
In the modern fast digital world, new technology is something the companies are in constant search of to make business easier, increase security, and increase efficiency. RFID tags i.e. Radio Frequency Identification is one of the inventions that have transformed inventory management, asset tracking and identification systems. It is a small and powerful device that, at the heart of this technology is transforming industries around the world.
What Is RFID Tag Technology?
A RFID tag is a small electronic device consisting of a microchip and an antenna where the information is stored and transmitted wirelessly within radio waves. The intelligent tags are now invaluable in business operation as opposed to the traditional barcodes that require the use of the line-of-sight when scanning, the new tag can be read any distance without necessarily having a clear view of the tag, making it much more useful in business today.
So what is RFID tag technology? It is a system through which electromagnetic fields are used to easily capture and identify data automatically. The tag contains electronically stored information that can be read by compatible readers hence the exchange of data is smooth and in the real sense, does not involve human interference.
Important Components of an RFID Tag.
The standard RFID tag consists of three basic components:
– Microchip:
Contains identification information, which is unique, with additional useful information.
– Antenna:
Makes the interaction between the tag and the reader possible through radio frequency signals.
– Substrate:
This material is the material which wraps around the chip and antenna assembly, and provides protection to them.
Types of RFID Tags on Offer
Knowledge of the different kinds of RFID tag technology will help companies to identify which type of solution to use depending on their specific needs.
Passive RFID Tags
The most popular and the cheapest option today is the passive tags. These tags do not contain an internal power source, but rather only capture the energy of the electromagnetic field of an RFID tag reader. The most significant characteristics are:
– Does not require a battery, i.e. unlimited life span.
– Small and light size
– RFID tag cost is less as compared to active.
– Reading distance normally 1-10 meters
– Could be used in inventory tracking and access control.
Active RFID Tags
Active RFID tag systems contain their own source of power, usually a battery, so that they can send signals at a constant rate or at a fixed rate. The advantages are:
– Read range of up to 100 meters or more.
– Huge volumes of information can be stored.
– Capable of self transmission.
– The RFID tag is more expensive and more functional.
– Suited where high-value assets are to be tracked.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags
They are also known as battery assisted passive tags and assume both features. The circuitry of the chip is powered by battery power and communicated by reader signals such that there is a middle-ground approach with a balanced approach.
Technical Process in how RFID Tags Work.
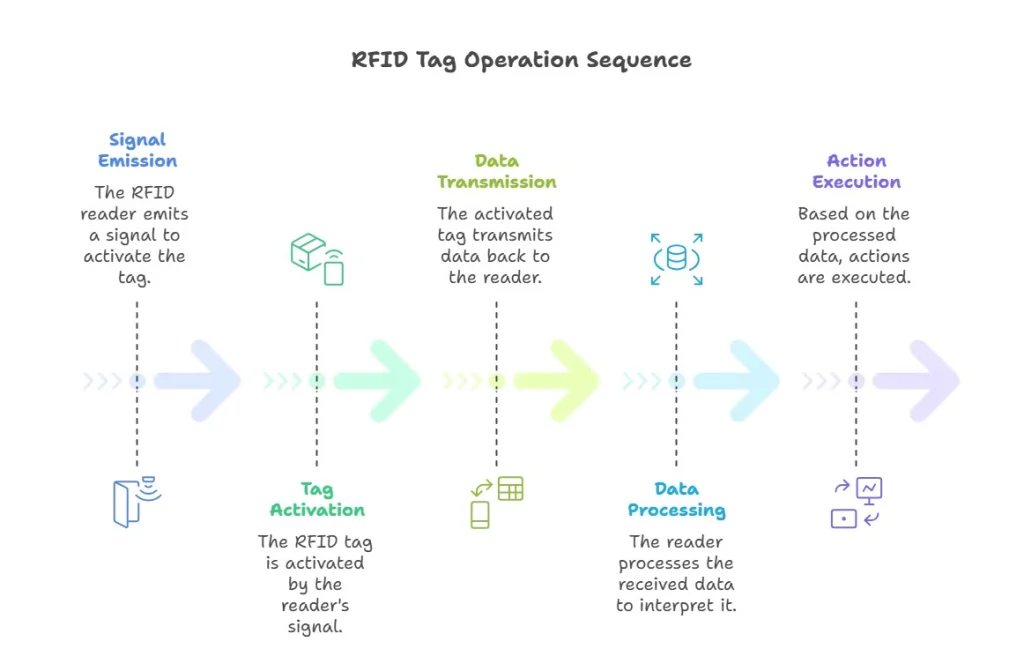
An RFID tag is a complicated, yet a rapid process:
