
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of global business, staying ahead in Supply Chain Management (SCM) Best practices is imperative. As we approach 2024, the importance of implementing robust strategies cannot be overstated. This article delves into the essential best practices, encompassing logistics, the three stages of SCM, and emerging trends that will shape the industry.
Supply Chain and Operations Management
Supply chain risk management is not only the key to business survival, it also is a good business practice that will help keep a business healthy. Good logistics management enables timely deliveries and cost efficiency.
- Supply chain risk management enables organizations to better prepare for global uncertainties.
- Logistics management plays a critical role in the flow of a product and satisfaction of the customer.
- The combination of supply chain risk management and logistics management, creates sustainable resilience, minimizes disruptions at the network level and thereby ensuring seamless flow.
Best Practices In Logistics And Supply Chain Management
The orchestration of logistics and supply chain management is instrumental in facilitating the seamless movement of goods and services from producers to end-users. The integration of optimal approaches is imperative for maximising efficiency, minimising costs, and elevating overall customer satisfaction.
1. Defining Optimal Approaches:
Optimal approaches in logistics and supply chain management (scm) refer to the most efficient and effective methodologies adopted by organizations to streamline their operations comprehensively. These encompass a spectrum of components, including procurement, transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and distribution.
2. Strategic Supplier Partnerships:
Fostering robust relationships with suppliers forms the bedrock of effective supply chain management (scm). Organizations should prioritize collaborative partnerships, transparent communication, and periodic assessments of supplier performance. Maintaining an open dialogue aids in swiftly addressing any issues that may arise.
3. Incorporation of Advanced Technologies:
Harnessing cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, data analytics, and blockchain significantly enhances logistics and supply chain management. Real-time visibility, optimized route planning, and precise demand forecasting are outcomes of integrating such technologies into daily operations. This integration is pivotal for heightened efficiency and error reduction.
4. Effective Inventory Optimization:
Maintaining optimal inventory levels is critical for minimizing holding costs and preventing stockouts. The adoption of inventory management systems utilizing demand forecasting and real-time data aids organizations in striking the right equilibrium between supply and demand, thus reducing excess inventory and associated costs.
5. Adoption of Sustainable Practices:
Embracing sustainable practices is gaining prominence in logistics and supply chain management. Companies can curtail their environmental footprint by optimizing transportation routes, implementing eco-friendly packaging, and selecting environmentally conscious suppliers. Beyond the environmental benefits, embracing sustainability enhances brand reputation.
6. Optimal Approaches Keyword Placement:
Now, let’s underscore the significance of consistently applying optimal approaches in logistics and supply chain management. These approaches contribute holistically to an organisation’s success, providing a competitive edge through operational excellence and meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
7. Continuous Process Enhancement:
Regular scrutiny and refinement of processes are essential for maintaining agility in a dynamic business environment. The implementation of continuous improvement methodologies, such as Six Sigma or Lean Management, aids in identifying inefficiencies, reducing waste, and refining overall supply chain performance.
8. Cross-Functional Synergy:
Fostering collaboration between different departments within an organization, such as procurement, logistics, and marketing, promotes a comprehensive approach to supply chain management. Cross-functional collaboration ensures decisions are made with a thorough understanding of the entire supply chain, leading to well-informed and effective choices.
The adoption of optimal approaches in logistics and supply chain management is imperative for organizations aiming to cultivate resilience and competitiveness in the contemporary business landscape. Strategic supplier partnerships, incorporation of advanced technologies, effective inventory optimization, adoption of sustainable practices, continuous process enhancement, and cross-functional synergy collectively contribute to creating a resilient and responsive supply chain. By incorporating these optimal approaches, companies can amplify operational efficiency, curtail costs, and ultimately deliver enhanced value to their customers.
3 Stages Of Supply Chain Management
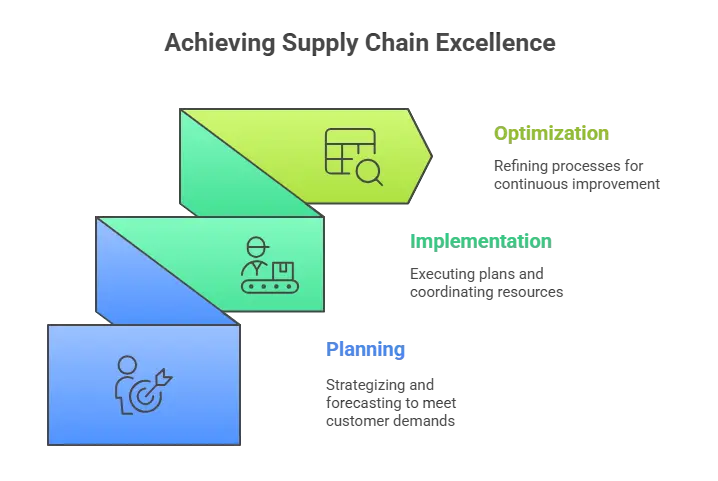
Supply Chain Management (SCM) stands as a linchpin for the triumph and efficiency of businesses operating across diverse industries. It orchestrates a network of processes that ensures a seamless flow of goods and services from the initial production stage to the final delivery to customers. Grasping the intricacies of the three foundational stages of supply chain management is indispensable for businesses aiming to optimise their operations and bolster overall performance.
Stage 1: Planning
In the inaugural phase of supply chain management, the spotlight shines on strategic planning. This stage involves formulating a comprehensive strategy that aligns with the organisation’s overarching goals. Key considerations encompass demand forecasting, judicious resource allocation, and adept risk management. Strategic planning enables organisations to streamline production processes, cut down costs, and respond nimbly to market dynamics. The seamless exchange of information within the organisation and with external partners is paramount during this planning stage of supply chain management.
