
When COVID-19 hit, “supply chains” suddenly became everyone’s favorite topic but for entrepreneurs like you, launching a new product means discovering just how vital these invisible networks really are. Imagine your team: the dreamer with a sketchbook full of wild ideas, the logistics wizard who can find a shipping container in a blizzard, the customer whisperer who knows exactly what people want before they do, and the tech guru who automates everything but still can’t fix the office coffee machine. Together, you’re not just building a product you’re building a way to get it into the hands of customers, no matter what the world throws your way.
The pandemic shone a spotlight on supply chain chaos, but it’s not the only villain in the story. There were also those headline-grabbing trade tensions with China, unexpected shortages, and the ever-present question: “Will people still want this next week?” For your team, getting supply chains right isn’t just about making money it’s about being nimble, creative, and resilient, ready to pivot when the latest challenge arrives.
Defining Supply Chain
Imagine supply chain management strategy as the roadmap guiding a treasure hunt from the hidden chest of raw materials to the eager hands of customers, all while dodging obstacles and navigating twists and turns.
It’s like a well-thought-out game plan for orchestrating the journey of goods, from their humble beginnings to their grand finale. Picture it as a clever strategy, plotting the best routes, optimizing resources, and ensuring smooth sailing through production, storage, and delivery.
Whether it’s slashing costs like a savvy shopper, speeding up processes like a race car driver, or ensuring quality like a master craftsman, this strategy keeps the adventure exciting and the customers satisfied, creating a win-win for everyone involved.
Importance of a Supply Chain Strategy
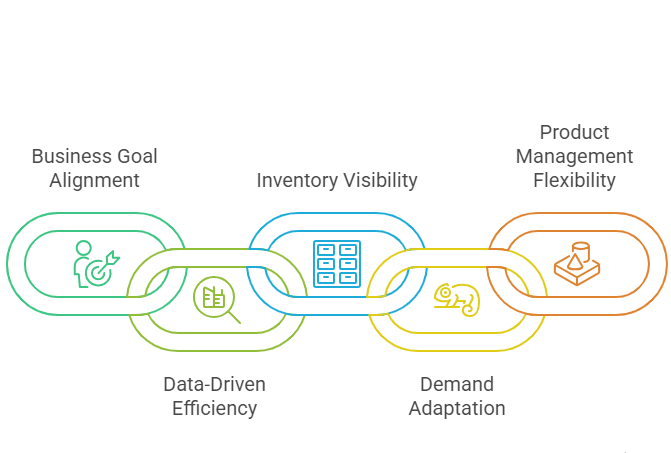
1. Supporting Your Business Goals
To achieve your business goals, it’s crucial to understand what you need from your vendors and distributors. Start by tracing how your products move from suppliers to customers. Consider hiring a consultant if it’s too complex. Map out the flow, considering factors like availability, quality, delivery times, and cost.
2. Harnessing Historical Data for Efficiency
Understanding where your company has been helps determine where it should go. Analyze past supplier performance to predict future reliability. Historical data aids in inventory management, enhancing forecasting accuracy and identifying cost trends for better budgeting.
3. Ensuring Inventory Visibility
Cloud-based technologies offer real-time visibility of inventory across the supply chain. Systems like POS, warehouse, inventory, and logistics management solutions facilitate tracking from vendor warehouses to customer delivery. This end-to-end visibility is essential for effective supply chain management.
4. Adapting to Changing Demand
Agile supply chain strategies prioritize flexibility and responsiveness. Cloud-based tools enable dynamic adjustments based on real-time data, allowing companies to swiftly respond to changing customer demands and market dynamics. This agility prevents missed opportunities and minimizes risks.
5. Facilitating Changes in Product Design or Management
Innovation is crucial for growth, but it must align with production capabilities and cost-effectiveness. A robust supply chain strategy ensures product designs optimize manufacturability and long-term supply. Early decisions in product development, informed by committed delivery rates and raw material prices, impact profitability and success.
Types of Supply Chain Management Strategies
There are four main types of supply chain management strategies, let’s look at them together!