1. Signal Emission: The RFID tag reader emits an electromagnetic field, through its antenna.
2. Tag Activation: Once an RFID tag is in the proximity of this field, it switches on (passive) or responds (active).
3. Data Transmission: The tag transmits the data it is holding back to the reader in radio waves.
4. Data Processing: The signal is transmitted to the reader who then transmits the data to a computer system to be processed.
5. Action Execution: It is a system that carries out pre-programmed actions based on information that it receives.
This entire process can occur in milliseconds and hence a number of tags can be scanned in a short period of time.
RFID Tag Frequency Ranges
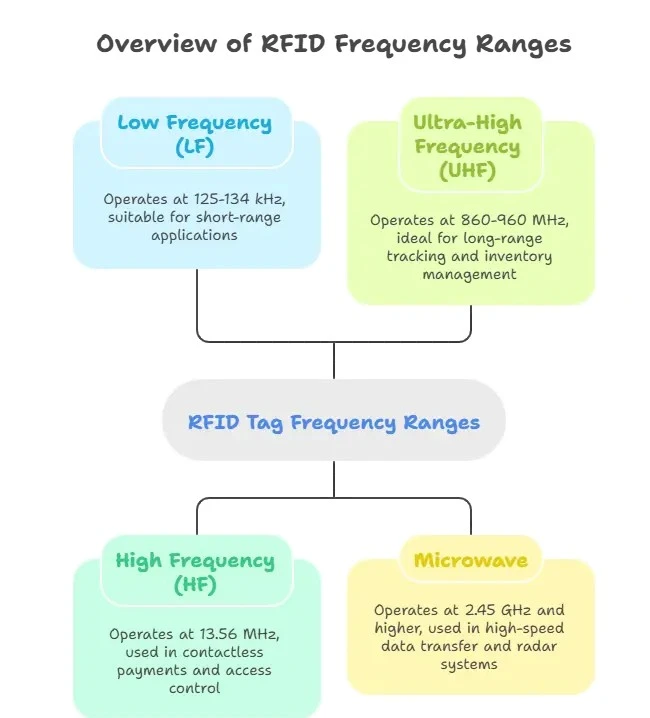
RFID tag systems operate on different frequency bands that are suitable to different applications:
Low Frequency (LF) – 125-134 kHz
– short reading range (10 cm)
– Large permeability of water and metal.
– To be used in animal tracking and access control.
High Frequency (HF) – 13.56 MHz
– Medium range of reading (up to 1 meter)
– Generally used in library applications and payment cards.
– Excellent working conditions in metal nearby.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) – 860-960 MHz
– Visual range (to 12 meters)
– Mass scanning at high speed.
– Widely used in retail and logistics.
Microwave – 2.45 GHz and higher
– Longest reading range
– Directional signals
-Used in vehicle toll systems.
Real-World RFID Tag Examples
The versatility of the technology can be explained by understanding some practical examples:
Inventory and Retail.
– Clothing labels: Fashion retailers place tags in clothes to deter theft as well as track their inventory.
– Product labeling: Smart shelves identify when products must be refilled.
– Loss prevention: Store exits: Electronic article surveillance.
Healthcare Applications
– Wristbands of patients: Proper administration of medication and identification of patient.
– Tracking of medical equipment: Find important instruments and equipment within seconds.
– Pharmaceutical authentication: Combat fake drugs with supply chain verification.
Transportation and Logistics
– Toll collection tags: Enables road and bridge contactless payment.
– Baggage monitoring: Luggage monitoring Airlines monitor the luggage throughout the way.
– Container shipping: Track cargo along global supply chains.
Access Control and Security
– Worker identifiers: Control access to the building and check attendance.
– Hotel key cards: Provide access to rooms without use of physical keys.
– Access control: Manage access to conferences and festivals.
Agriculture and Livestock
– Animal ear tags: Monitor livestock health, movement and mating information.
– Crop tracking: Farm to table produce tracking.
– Equipment management: Keep track of farm equipment and instruments.