Stage 2: Implementation
Once the planning stage concludes, the focal point shifts to implementation. This phase involves translating the devised strategies into actionable steps. This includes the procurement of raw materials, manufacturing, logistics, and distribution. Effective communication and collaboration with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors are imperative to ensure a smooth flow of goods through the supply chain. The integration of advanced technologies, such as blockchain and RFID, can elevate visibility and traceability, thereby minimising the likelihood of errors and delays.
Stage 3: Optimization
The optimization stage constitutes an ongoing process of refining and enhancing the supply chain based on performance data and market feedback. Continuous monitoring, analysis, and adaptability are key tenets of this phase. Businesses must harness the power of data analytics to pinpoint areas for improvement, enhance efficiency, and curtail costs. This stage also involves nurturing robust relationships with partners, exploring innovative technologies, and fostering agility to adapt to evolving market conditions. By consistently optimising the supply chain, organisations can fortify their competitiveness and resilience in a dynamic business environment.
The three stages of supply chain management – strategic planning, implementation, and optimization – stand as pivotal components contributing to the triumph of businesses in today’s fiercely competitive landscape. By placing emphasis on effective communication, leveraging cutting-edge technology, and embracing a mindset of continuous improvement, organisations can construct robust and agile supply chains that adeptly meet the demands of the modern market.
New Trends In Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) stands at the forefront of innovation, with dynamic shifts continually shaping its landscape. In recent times, a slew of groundbreaking trends has emerged, reshaping conventional SCM practices. This exploration into novel methodologies reveals a transformative journey marked by technological advancements and strategic shifts.
1. Blockchain Integration:
One of the most disruptive elements making waves in contemporary SCM is the seamless integration of blockchain technology. This decentralised ledger system not only fortifies security but also enhances transparency and traceability across the entire supply chain. The emphasis on blockchain technology mitigates the risks associated with fraud and ensures the authenticity of products, fostering consumer trust.
2. Sustainability and Green Practices:
In response to an escalating global emphasis on environmental consciousness, sustainability has become a cornerstone in SCM. Companies are actively embracing eco-friendly sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution practices. This paradigm shift involves harnessing renewable energy sources, implementing waste reduction initiatives, and adopting circular economy principles, aligning supply chain operations with broader environmental objectives.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Synergy:
The infusion of artificial intelligence into SCM processes has catalysed a paradigm shift, particularly in forecasting, demand planning, and inventory management. AI algorithms, leveraging vast datasets, empower businesses to predict market trends, optimise inventory levels, and streamline logistics. This not only reduces costs but also amplifies overall operational efficiency, providing a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
4. Resilience as a Core Tenet:
The unprecedented challenges brought forth by the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in traditional supply chain models, prompting a renewed focus on resilience and adaptability. Companies are strategically investing in technologies and methodologies that enable swift adaptation to disruptions, be they caused by natural disasters, geopolitical events, or global health crises. The overarching goal is to ensure continuous operations and minimise the impact of unforeseen disruptions on the supply chain.
5. The Pervasive Influence of 3D Printing:
Additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as 3D printing, is revolutionising traditional manufacturing processes. This technology facilitates on-demand production of parts and components, mitigating the need for extensive warehousing and logistics. Integrating 3D printing into SCM not only enables flexible and efficient production but also leads to substantial cost savings and a diminished environmental footprint.
6. Emerging Paradigms in Supply Chain Management:
As we navigate the uncharted waters of emerging SCM trends, it is abundantly clear that these innovations are reshaping the industry’s landscape. Whether through blockchain integration, sustainability initiatives, AI synergies, or resilience-focused strategies, companies that embrace these paradigm shifts are positioned for competitive advantage.
The dynamic nature of SCM demands an acute awareness of emerging trends for sustainable growth and success. The integration of blockchain, the focus on sustainability, AI augmentation, resilience-building, and the adoption of 3D printing are pivotal factors propelling the evolution of SCM practices. Companies that adeptly leverage these trends will not only navigate the complexities of the modern supply chain landscape but will also emerge as trailblazers in a rapidly transforming industry.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, as businesses gear up for the challenges of 2024, implementing these supply chain management best practices is paramount. Stay ahead, stay agile, and secure success in your supply chain endeavours. This article is brought to you by Qodenext, empowering businesses with innovative solutions for a seamless supply chain future.
FAQs:
1. What are the key best practices in logistics and supply chain management?
Logistics and supply chain best practices involve optimizing technology, fostering collaboration, embracing sustainability, and implementing robust risk management strategies.
2. What are the three stages of supply chain management?
The three stages are planning, production, and delivery. Each stage plays a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain.
3. What new trends can be expected in supply chain management in 2024?
Emerging trends include increased adoption of AI and analytics, a focus on sustainability, and a shift towards circular economy principles.
4. How can technology optimization benefit supply chain management?
Technology optimization enhances visibility, facilitates real-time decision-making, and improves overall operational efficiency in supply chain management.
5. Why is collaboration crucial in supply chain management?
Collaboration fosters efficient communication, reduces lead times, and helps in creating a more responsive and resilient supply chain.
6. How does risk management contribute to supply chain resilience?
Risk management identifies potential disruptions and establishes contingency plans, ensuring the supply chain can adapt and recover quickly.
7. Why is continuous training important in supply chain management?
Continuous training ensures that the workforce is equipped with the latest skills and knowledge, enabling them to adapt to new technologies and industry changes.







