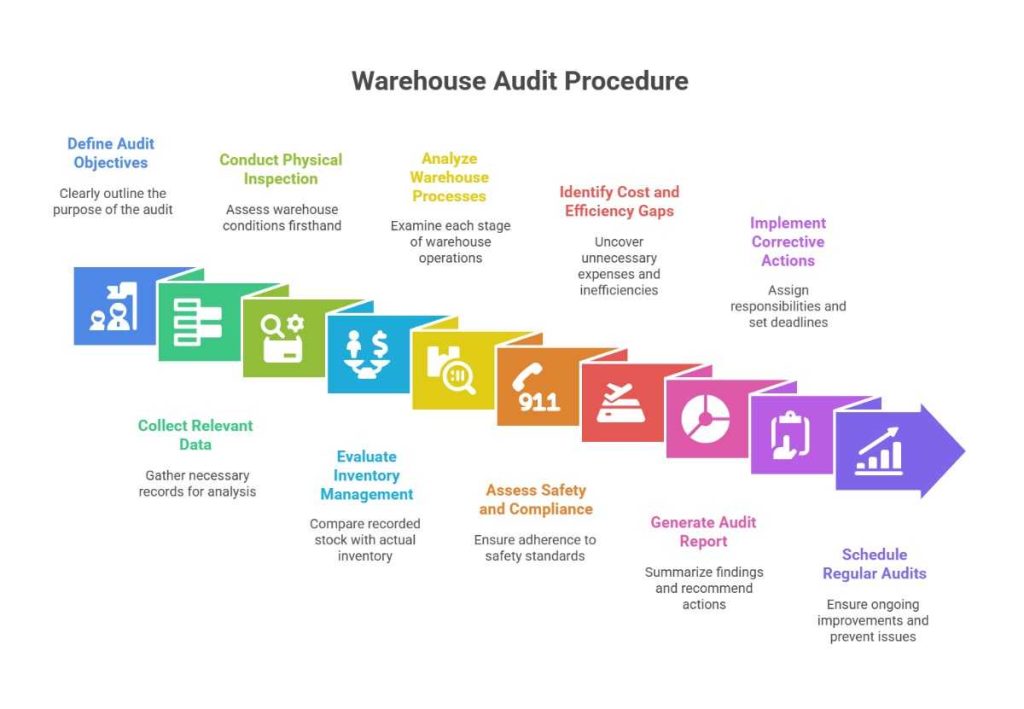
A warehouse health and safety audit checklist is the foundation of inventory management. Here is how to plan the entire process:
Step 1: Define Audit Objectives
Clearly outline the purpose of your warehouse audit. Focus areas may include inventory control, safety compliance, or workflow efficiency.
Key Questions to Consider:
- What are the most pressing warehouse challenges?
- Are there specific inefficiencies or errors to address?
- How will success be measured?
Step 2: Collect Relevant Data
Gather necessary records such as:
- Inventory reports
- Order processing logs
- Employee performance metrics
- Equipment maintenance records
- Safety compliance checklists
- Having accurate data ensures a more thorough and reliable warehouse audit.
Step 3: Conduct a Physical Warehouse Inspection
A physical walkthrough allows auditors to assess warehouse conditions firsthand.
Checklist for Inspection:
- Inventory tools, storage and organization
- Cleanliness and safety compliance
- Functionality of equipment and automation tools
- Accessibility of emergency exits and first aid stations
- Order picking and packing efficiency
Step 4: Evaluate Inventory Management
Inventory discrepancies can lead to financial losses and operational inefficiencies. Compare recorded stock levels with actual inventory.
Best Practices for Inventory Auditing:
- Conduct cycle counts instead of relying on annual stock takes.
- Use RFID tracking and barcode scanning for accuracy.
- Monitor slow-moving inventory and phase out obsolete stock.
- Assess the picking and packing processes to ensure correct order fulfillment.
Step 5: Analyze Warehouse Processes
Examine each stage of warehouse operations:
- Receiving & Putaway: Are goods stored in optimal locations?
- Picking & Packing: Are orders fulfilled efficiently and accurately?
- Shipping & Returns: Are there bottlenecks in dispatch and return management?
- Workforce Productivity: Are staff operating at peak efficiency?
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like order accuracy rate, inventory turnover ratio, and dock-to-stock time helps pinpoint improvement areas.
Step 6: Assess Safety and Compliance Measures
Warehouses must adhere to safety standards to protect employees and operations.
Key Areas to Audit:
- Emergency exits and fire extinguishers
- Use of PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
- Proper storage of hazardous materials⚙ Maintenance and training records for machinery and equipment
Step 7: Identify Cost and Efficiency Gaps
A financial review helps uncover unnecessary expenses and inefficiencies.
- Storage Costs – Are you paying for unused space?
- Order Fulfillment Costs – Are labor and shipping expenses optimized?
- Technology Investments – Is warehouse automation providing ROI?
Step 8: Generate a Comprehensive Audit Report
Your warehouse audit report should include:
- Summary of key findings
- Performance metrics and data comparisons
- Identified problem areas and recommended actions
- Timelines for implementing corrective measures
Step 9: Implement Corrective Actions
Assign responsibilities and set deadlines for resolving audit issues.
| Issue Identified | Solution | Responsible Team | Timeline |
| Inventory discrepancies | Implement barcode scanning | Inventory Team | 3 months |
| Safety violations | Conduct employee training | HR/Safety Team | 1 month |
| Inefficient picking process | Optimize warehouse layout | Operations Team | 3 months |
Step 10: Schedule Regular Warehouse Audits
Performing warehouse audit checklists on a scheduled basis—whether annually, quarterly, or monthly—ensures ongoing improvements and prevents recurring issues.
Best Practices for an Effective Warehouse Audit
- Use Warehouse Management Software (WMS) – Automate tracking and reporting.
- Engage Employees – Encourage feedback from warehouse staff.
- Benchmark Performance – Compare results with previous audits.
- Standardize Audit Checklists – Ensure consistency in evaluations.
- Address Issues Promptly – Fix inefficiencies before they escalate.
Conclusion
A well-executed warehouse audit enhances efficiency, ensures compliance, and reduces operational costs. By following a structured approach—from defining objectives to implementing corrective actions—you can optimize your warehouse performance and drive long-term success. Regular inventory audits not only prevent disruptions but also create a foundation for continuous improvement in supply chain management.
Want to streamline your logistics operations with state-of-the-art traceability solutions? Contact Qodenext today.
FAQs – Warehouse Audit
1. How to audit a warehouse?
Define clear goals and conduct a physical audit inspection. Observe operations, analyze data and speak to the staff about possible issues. Plan, strategize and repeat the process weekly, monthly or annually.
2. What are the common issues found during an inspection audit?
Some of the most common problems include inventory discrepancies, inefficient workflows, non-compliance with safety regulations, and excessive operational costs.
3. What tools can help in an inventory assessment?
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), barcode scanners, RFID technology, and AI-driven analytics improve the accuracy and efficiency of warehouse systems.
4. How can I reduce warehouse errors identified in an audit?
Implement automation, conduct employee training, optimize inventory tracking, and streamline warehouse workflows to minimize errors.
5. How can technology improve warehouse inspection?
Technology such as AI, IoT sensors, and cloud-based WMS can provide real-time insights, automate reporting, and enhance accuracy in audits.
6. What role does employee training play in inventory audits?
Well-trained employees help maintain compliance, minimize errors, and improve overall efficiency in warehouse operations.
7. How do I ensure audit recommendations are implemented?
Set clear timelines, assign responsibilities, and regularly follow up to ensure corrective actions are successfully executed.