The main advantages of RFID Tag Systems are as follows.
RFID tag technology revolutionizes the way business activities are conducted in that it allows automatic data collection and elimination of time-consuming manual procedures which are likely to introduce human error. Organizations achieve excellent rates of inventory accuracy of over 95 percent compared to traditional methods of only 65- 75 percent accuracy.
The technology enables scanning of various items simultaneously without the line of sight, which accelerates warehouse processes, checkout and shipment verification considerably. Real-time visibility of assets helps businesses reduce theft, minimize inventory shrinkage, and adjust their stocks optimally and reduce operating labor costs significantly.
Superior security measures like checking products and detecting tampering also help avoid forgery and keep regulatory requirements within the complex supply chains.
RFID tag technology gives organizations a number of benefits:
Operational Efficiency
– Automated collection of data: No further mistakes in manual scanning and data entry.
– Concurrent reading Read multiple tags simultaneously without line-of-sight.
– Reduction in manpower: Reduce the time required to count the inventory and asset audit.
– More processing: Enhance checkout, shipping and receiving.
Improved Accuracy
– Reduced human error: The automatic identification minimizes human errors during data capture.
– Real-time information: synchronize assets in terms of status and location.
– Accurate inventory: Achieve 95 percent or higher accuracy as compared to 65-75 percent using traditional methods.
Cost Savings
-Lower operation expense: minimize labor expense in the manual tracking.
– Less shrinkage: Less loss and theft through better visibility.
– Better inventory: Reduce stockout and overstock.
– Prolonged asset life: Scheduling of maintenance in time in accordance with automated monitoring.
Security and Compliance
– Authentication checking: Check the authenticity of the products and prevent counterfeiting.
– Chain of custody: Full history of product on record, also used in regulation.
– Access control: Restrict unauthorized access to sensitive locations.
– Tamper detection: Reference to whether tags have been tampered with or stolen.
Knowledge of RFID Tag cost Drivers.
The RFID tag price is very varied according to a number of factors:
Tag Function and Type
– Passive tags: $ 0.1 -2.00 per unit to simple applications.
– Active tags: $20 to $100+ based on functionality and run time.
– Special tags Ruggedized or sensor versions are sold at higher prices.
Volume Factors
Purchasing RFID tag inventory in bulk reduces the price per tag considerably. Those companies that buy thousands of tags or millions of tags benefit by economies of scale.
Customization Requirements
– Less expensive generic tags than customized tags with:
– Strengths Special factors that are optimized to a given application.
– Predefined information or bespoke printing.
– Environmentally-challenging materials.
– Temperature or moisture sensors embedded in them.
Total System Investment
the implementation of total cost has:
– RFID tag reader equipment and installation.
– Data management computer systems.
– Interaction with existing enterprise systems.
– Staff training
– periodic maintenance and support.
The choice of the Correct RFID Tag Reader.
Choosing an RFID tag reader is a process of matching the device capability with your business requirement and your business environment.
When permanent mounting is required, like at warehouse entrance, fixed readers are the best choice, but when flexibility is needed during inventory audits and mobile scanning operations, hand-held models are the ideal choice.
Vital considerations are the read range requirements, processing speed in detection of the tags concurrently as well as robustness in harsh conditions. Ensure that your preferred reader is also compatible with the existing software platforms like the inventory management, the ERP systems, and the data analytics programs.
Types of Readers
– Fixed readers: Fixed at a particular place like a door or conveyor belt.
– Handheld readers: Handheld variable scanning readers used in warehouses or on retail floors.
– On-board readers: Smart phone solutions installed on smart phones.
Performance Specifications
– Range of reading: Distance at which the reader is able to read tags.
– Reading rating: Tags read/s.
– Environment resistance: Strength in extreme circumstances.
– Connectivity possibilities: Transportation of data either over a cable or wireless.
Integration Capabilities
Be sure your RFID tag reader is easily compatible with:
– Software inventory management.
– enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
– Warehouse management software.
– Point-of-sale systems
Best Practices of Implementation.
A successful RFID tag implementation begins with a thorough examination of the specific operational problems and desired outcome of your company. To select the optimal type of tag and frequency, companies have to be very keen in analyzing the environmental conditions such as metal interference, liquid exposure, and reading distance requirements.