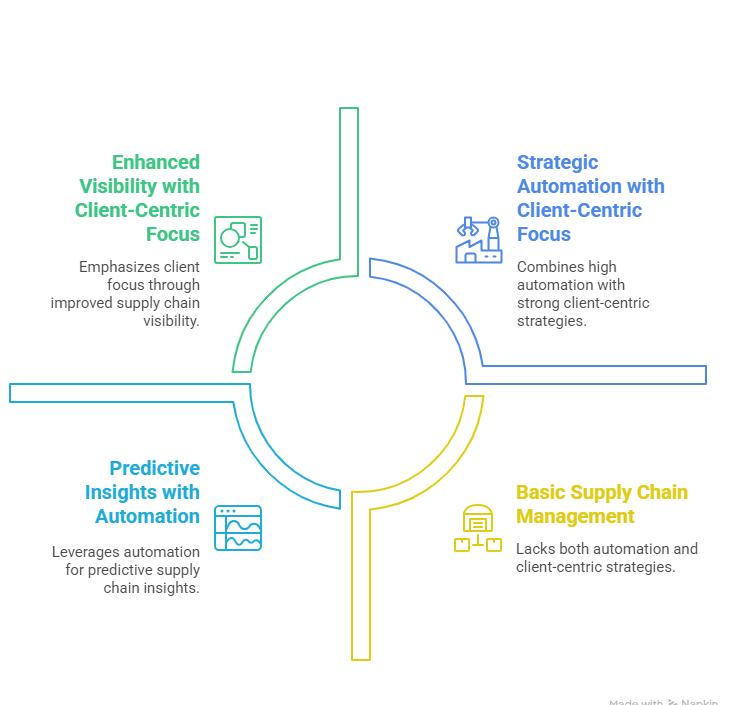
1. Client-Centric Focus
Meeting client demand is a top priority in supply chain management, especially in today’s digital age. Automating processes that prioritize client needs is essential. Real-time forecasting with diverse data, like sentiment analysis and social media, enhances understanding, improving decision-making and performance.
2. Predictive Insights
Predictive tools anticipate and adjust shipments based on factors like weather and traffic. Leveraging digital twins enables comprehensive network management, providing full visibility of assets, products, and equipment through IoT sensor integration. This insight helps preempt disruptions and meet customer needs effectively.
3. Enhanced Visibility
Supply chain visibility provides real-time insights into goods, enabling analysis of factors like weather and traffic disruptions to optimize sales. Enhanced collaboration across industries, partners, and distribution centres boosts efficiency, streamlines transactions, and promotes sustainability in the global supply chain.
4. Strategic Automation
Smart automation strategies optimize warehousing solutions to enhance processes involving systems, human workers, and robots. This approach enables benefits like mass product customization, streamlined delivery, distribution processes, and flexibility to minimize carrying costs.
Effective Supply Chain Management Strategies
Here are two brilliant examples of strategic supply chain management, make sure to read the entire analysis!
1. Unilever – CPFR Strategy
In the early 2000s, Unilever revamped its supply chain management as part of a five-year growth strategy. By prioritizing governance, global procurement, supplier engagement, and technology adoption, Unilever saved $14.24 billion and became a technology leader in the consumer goods industry.
Unilever implemented the Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR) strategy to optimize logistics and achieve growth goals. By consolidating warehouses into five hubs and forming CPFR agreements with retail partners, Unilever increased asset utilization, reduced inventory, and improved efficiency.
Improved communication between producers and retailers was key for enhancing forecast accuracy, especially in a volatile environment. This led Unilever’s logistics department to strengthen partnerships with retailers, resulting in better forecast accuracy and more efficient promotion management.
Key takeaways from Unilever’s success include a 10% boost in forecast accuracy, a 10% drop in inventory holding, and a 5% rise in sales volume from its CPFR strategy.
2. Walmart – Strategic Vendor Relations and Cross-Docking
Over the past two decades, Walmart has emerged as a retail leader with the highest sales per square foot, transitioning from a regional store to a global powerhouse. Central to its success is a streamlined supply chain, driven by the imperative to fulfil customer demands swiftly while maintaining low prices.
Walmart’s supply chain strategy revolves around strategic sourcing and forming long-term alliances with vendors to ensure competitive pricing. By fostering robust communication networks with suppliers, Walmart has optimized material flow and reduced inventory levels, creating a seamless global network akin to a single entity.
At the core of Walmart’s efficiency lies cross-docking, a logistics tactic that minimizes inventory and transportation costs while expediting product replenishment. This strategy has contributed to a remarkable 16% reduction in out-of-stock occurrences.
