Supply chain efficiency is the only way for businesses to stay relevant. With rising customer expectations, global uncertainties, and increasing complexity in logistics, companies are turning to emerging technologies to build more resilient and responsive systems. Digital twin supply chains have become the next big thing.

A manager can create a virtual replica of a business problem. When applied to supply chains, digital twins offer a real-time, data-driven model that mirrors actual operations. This enables businesses to simulate various scenarios, predict outcomes, and make smarter decisions before taking costly actions in the real world.
What Is a Digital Twin in the Context of Supply Chains?
Think of a digital twin supply chain as a virtual version of supply chain systems. This includes suppliers, production facilities, inventory systems, transportation networks, and customer demand behaviour. The digital twin continuously updates using data from Iot devices, ERP systems, and other enterprise software to reflect real-time conditions.
This evolving mirror of the actual supply chain empowers managers to run simulations, test optimizations, detect bottlenecks, and plan for disruptions—all in a risk-free virtual environment.
Key Roles of Digital Twins in Supply Chain Simulation
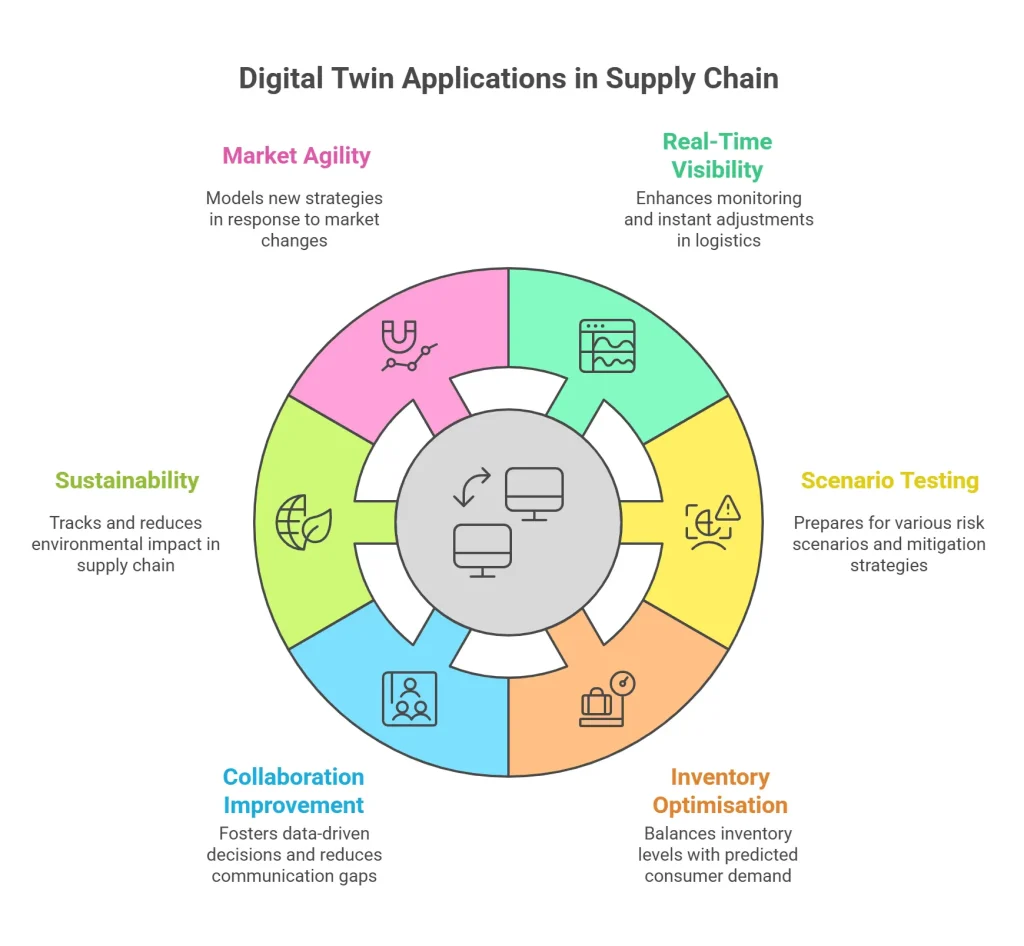
1. Real-Time Visibility and Monitoring
The foundation of any effective supply chain simulation is accurate data. A digital twin supply chain decodes data from infinite sources to provide a single point of truth. This transparency helps companies monitor performance, track delays, and adjust logistics instantly.
For example, if a storm disrupts a shipping route, the digital twin can simulate alternate routes and calculate the best way to minimise delays or costs.
2. Scenario Testing and Risk Management
In an unpredictable world, being prepared for “what-if” situations is invaluable. Digital twins in the logistics market enable companies to simulate various risk scenarios like supplier failures, sudden demand spikes, or geopolitical disruptions.
