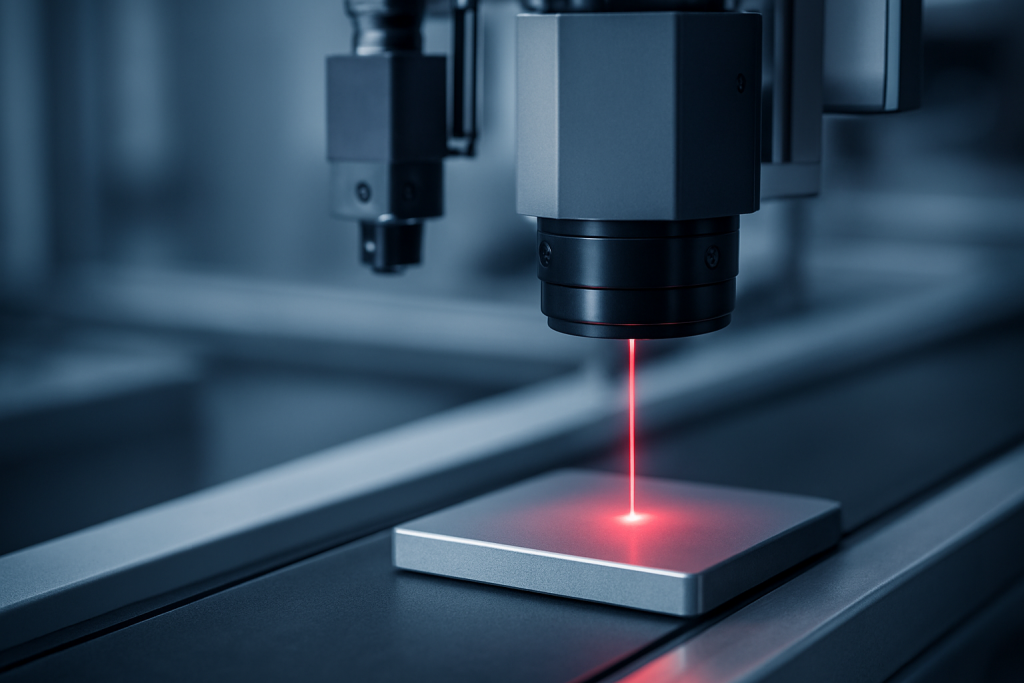
In the industrial landscape, precision and consistency are no longer optional; they are essential. From automotive to pharmaceuticals, the demand for error-free products has grown exponentially as customers expect flawless performance and regulatory standards tighten.
Traditional manual inspection methods often fail to meet these demands due to human error, fatigue, and limitations in accuracy. This is where automated machine vision sensors are revolutionising quality control, enabling industries to detect defects, measure dimensions, and ensure compliance with unmatched precision.
This blog explores how these sensors work, their advantages, use cases across industries, and their growing role in shaping modern manufacturing.
Understanding Automated Machine Vision Sensors
Machine vision sensors are advanced imaging systems integrated with cameras, lighting, and algorithms that replicate human vision but with greater accuracy, speed, and repeatability. Unlike manual inspection, these systems can analyse thousands of parts per minute, detect micron-level deviations, and ensure product uniformity at scale.
They typically involve three core components:
- Optics and Cameras: Capture high-resolution images of the product or part.
- Lighting Systems: Enhance contrast to highlight features or defects invisible to the naked eye.
- Image Processing Algorithms: Analyse the captured data, compare it against defined parameters, and classify products as pass or fail.
With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, these sensors continuously improve by learning from new data, thereby enhancing accuracy over time.
Why Precision Quality Control Matters
Machine vision automated inspection is not just about identifying defects; it’s about building trust, reducing costs, and staying compliant. Faulty products can damage brand reputation, increase recalls, and lead to regulatory penalties. For example:
- A hairline crack in an automotive component can cause accidents.
- A mislabeled pharmaceutical package can jeopardise patient safety.
- A contaminated food product can lead to widespread recalls.
Machine vision sensors provide real-time assurance that every product leaving the production line meets predefined standards, ensuring that businesses avoid these risks while optimising efficiency.
Advantages of Machine Vision Sensors in Quality Control
The adoption of automated machine vision sensors is accelerating due to their ability to deliver measurable improvements in inspection and production. Some key advantages include:
1. Unparalleled Accuracy
They can detect defects smaller than 10 microns, far beyond human capability, ensuring that even the tiniest deviations are caught before products reach the customer.
2. High-Speed Inspection
These systems inspect thousands of units per minute without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume industries such as electronics and packaging.
3. Consistency and Repeatability
Unlike human inspectors, sensors do not suffer from fatigue, distractions, or bias. Every product is measured against the same standard, ensuring uniformity.
4. Cost Efficiency
By reducing rework, scrap, and recalls, companies can significantly lower operational costs while maintaining profitability.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Industries such as pharmaceuticals and food manufacturing must adhere to stringent regulatory standards. Automated vision systems ensure traceability and compliance documentation.
6. Data-Driven Insights
Machine vision for quality systems not only detects defects but also collects valuable process data. This information can be analysed to identify root causes, reduce downtime, and optimise production processes.
Industrial Applications of Vision Quality Control Sensors
The versatility of automated machine vision sensors makes them applicable across industries:
1. Automotive
They inspect components such as gears, engines, and airbags for dimensional accuracy, cracks, or assembly errors. A single faulty part could compromise driver safety, making vision sensors indispensable.
2. Pharmaceuticals
Sensors verify pill sizes, packaging integrity, label accuracy, and expiration dates. Even a small deviation can result in costly recalls or harm to patients.