Perform a Comprehensive Needs Assessment.
– Establish specific pain points and objectives.
– Establish environmental requirements and read ranges required.
– Assess the existing infrastructure compatibility.
– Specify specific ROI indicators and performance indicators.
Begin with a Pilot Program
Prior to large-scale rollout:
– Test RFID tag operation under real-life working conditions.
– Become aware of potential issues in interference.
– Educate a simulation team on how to operate the system.
– Get feedback and refine processes.
Fight the Environmental Problems.
– Metal interference: There are materials that disrupt radio wave transmissions.
– Liquid absorption: Water-based products have the potential to weaken read effectiveness.
– Tag orientation Place tags to detect the maximum number of readers.
– Signal collision: Anti-collision protocols should be used in the case of a high density tag environment.
Ensure Data Security
– Use tags to store sensitive data which is encrypted.
– Apply access controls to reader systems.
– Upgrade firmware and security frequently.
– Meet data privacy laws
General Problems and Remedies.
Issue: Preliminary Investment Issues.
Solution: Estimate the total cost of ownership including labor savings, reduction in shrinkage and improvement in efficiency. The annual payback period of most organizations is 18-24 months.
Problem: Tag Reading Problems.
Solution: Do site surveys to identify sources of interference. Use appropriate tags types and frequencies in your specific environment and materials.
Difficulty: Complexity of Integration.
Resolution: Find adept system integrators with experience in both RFID tag technology, and the requirements of your business sector. The platforms with open APIs should get a high priority as they are easier to integrate with.
Challenge: Staff Resistance
Solution: Benefits should be communicated well, there should be comprehensive training and the staff should be part of the implementation process. Demonstrate how their work is made easier by the technology.
Future trends in RFID Tag technology
RFID tags are becoming tremendously smaller and yet have powerful performance capacity to be used in new applications. Internet of Things convergence is the integration of smart cities, self-driving vehicles and robotic factories into smart ecosystems.
New-generation tags are advanced sensors that monitor temperature, shock, humidity and GPS position in real-time.
The companies are developing sustainable and environmental friendly tags using biodegradable materials and recyclable components to reduce the environmental footprint. Artificial intelligence interprets RFID patterns of information to predict equipment failures, automatically optimize stocks and detect suspicious activity in real time.
Miniaturization
Tags are becoming smaller and smaller but still performing like they can, which enables new uses in areas that were not yet sufficiently served.
Internet of Things Integration.
This technology is becoming increasingly interconnected with the IoT platforms to create end-to-end ecosystems of smart cities, connected cars, and smart factories.
Better Sensor Technology.
Sensors are incorporated in future tags:
– Temperature monitoring of the cold chain logistics.
– Electronic identification of fragile products.
– Humidity monitoring of perishable products.
– GPS based location services.
Green Solutions
Manufacturers are producing greener labels that have:
– Biodegradable materials
– Less plastic content
– Recyclable patterns
– Reduced impact production.
Synergy of Artificial Intelligence.
The computer programs based on AI analyze the RFID tag pattern data to:
– Plan ahead to avoid failure.
– Automatically streamline stock levels.
– Identify suspicious activity that can result in theft.
– Personalise customer experience in retailing.
Industry-Specific Applications
Manufacturing
RFID tag systems will revolutionize shop floors by:
– Trace of work-in-progress on assembly lines.
– Tool and equipment control.
– Quality management at all levels of production.
– Supply chain replenishment by automation.
Libraries and Education
RFID tag examples used in educational institutions include:
– Checkout self-service saves on waiting time.
– Automated scan of books millions of books.
– Exit point theft prevention.
– Patron history management
Waste Management
RFID tag technology can be used with Smart cities in:
– tracking waste bin location and fill levels.
– Traffic optimise on actual demand.
– Bill by use assessed on the basis of usage statistics.
– Track recycling compliance
Compliance and Standards
Interoperability and regulatory compliance: Knowledge of standards applicable will ensure interoperability and regulatory compliance:
International Standards
– ISO 18000 Series: Air interface protocols at different range of frequencies.
– EPC Gen2: Widespread standard of UHF RFID tag systems.
– ISO 14223: Intended to be used in animal tracking.
– ISO 15693: Standards vicinity cards.
Privacy Regulations
When implementing RFID tag systems that are involved with personal data:
– Kenyon – compliant with GDPR in Europe.
