In the realm of business operations, the procure-to-pay process stands as a cornerstone, facilitating the seamless flow of purchasing activities from procurement to payment. But what exactly is the procure-to-pay process? Let’s delve into its intricacies, steps, challenges, applications, and solutions to optimize your organization’s procurement journey.
What Is Procure To Pay
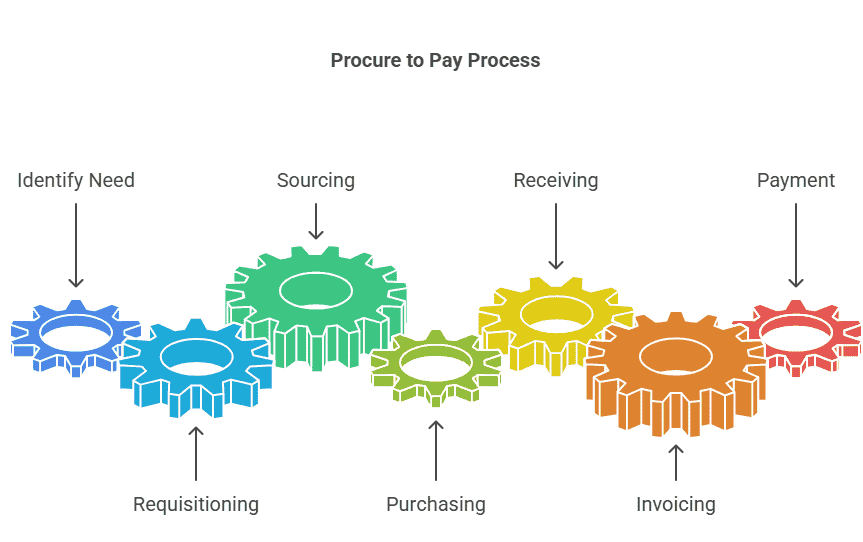
Procure to Pay (P2P) is a business workflow that manages the entire procurement lifecycle—from the initial identification of a need for goods or services to the final payment to suppliers. It encompasses requisitioning, sourcing, purchasing, receiving, invoicing, and payment, ensuring that every step is tracked, controlled, and optimized for efficiency and compliance.
At its core, P2P is designed to eliminate silos, reduce manual intervention, and provide end-to-end visibility across procurement activities. By centralizing and automating these processes, organizations can achieve greater control over spending, minimize risks, and foster stronger relationships with suppliers.
Definition of Procure to Pay:
At its core, Procure to Pay refers to the end-to-end process of acquiring goods or services, from the initial requisition to final payment settlement. It involves multiple steps, including sourcing suppliers, negotiating contracts, purchasing, receiving, invoicing, and payment.
Key Components of Procure to Pay Process:
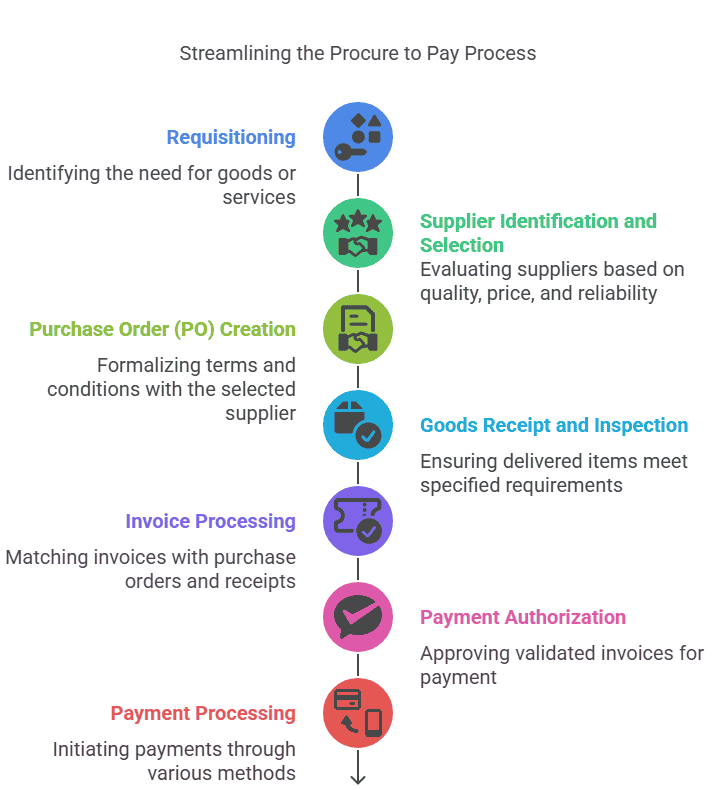
- Requisitioning: The process begins with identifying the need for goods or services within an organization. This involves creating purchase requisitions detailing the requirements.