3. Food and Beverage
From checking bottle seals to detecting contaminants, vision systems ensure safety and hygiene in consumable products.
4. Electronics
In semiconductor and PCB manufacturing, sensors detect soldering errors, missing components, or micro-cracks invisible to the human eye.
5. Textiles and Printing
They help identify colour mismatches, print defects, or misaligned labels, ensuring brand quality consistency.
6. Logistics and Packaging
Automated sensors verify barcodes, labels, and sealing integrity, ensuring error-free distribution.
How Automated Machine Vision Sensors Work in Practice
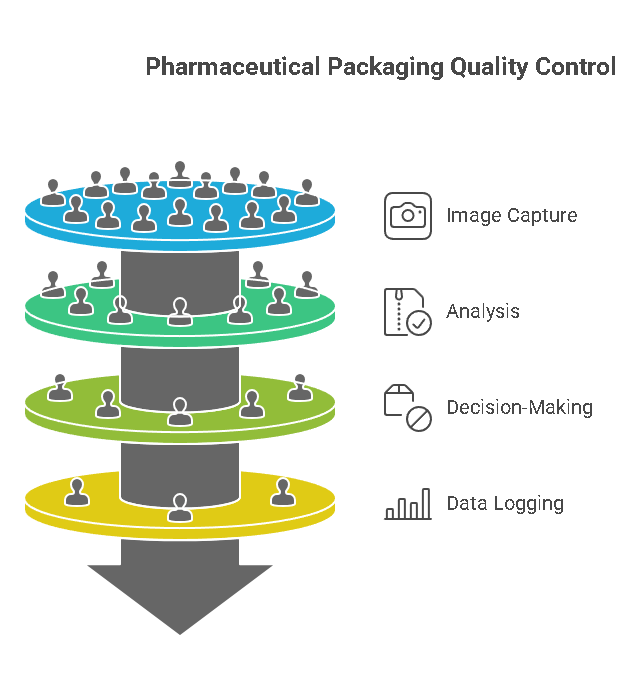
Imagine a pharmaceutical company packaging tablets into blister packs. Here’s how machine vision sensors streamline the process:
• Image Capture:
A high-resolution camera captures the blister pack under specialised lighting.
• Analysis:
Algorithms verify that each cavity is filled, the foil is sealed, and the printed lot number matches the batch record.
• Decision-Making:
The system automatically flags defective packs and diverts them from the main line.
• Data Logging:
Each decision is recorded, ensuring traceability for audits and compliance.
This automated, real-time approach eliminates the risk of oversight while improving throughput.
The Role of Quality Control and Machine Vision Sensors
The next frontier of automated machine vision sensors is their integration with AI and deep learning models. Traditional rule-based systems work well for predictable defects but struggle with complex variations. AI-enhanced vision systems can:
- Recognise patterns in unstructured data.
- Adapt to variations in lighting, orientation, or product appearance.
- Continuously learn from new defect data to improve detection accuracy.
This makes them suitable for industries where defect patterns are unpredictable, such as textiles or natural food products.
Challenges in Implementing Machine Vision Sensors
While the benefits are substantial, deploying automated vision sensors also comes with challenges:
• High Initial Investment:
Advanced cameras, lighting, and computing systems require significant capital expenditure.
• Integration Complexity:
Seamlessly integrating sensors into existing production lines requires skilled expertise.
• Environmental Factors:
Variations in lighting, dust, or vibration can affect performance if not managed properly.
• Data Overload:
Collecting large volumes of data requires robust infrastructure for storage, processing, and analysis.
Despite these challenges, the long-term return on investment (ROI) makes them a valuable addition for companies aiming for zero-defect manufacturing.
Future Outlook
The future of automated machine vision sensors is closely tied to Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). In the coming years, we can expect:
• Smarter Sensors:
Embedded AI chips that process data locally, reducing latency.
• Edge Computing Integration:
Faster decision-making without reliance on centralised servers.
• Cloud Connectivity:
Real-time analytics across multiple factories for centralised quality monitoring.
• Predictive Quality Control:
Using machine learning to predict defects before they occur, reducing downtime and improving yields.
As industries continue to push for higher efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, automated vision systems will remain at the forefront of digital transformation.
Conclusion
Automated machine vision sensors are transforming how industries approach quality control. They deliver accuracy, efficiency, and consistency that far exceed human capabilities, helping businesses safeguard brand reputation, meet regulatory demands, and optimise operations. With advancements in AI, edge computing, and IIoT, the future of quality control lies firmly in the hands of these intelligent, automated systems. Explore precision-based vision inspection with Qodenext today.
FAQs on Automated Machine Vision Sensors
1. What are machine vision sensors?
Machine vision sensors are systems that use cameras, lighting, and algorithms to inspect and analyse products in real-time, ensuring precision and consistency in quality control.
2. How do machine vision sensors differ from traditional inspection methods?
Unlike manual inspection, they provide higher accuracy, speed, and consistency, eliminating human error and ensuring every product is measured against the same benchmark.
3. Which industries benefit the most from machine vision sensors?
Industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, electronics, food and beverage, and packaging see the highest benefits due to their stringent quality requirements.
4. Can machine vision sensors detect microscopic defects?
Yes, advanced systems can detect defects as small as a few microns, making them suitable for applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
5. Are machine vision sensors expensive to implement?
While the initial investment can be high, the reduction in rework, recalls, and downtime typically results in a strong return on investment over time.
6. What role does AI play in modern vision sensors?
AI and deep learning enhance defect recognition, allow adaptability to variations, and enable predictive quality control.