A digital twin supply chain can model these stress scenarios and evaluate the best mitigation strategies. This helps businesses build resilience, rather than reactively firefighting after a crisis hits.
3. Optimisation of Inventory and Production
Overstocking shrinks resources and profit margins while understocking leads to missed sales. Using simulation tools powered by digital twins, companies can forecast demand, balance inventory, and fine-tune production schedules.
The digital twin supply chain aligns inventory levels with predicted consumer demand, ensuring that products are available when and where they’re needed, without unnecessary surplus. This is the era of logistics 4.0.
4. Improved Collaboration and Decision-Making
A digital twin acts as a single source of truth across departments and partners. This shared virtual environment enhances collaboration between supply chain managers, planners, vendors, and even customers.
With a digital twin supply chain, decisions become more data-driven and aligned, reducing the friction caused by information silos or communication gaps.
5. Sustainability and Efficiency Improvements
Sustainability has become a critical business priority. Digital twins can help companies track energy usage, carbon emissions, and waste throughout their supply chain.
By simulating different sourcing, packaging, and distribution options, a virtual supply chain enables companies to reduce their environmental impact while optimising cost and performance.
6. Agility in a Changing Market
Today’s markets are volatile, and customer preferences evolve rapidly. A digital twin lets companies model new strategies, like switching suppliers, launching a new product, or entering a new geography, before actually doing it.
This allows businesses to be agile and innovative, testing new concepts safely within the digital twin supply chain software.
Use Cases of Supply Chain Digital Twin in Action
1) Automotive Industry
Car manufacturers are using digital twins to manage global component sourcing, simulate assembly line efficiencies, and forecast demand shifts due to regulatory changes or fuel prices.
2) Retail and eCommerce
Retailers use digital twins to model seasonal spikes, optimize warehouse locations, and align marketing campaigns with product availability in real time.
3) Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical supply chain demands strict temperature control and regulatory compliance. A digital twin supply chain helps ensure product integrity, especially in vaccine distribution.
Technologies That Power Digital Twins
Several technologies enable the successful implementation of digital twins in supply chain simulations:
- Internet of Things (Iot): Provides real-time tracking of goods, machinery, and vehicles.
- AI & Machine Learning: Analyses data patterns, predicts disruptions, and suggests optimisations.
- Cloud Computing: Ensures seamless data integration and accessibility across global operations.
- Blockchain: Adds transparency and security to supply chain transactions.
When these technologies converge within a digital twin supply chain, companies gain unmatched foresight and control.
Challenges and Considerations
Every new technology has its merits and demerits. Here are a few digital twin challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Setting up a digital twin infrastructure requires substantial investment in sensors, software, and skilled talent.
- Data Accuracy: A digital twin is only as good as the data it receives. Inaccurate data can create wrongful simulations.
- Change Management: Employees need training and confidence to trust simulation-based decisions.
Despite these hurdles, the long-term ROI of a well-designed virtual supply chain far outweighs the setup costs, especially in industries with complex logistics and high stakes.
The Future of Digital Twins
As AI, Iot, and predictive analytics evolve, digital twins will become even more intelligent and autonomous. Without human intervention, we may soon see fully self-optimising supply chains that react in real time to global events.
The digital twin supply chain will not just simulate what might happen—it will recommend what should happen, and eventually take action on its own.
Conclusion
The complexity of modern supply chains demands a smarter, more adaptive approach. Digital twins offer a powerful way to simulate, analyse, and optimise every link in the chain. From minimising disruptions to improving sustainability, the digital twin supply chain is transforming how businesses plan and operate. Want a digital twin-based traceability solution to optimise your supply chain? Contact Qodenext today.
FAQS – Digital Twin Supply Chain
1. What is digital supply chain management?
Digital supply chain models are virtual counterparts of physical supply chain processes. They use real-time data to simulate and optimise logistics, inventory, production, and delivery systems.
2. How does a virtual supply chain improve efficiency?
It enables businesses to test different scenarios, predict outcomes, and adjust processes without disrupting real operations. This leads to faster decisions, reduced costs, and fewer errors.
3. Is implementing a digital twin expensive?
While initial setup costs can be high, the long-term benefits, like reduced downtime, better forecasting, and improved customer satisfaction, often outweigh the investment.
4. Can small businesses benefit from a digital supply chain?
Yes. Cloud-based digital twin solutions and third-party platforms make it accessible to smaller businesses, helping them compete more effectively with larger players.
5. What industries are using digital twins in their logistics networks?
Industries like automotive, retail, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and manufacturing are leading adopters of digital twin technology in their supply chains.
6. How many times should a digital twin be updated?
Ideally, a virtual supply chain should update in real time or near real time, using live data feeds from sensors, ERP systems, and external sources to stay accurate.