- Supplier Identification and Selection: Once requisitions are approved, organizations identify potential suppliers through a sourcing process. Suppliers are evaluated based on various factors such as quality, price, delivery terms, and reliability.
- Purchase Order (PO) Creation: After selecting a supplier, a formal purchase order is generated outlining the agreed-upon terms and conditions, including quantities, prices, delivery dates, and payment terms.
- Goods Receipt and Inspection: Upon delivery of the goods or completion of services, the receiving department inspects the items to ensure they meet the specified requirements and match the purchase order.
- Invoice Processing: Suppliers submit invoices for the goods or services provided. These invoices are matched with the corresponding purchase orders and receipts to verify the accuracy of charges.
- Payment Authorization: Once invoices are validated, they undergo approval processes based on predefined workflows. Authorized invoices are then scheduled for payment within the agreed-upon terms.
- Payment Processing: Payments are initiated either through manual methods like checks or electronic methods such as electronic funds transfer (EFT) or automated clearinghouse (ACH) payments.
Benefits of Procure to Pay Process:
- Cost Savings: Streamlining procurement processes can lead to cost savings through better supplier negotiations, reduced maverick spending, and improved contract compliance.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of P2P processes eliminates manual errors, reduces processing time, and enhances overall efficiency.
- Improved Visibility and Control: P2P systems provide real-time visibility into procurement activities, enabling better tracking of spend, compliance monitoring, and risk management.
- Supplier Relationship Management: By establishing standardized processes and timely payments, organizations can strengthen relationships with suppliers, leading to better collaboration and improved supplier performance.
Challenges in Procure to Pay Process:
- Poor Data Quality: Inaccurate or incomplete data can hinder the efficiency of P2P processes, leading to errors, delays, and compliance issues.
- Compliance Risks: Non-compliance with procurement policies, regulatory requirements, or contractual obligations can result in penalties, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
- Integration Issues: Integrating disparate systems and technologies across procurement functions can pose challenges, impacting data flow, process visibility, and automation capabilities.
- Resistance to Change: Cultural resistance within organizations and reluctance to adopt new technologies or processes can impede the successful implementation of P2P initiatives.
Best Practices for Procure to Pay Process:
- Standardize Processes: Establish standardized procedures and workflows for procurement activities to ensure consistency, efficiency, and compliance.
- Leverage Technology: Invest in robust P2P software solutions that automate manual tasks, facilitate electronic document exchange, and provide analytics for informed decision-making.
- Implement Controls: Define clear authorization levels, segregation of duties, and approval workflows to mitigate fraud risks and ensure compliance with policies and regulations.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluate P2P processes, gather feedback from stakeholders, and identify opportunities for optimization and innovation to drive continuous improvement.
In conclusion, Procure to Pay is a critical business process that encompasses the entire procurement lifecycle, from requisitioning to payment settlement. By understanding its key components, benefits, challenges, and best practices, organizations can optimize their P2P processes to drive efficiency, cost savings, and strategic value creation.
Procure To Pay Process Steps
The procure to pay process (P2P) is a critical component of any organization’s operations, encompassing the steps from requisitioning goods or services to making payments to suppliers. It’s a structured approach that ensures efficient procurement, minimizes risks, and optimizes resource utilization. In this guide, we’ll delve into the key steps of the procure to pay process along with best practices to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
STEP 1: Requisitioning:
- The process begins with the identification of the need for goods or services within the organization.
- Departments or individuals initiate requisitions, detailing specifications, quantities, and desired delivery timelines.
- Requisitions are often routed through an approval workflow to ensure compliance with budgetary constraints and procurement policies.
STEP 2: Vendor Selection and Negotiation:
- Once requisitions are approved, the procurement team initiates vendor selection.
- This involves evaluating potential suppliers based on factors like price, quality, reliability, and past performance.
- Negotiations may occur to finalize terms and conditions, including pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms.
STEP 3: Purchase Order Generation:
- Upon vendor selection and agreement on terms, a purchase order (PO) is generated.
- The PO serves as a legally binding document outlining the details of the transaction, including item descriptions, quantities, prices, and delivery dates.
- It provides clarity and accountability for both the buyer and the supplier.