– Compliant with the CCPA rules in California.
– Implement the principles of privacy-by-design.
– Provide data collection transparency.
Lifecycle Management and Maintenance.
To maximize the life of RFID tags systems, it requires:
Regular conduct of System Audits.
– Periodically check the performance of the reader and signal strength.
– Read rates of insure tags meet performance standards.
– Automatically update software and firmware.
– Antennas and equipment Cleaner.
Tag Replacement Strategies
– Measure passive RFID tag adhesive breakdown.
– Track active tag battery life and replacement.
– Have back stock of priority applications.
– Patterns of record tag failure to be improved upon.
Conclusion
RFID tags technology has an ever-evolving capacity of transforming how companies conduct business in all industries. The wireless identification system can deliver measurable value at every level of deployment whether it is reducing the cost of operation and improving precision or improving the customer experience and supporting new business models.
The uses will only grow as the technology further develops with even smaller sizes, greater capabilities, and more combined utilization with new technologies like AI and IoT.
Be it keeping things in stock at a store, supervising machines at a hospital or securing building access, RFID tag systems offers a proven, high-quality solution that has short-term and long-term benefits.
To businesses that are ready to get an RFID feeting wet, the partnership with more experienced tech companies is the difference between successful implementation and monetary disasters.
Qodenext offers end-to-end solutions that bring RFID concepts to life and ensure your investment is worth as much as it can be via experienced guidance, sound technology and ongoing assistance.
Most commonly asked questions (FAQs).
1. What is RFID tag and its functionality?
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag is a miniaturized device that can hold any information and transmit it over the radio waves. It is made up of a microchip (to hold information), and an antenna (to transmit data). Upon the issuance of a signal by an RFID reader, the tag will react and will transmit back the stored data. This is done wirelessly and without the line-of-sight. RFID tags are the devices that can be used to trace, identify and control objects effectively.
2. How much do RFID tags cost?
The RFID tags are of different costs depending on their type and functionality.
Passive tags: $0.05 to $0.50 (cheapest)
Active tags: $5 and up to or above the battery + increased range.
Semi passive tags: intermediate, as per characteristics.
Other factors that may influence the pricing are bulk orders and industry needs.
3. What are typical examples of RFID tags being used?
RFID tags are popular in different industries.
Retail: to monitor inventory and prevent theft.
Logistics: to monitor goods within a warehouse and during their transit.
Access control: Key fobs and ID cards to access security.
Healthcare: patient monitoring and IDs.
Such applications enhance speed, precision and automation in operations.
4. What is the way that an RFID reader recognizes tags?
RFID reader sends radio waves to energize and communicate with tags around it.
The tags all react to their own identifiers or stored information.
This data is captured by the reader and forwarded to software system to process it.
Depending on the system, various tags may be read at the same time.
There should be no direct contact and visual line between the reader and tag.
5. Which are the various forms of RFID tags?
The RFID tags can be largely divided by the source of power and the frequency:
Passive tags: no battery, reader signal powered.
Active tags: include a battery, extend their range.
Semi-passive (also battery-assisted passive): battery-powered chip, but reader activated.
There are also differences in tags by frequency: Low (LF), high (HF) and ultra-high frequency (UHF).
All the types are applicable to various applications and settings.
6. In what ways are RFID tags similar to barcodes?
RFID tags do not need line of sight as barcodes do.
RFID has the ability to read more than one item at a time; barcodes can only read a single item at a time.
Tags have the ability to hold more data than barcodes.
RFID is operable in extreme conditions (dust, moisture).
RFID systems are however costlier to institute as compared to barcode systems.
7. Is it possible to update RFID tags with new information?
Yes, it is, but only some kinds of RFID tags can be rewritten.
RFID writer can be used to update passive read/write tags.
Active tags also tend to have more memory and update data.
Rewritable labels can be applied in reusable containers or in the process of varying data requirements.
Certain tags are however read only and cannot be changed once it is coded.
8. Where are RFID tags used?
RFID tags find application in the following industries:
Retail: to monitor products and prevent theft.
Supply chain: to track the movements and location in real-time.
Healthcare: to monitor patients, drugs and equipment.
Security: with ID cards and access control systems.
Transportation: to collect tolls and control the fleet.






