The world of manufacturing and warehousing is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by automation, data, and digital connectivity. One of the technologies at the heart of this change is RFID technology. Once seen as futuristic, RFID is now a proven tool that is helping companies boost efficiency, cut costs, and improve accuracy across operations. From tracking raw materials to streamlining shipping, RFID is reshaping how industries work.In this blog, we’ll dive into what is RFID technology, explore its role in manufacturing and warehousing, look at RFID examples, discuss RFID advantages and disadvantages, and even touch on how RFID technology in IoT is creating smarter supply chains.
What is RFID Technology?

RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. It is a wireless technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects automatically. Think of it as a smarter version of barcodes, but without the need for line-of-sight scanning.An RFID system generally consists of three components:
- RFID Tags – Tiny chips with antennas that store data and transmit it.
- RFID Readers – Devices that send out radio signals and capture data from tags.
- Software/Database – Where the collected information is processed and managed.
Unlike barcodes that need manual scanning, RFID tags can be read automatically, in bulk, and from a distance. This makes them highly valuable in fast-moving and complex environments like factories and warehouses. Therefore, RFID in omnichannel fulfilment steps in as a game-changer. By giving retailers the ability to track inventory with precision and speed
RFID Technology in Manufacturing: Smarter Production Lines
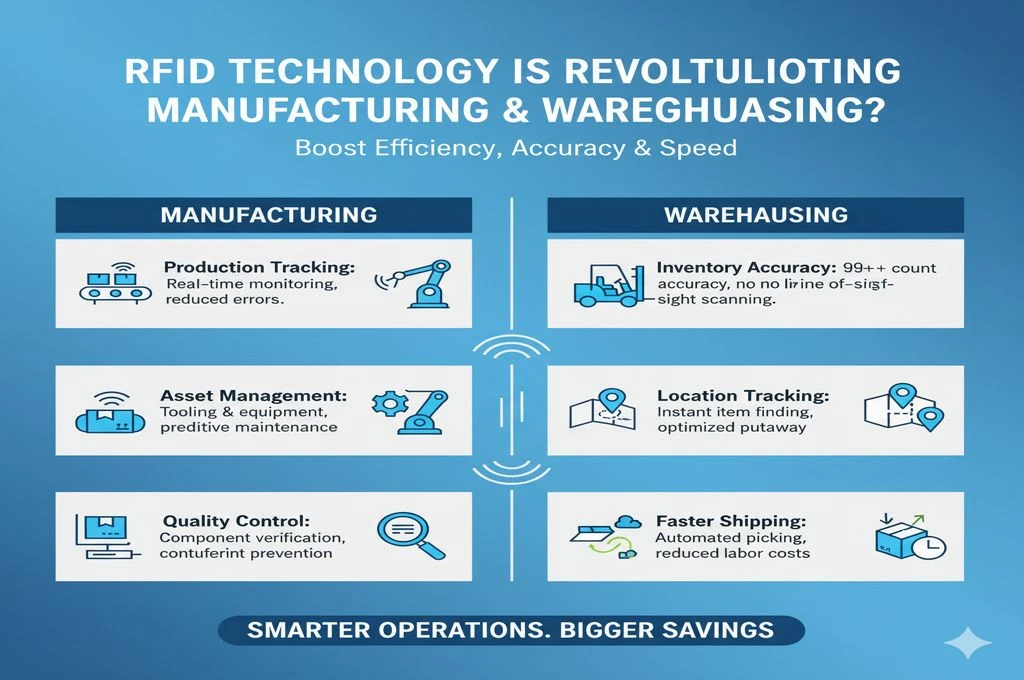
Manufacturing involves countless moving parts. From raw materials to finished products, the need for precision, speed, and accuracy is immense. RFID technology addresses these needs by providing real-time visibility and automation.Here’s how RFID is transforming manufacturing:
- Raw Material Tracking: RFID tags attached to materials help ensure that the right inputs are available when needed.
- Work-in-Progress Monitoring: As products move along the assembly line, RFID readers automatically update their status.
- Tool Management: Expensive tools can be tagged, reducing theft and ensuring timely calibration.
- Quality Control: Automated identification helps reduce human errors, ensuring products meet strict standards.
RFID examples in manufacturing include companies like Ford and Boeing, which use RFID to track components during production, reducing bottlenecks and improving efficiency.