STEP 4: Receipt of Goods or Services:
- Upon delivery, the receiving department verifies the goods or services against the PO and packing slip.
- Any discrepancies or damages are noted, and necessary actions are taken, such as rejection of items or initiation of replacements.
STEP 5: Invoice Processing:
- Suppliers submit invoices for the delivered goods or services based on the terms agreed upon.
- Invoices undergo validation to ensure accuracy and compliance with the PO and contractual terms.
- Approved invoices are then entered into the accounting system for payment processing.
STEP 6: Payment Authorization:
- Once invoices are validated, payment authorization is obtained.
- This step involves verifying that the goods or services were received satisfactorily and that there are no outstanding issues or disputes.
- Authorized payments are scheduled based on agreed-upon terms, which may include early payment discounts to incentivize prompt settlement.
STEP 7: Payment Execution:
- Payments are executed through the organization’s chosen payment method, whether it’s electronic funds transfer (EFT), checks, or other forms of remittance.
- Timely execution of payments is crucial to maintaining strong supplier relationships and avoiding late payment penalties.
STEP 8: Supplier Performance Evaluation:
- Periodic evaluation of supplier performance is essential to assess adherence to contract terms, quality of goods or services, and timeliness of deliveries.
- Feedback gathered during evaluations informs future vendor selection decisions and helps drive continuous improvement in the procurement process.
Best Practices:
- Implement an integrated procurement system to automate and streamline P2P workflows, reducing manual errors and processing time.
- Establish clear procurement policies and guidelines to ensure consistency and compliance across the organization.
- Foster collaboration between procurement, finance, and other relevant departments to facilitate seamless information flow and decision-making.
- Leverage data analytics to gain insights into spending patterns, supplier performance, and opportunities for cost savings or process optimization.
- Regularly review and update vendor contracts to reflect changing business needs and market conditions.
- Encourage feedback from both internal stakeholders and suppliers to identify areas for improvement and address any issues proactively.
- Invest in supplier relationship management (SRM) initiatives to cultivate long-term partnerships based on trust, transparency, and mutual value creation.
The procure to pay process is a vital function that impacts the overall efficiency and profitability of an organization. By understanding the key steps involved and implementing best practices, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and drive value throughout the procurement lifecycle. Continuous improvement and collaboration across departments and with external partners are essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business environment.
Procure To Pay Applications
In today’s dynamic business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline their operations and enhance efficiency. One area that plays a pivotal role in achieving these objectives is the procurement process.
Procure-to-pay (P2P) applications have emerged as a crucial tool in modernizing and optimizing procurement processes, offering a seamless end-to-end solution from purchasing to payment. In this article, we delve into the significance of P2P applications, their key features, benefits, and considerations for implementation.
Understanding Procure-to-Pay Applications:
Procure-to-pay applications encompass a suite of software solutions designed to automate and streamline the entire procurement lifecycle. From requisitioning and purchasing to invoicing and payment, these applications integrate various stages of the procurement process into a unified platform. By digitizing traditionally manual processes, P2P applications offer organizations greater control, visibility, and efficiency in managing their procurement activities.
Key Features of Procure-to-Pay Applications:
- Requisition Management: P2P applications facilitate the creation and approval of purchase requisitions, ensuring compliance with organizational policies and budgetary constraints.
- Supplier Management: These applications centralize supplier information, enabling organizations to evaluate vendor performance, negotiate contracts, and maintain supplier relationships effectively.
- Purchase Order (PO) Automation: P2P applications automate the generation and routing of purchase orders, reducing the cycle time for procurement transactions and minimizing errors associated with manual entry.
- Invoice Processing: With built-in invoice matching capabilities, P2P applications streamline the verification and approval of supplier invoices against corresponding purchase orders and receipt documentation.
- Payment Processing: From electronic funds transfer to virtual card payments, P2P applications offer flexible payment options while enforcing payment terms and facilitating reconciliation with accounting systems.
Benefits of Procure-to-Pay Applications:
- Cost Savings: By optimizing procurement processes and negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, organizations can realize significant cost savings through reduced maverick spending and improved contract compliance.
- Operational Efficiency: P2P applications eliminate manual tasks, such as data entry and paper-based approvals, allowing procurement teams to focus on strategic activities that add value to the organization.
- Enhanced Visibility: Real-time dashboards and reporting functionalities provide stakeholders with visibility into procurement performance, supplier relationships, and spending patterns, enabling informed decision-making.