Emulating Walmart’s approach, businesses can harness strategic vendor partnerships and implement cross-docking to access new markets, enhance operational efficiency, and drive cost savings in inventory management and transportation.
Advantages of Strategic Supply Chain Management
1. Enhanced Supplier Collaboration
Close collaboration with suppliers is vital for businesses with tight margins. Negotiating fair raw material prices and maintaining long-term relationships offer flexibility during market volatility, averting profit squeezes and providing support during cash flow challenges.
2. Improved Quality Control
Aligning with suppliers on quality standards facilitates early detection and resolution of quality control issues. Open communication enables swift responses to deviations, preventing potential disruptions and fostering trust-based relationships.
3. Streamlined Shipping
Optimizing shipping processes through consolidated distribution channels and logistics specialists can mitigate rising logistics costs. By reducing the number of suppliers and leveraging storage and shipping aggregators, businesses can enhance cost efficiency and maintain strong cash flow.
4. Reduced Inventory and Overhead Costs
Efficient supply chains minimize inventory needs, thereby cutting storage and security overheads. However, striking a balance is crucial to avoid excessive lean inventory, ensuring resilience to supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, strategic supply chain management plays a pivotal role in the success of businesses, especially in navigating challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic and global trade disruptions.
By prioritizing collaboration, quality control, streamlined shipping, inventory optimization, and risk mitigation, companies can achieve resilience, efficiency, and agility in their operations. Embracing strategies like those of Unilever and Walmart can lead to improved forecasts, lower inventory, and higher sales.
To embark on this transformative journey, businesses can leverage the expertise and support of organizations like Qodenext, empowering them to thrive in dynamic market landscapes.
FAQs: Why Strategic Supply Chain Management is Important
1. What are the disadvantages of supply chain management?
Disadvantages of supply chain management include increased complexity, potential for disruptions, and reliance on external partners. However, effective management can mitigate these risks.
2. What is sourcing in supply chain management?
Sourcing in supply chain management involves selecting suppliers and acquiring materials or services necessary for production, aiming for cost-effectiveness and quality.
3. What are pricing strategies in supply chain management?
Pricing strategies in supply chain management include cost-based, value-based, and competition-based approaches, balancing profitability with market demand and competitive positioning.
4. What are competitive supply chain strategies?
Competitive supply chain strategies focus on differentiation, cost leadership, or focus, aligning supply chain activities to gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
5. What is strategic supply chain management?
Strategic supply chain management is the process of aligning long-term supply chain decisions with an organization’s overall business goals and vision. It involves making high-level choices about how the supply chain will operate—such as selecting suppliers, designing logistics networks, and setting performance standards—to support the company’s growth, competitive advantage, and customer satisfaction. This approach ensures that all supply chain activities are optimized for efficiency, cost reduction, quality, and resilience, ultimately delivering value to both customers and investors
6. What is supply chain strategy example?
A supply chain strategy example is a company deciding to source raw materials from multiple suppliers in different countries to reduce the risk of disruption. Another example is a retailer implementing a demand-driven supply chain by using real-time sales data to quickly adjust inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstocking. These strategies help businesses remain flexible, responsive, and competitive in changing markets
7. What are the 3 types of supply chain strategies?
The three main types of supply chain strategies are:
- Lean strategy: Focuses on minimizing waste and reducing costs by streamlining processes and maintaining only necessary inventory.
- Agile strategy: Prioritizes flexibility and quick response to changing customer demands or market conditions.
- Hybrid (or leagile) strategy: Combines elements of both lean and agile approaches, using lean methods for stable demand and agile tactics for volatile or unpredictable segments.
8. What are the 7 C’s of SCM?
While the “7 C’s of SCM” is not a universally standardized concept in mainstream supply chain literature, some sources and consultants use a set of “C’s” to summarize key principles. Commonly referenced “C’s” include: Collaboration, Coordination, Communication, Customer focus, Cost management, Cash flow optimization, and Continuous improvement. These principles emphasize working closely with partners, aligning activities, keeping customers at the center, managing costs and finances, and always striving for better performance. However, the exact list may vary by source and is less formalized than the 4 P’s of marketing or other frameworks.