RFID Technology in Warehousing: Smarter Inventory and Logistics
Warehouses act as the nerve centers of supply chains. Efficiency here directly impacts delivery timelines and customer satisfaction. RFID is making warehouses smarter and more agile.Here’s how RFID technology revolutionizes warehousing:
- Automated Inventory Counts: RFID readers can scan hundreds of items in seconds, reducing manual labor.
- Real-Time Location Tracking: Tags help identify the exact location of pallets, bins, or products inside large facilities.
- Error Reduction: RFID ensures the right products are picked, packed, and shipped, minimizing costly mistakes.
- Faster Returns Handling: Returned goods can be processed quickly as RFID instantly verifies product details.
RFID examples in warehousing include Amazon, which uses RFID-enabled robots and systems for precise inventory management, and Walmart, which applies RFID to streamline stock checks and replenishment.
RFID Technology in IoT: Building Smarter Systems
One of the most exciting applications of RFID is its integration with the Internet of Things (IoT). By combining RFID technology with sensors, cloud platforms, and analytics, businesses are creating hyper-connected ecosystems.
How RFID technology in IoT works:
- Connected Devices: RFID tags communicate with IoT platforms to provide continuous visibility.
- Predictive Analytics: Data from RFID can be analyzed to forecast demand, detect inefficiencies, and prevent equipment failures.
- Automation: Smart systems trigger actions automatically—for example, reordering raw materials when stock runs low.
Together, RFID and IoT are laying the foundation for “smart factories” and “intelligent warehouses.”
RFID Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any technology, RFID has strengths and limitations. Understanding both sides helps companies decide how best to use it.Advantages:
- Speed and Efficiency: Read hundreds of items simultaneously without line-of-sight.
- Accuracy: Reduces human error in data entry and inventory tracking.
- Durability: RFID tags are more durable than paper barcodes.
- Scalability: Works well for both small warehouses and large manufacturing plants.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: RFID tags and readers are more expensive than traditional barcodes.
- Privacy Concerns: Unauthorized tracking of tagged items is a potential risk.
- Interference: Metal surfaces or liquids can sometimes disrupt signals.
- Complexity: Integration with existing systems may require expertise and investment.
RFID Examples Across Industries
While manufacturing and warehousing are major users, RFID technology is making waves across industries:
- Retail: Zara and Decathlon use RFID to improve stock visibility and enhance customer shopping experiences.
- Healthcare: Hospitals use RFID to track medical equipment, supplies, and even patients.
- Automotive: Car makers use RFID for assembly line efficiency and tracking spare parts.
- Logistics: FedEx and UPS employ RFID for package tracking and route optimization.
These RFID examples highlight the versatility and impact of the technology.
Key Challenges in RFID Adoption
Despite its benefits, RFID adoption faces challenges:
- Initial Investment: Setting up RFID infrastructure requires upfront costs.
- Integration Issues: Compatibility with legacy systems can be complex.
- Data Overload: Managing and analyzing the vast amount of data generated by RFID systems can be overwhelming.
- Training Requirements: Employees need training to adapt to new workflows.
However, with costs reducing and technology improving, many of these barriers are becoming less significant.
At a Glance: How RFID Transforms Manufacturing & Warehousing
| Area | RFID Application | Benefit |
| Manufacturing | Work-in-progress tracking | Real-time visibility and efficiency |
| Warehousing | Automated inventory counts | Faster, more accurate stock checks |
| Logistics | Shipment tagging | Better traceability and accountability |
| IoT Integration | Smart automation | Predictive insights and automation |
Conclusion
As RFID merges with AI, blockchain, and IoT, its future looks promising. Imagine factories where every part self-reports its status, or warehouses where items guide workers to their exact location. These possibilities are closer than ever, and RFID is at the center of this evolution.In short, RFID technology is not just improving processes – it’s redefining how industries think about efficiency, transparency, and connectivity.
FAQs
Q1. How does RFID Technology differ from barcodes?
Barcodes need line-of-sight scanning, while RFID tags can be read remotely and in bulk.
Q2. Can RFID be reused?
Yes, passive RFID tags can be reused, making them cost-effective over time.
Q3. What industries benefit most from RFID?
Retail, logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive are top beneficiaries.
Q4. Is RFID secure for sensitive applications?
Yes, RFID can be secured with encryption and authentication to prevent misuse.
Q5. Does RFID work in harsh environments?
Specialized rugged RFID tags are designed for extreme temperatures, moisture, and chemicals.