- Compliance and Risk Mitigation: By enforcing policy adherence and audit trails, P2P applications help mitigate compliance risks associated with regulatory requirements and internal controls.
- Supplier Collaboration: Collaborative features within P2P applications foster transparency and communication between buyers and suppliers, leading to improved collaboration and better alignment of business objectives.
Considerations for Implementation:
- Organizational Readiness: Assessing the readiness of stakeholders and existing processes is crucial before implementing a P2P solution to ensure smooth adoption and integration.
- Scalability: Choose a P2P application that can scale with your organization’s growth and evolving business needs, accommodating changes in transaction volume and complexity.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing ERP systems, accounting software, and other procurement tools is essential for maximizing the benefits of a P2P solution.
- User Training and Support: Invest in comprehensive training programs and ongoing support to empower users and drive user adoption across the organization.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluate and refine P2P processes to identify areas for improvement and leverage new technologies and best practices to optimize performance.
Procure-to-pay applications play a pivotal role in modernizing procurement operations, offering organizations a comprehensive solution to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and drive cost savings. By leveraging the key features and benefits of P2P applications and carefully considering implementation considerations, organizations can unlock the full potential of their procurement function and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Challenges In Procure To Pay Process
The Procure to Pay (P2P) process is a vital component of any organization’s operations, encompassing the entire cycle from requisitioning goods or services to vendor payment. While essential for maintaining business continuity, the P2P process is not without its challenges. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for optimizing efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing overall performance.
1. Integration of Systems:
One of the primary challenges in the P2P process is the seamless integration of various systems involved, including procurement, inventory management, and finance. Inadequate integration often leads to data discrepancies, delays in processing, and inefficiencies in decision-making. Implementing robust integration solutions is essential to ensure smooth workflow and accurate information exchange throughout the P2P cycle.
2. Supplier Management:
Effective supplier management is integral to the success of the P2P process. However, managing numerous suppliers while maintaining quality standards, negotiating contracts, and ensuring timely deliveries can be daunting. Failure to effectively manage suppliers can result in disruptions, quality issues, and increased costs. Implementing supplier relationship management strategies and leveraging technology for vendor performance tracking can mitigate these challenges.
3. Compliance and Regulations:
Navigating regulatory requirements and compliance standards poses significant challenges in the P2P process. From tax regulations to industry-specific compliance mandates, organizations must adhere to various rules throughout the procurement and payment stages. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to fines, legal complications, and reputational damage. Implementing robust compliance frameworks, conducting regular audits, and staying abreast of regulatory changes are essential for mitigating compliance risks.
4. Invoice Processing and Approval:
Invoice processing and approval are critical stages in the P2P process, yet they are often plagued by inefficiencies and errors. Manual invoice handling is time-consuming, prone to errors, and lacks visibility, leading to delays in payment and strained vendor relationships. Implementing automated invoice processing solutions streamlines the approval workflow, reduces processing time, and enhances accuracy. Additionally, implementing electronic invoicing systems facilitates real-time tracking and visibility into payment status.
5. Cash Flow Management:
Optimizing cash flow within the P2P process presents a significant challenge for organizations. Delayed payments to suppliers can strain relationships and lead to supply chain disruptions, while early payments may impact cash reserves and working capital. Balancing payment terms to optimize cash flow while maintaining positive supplier relationships requires careful planning and strategic negotiation. Leveraging dynamic discounting options and payment scheduling tools can help organizations optimize cash flow within the P2P process.
6. Data Security and Fraud Prevention:
With the increasing digitization of the P2P process, data security and fraud prevention have become major concerns for organizations. Cyberattacks, invoice fraud, and payment scams pose significant risks, potentially resulting in financial losses and reputational damage. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, is essential for safeguarding sensitive financial data and preventing fraudulent activities.
7. Change Management and User Adoption:
Introducing new technologies or processes within the P2P process often faces resistance from users accustomed to traditional methods. Change management and user adoption pose significant challenges, requiring effective communication, training, and stakeholder engagement. Failure to gain user buy-in can lead to implementation delays, inefficiencies, and suboptimal outcomes.
Investing in comprehensive training programs, soliciting feedback from end-users, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are essential for driving successful change within the P2P process.
The Procure to Pay process is vital for organizational success, but it is not without its challenges. From system integration to compliance, invoice processing, and user adoption, addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach encompassing technology, process optimization, and stakeholder engagement.
By proactively identifying and mitigating these challenges, organizations can streamline their P2P process, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency, ultimately driving sustainable growth and competitiveness.
Procure To-Pay Solutions
Procure-to-Pay (P2P) solutions have become integral for organizations aiming to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and mitigate risks in their procurement processes. From sourcing suppliers to processing invoices, P2P solutions offer a seamless end-to-end approach that streamlines operations and drives value. Let’s delve into the details of how P2P solutions revolutionize procurement management.
1. Automating Procurement Processes:
P2P solutions automate various stages of procurement, starting from requisitioning to payment. By digitizing and standardizing workflows, organizations can eliminate manual errors, reduce processing times, and ensure compliance with policies and regulations. This automation fosters greater transparency and accountability throughout the procurement lifecycle.
2. Supplier Management and Collaboration:
Effective supplier management is crucial for maintaining strong vendor relationships and securing favorable terms. P2P solutions provide centralized platforms for managing supplier information, performance evaluations, and contracts. Enhanced collaboration tools facilitate communication between buyers and suppliers, fostering strategic partnerships and driving continuous improvement initiatives.
3. Cost Control and Spend Visibility:
With P2P solutions, organizations gain real-time visibility into their spending patterns and procurement activities. By analyzing data insights, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities, negotiate better terms with suppliers, and enforce compliance with budgetary constraints. Moreover, robust analytics capabilities enable stakeholders to make informed decisions and optimize their procurement strategies.
4. Enhanced Compliance and Risk Management:
Compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies is paramount in procurement operations. P2P solutions incorporate built-in controls and approval workflows to enforce compliance at every stage of the procurement cycle. Additionally, by centralizing data and documentation, organizations can mitigate risks associated with fraud, errors, and supplier non-compliance, safeguarding their reputation and financial integrity.
5. Streamlined Invoice Processing:
Manual invoice processing is prone to errors, delays, and inefficiencies. P2P solutions automate invoice capture, validation, and approval processes, accelerating payment cycles and reducing the risk of duplicate payments or discrepancies. Integration with accounting systems ensures seamless reconciliation and accurate financial reporting, enhancing overall financial management.
6. Scalability and Flexibility:
Whether catering to small businesses or large enterprises, P2P solutions offer scalability and flexibility to adapt to evolving business needs. Cloud-based platforms enable organizations to scale their procurement operations without significant infrastructure investments. Moreover, configurable workflows and customization options allow businesses to tailor P2P solutions according to their unique requirements and industry-specific workflows.
7. Continuous Improvement and Innovation:
P2P solutions drive continuous improvement initiatives by providing actionable insights and performance metrics. Through performance tracking and benchmarking, organizations can identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and implement best practices. Furthermore, integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain enhances efficiency, transparency, and security within the procurement ecosystem.
Procure-to-Pay solutions offer a comprehensive framework for optimizing procurement processes, enhancing collaboration with suppliers, and driving strategic decision-making. By leveraging automation, data analytics, and compliance mechanisms, organizations can achieve cost savings, mitigate risks, and foster sustainable growth. Embracing P2P solutions is not just about improving operational efficiency but also about transforming procurement into a strategic function that adds tangible value to the business.
FAQs: What Is A Procure-To-Pay Process?
1. What are the primary objectives of the procure-to-pay process?
The primary objectives include optimizing procurement processes, controlling costs, and improving supplier relationships.
2. How does automation benefit the procure-to-pay process?
Automation reduces manual errors, speeds up processing times, and enhances data accuracy.
3. What are some common challenges faced in procure-to-pay implementation?
Challenges may include resistance to change, integration issues with existing systems, and data security concerns.
4. What role does Qodenext play in the procure-to-pay process?
Qodenext offers comprehensive procure-to-pay solutions, enabling organizations to streamline procurement operations and drive efficiencies.
5. How can organizations ensure compliance within the procure-to-pay process?
By implementing robust procure-to-pay systems like Qodenext, organizations can enforce compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies.
6. What metrics can be used to measure the effectiveness of the procure-to-pay process?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle time, cost savings, and supplier performance can gauge the effectiveness of the procure-to-pay process.
Conclusion
The procure-to-pay process is a cornerstone of modern business operations, enabling organizations to achieve end-to-end visibility, efficiency, and compliance in their procurement activities. By partnering with QodeNext, businesses can harness innovative technology, expert consulting, and comprehensive support to transform their P2P processes and unlock new levels of performance.
Ready to revolutionize your procure-to-pay journey? Contact QodeNext today to discover how our tailored solutions can empower your business to achieve operational excellence, cost savings, and strategic advantage.