Linear supply chains no longer support dynamic business systems. Businesses are dynamic, complex, and involve countless touchpoints across suppliers, distributors, warehouses, and retailers. To manage this complexity effectively, companies are turning to a powerful tool: Big Data.
Big Data has the potential to transform supply chain analytics by improving visibility, enhancing decision-making, and optimising processes at every stage. In this blog, we’ll explore how Big Data can be applied across supply chains, its key benefits, and best practices for successful implementation.
What is Big Data in Supply Chain Operations?
Big Data is the amalgamation of structured, unstructured, and cluttered data from multiple touchpoints. In supply chain operations, this includes:
- Transactional data (orders, invoices)
- Sensor and Iot data (temperature, humidity, GPS)
- Social media and customer feedback
- Supplier and logistics data
- Real-time transportation information
- Market trends and economic indicators
When harnessed properly, Big Data provides actionable insights that drive efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Big Data in the Supply Chain – Critical Applications
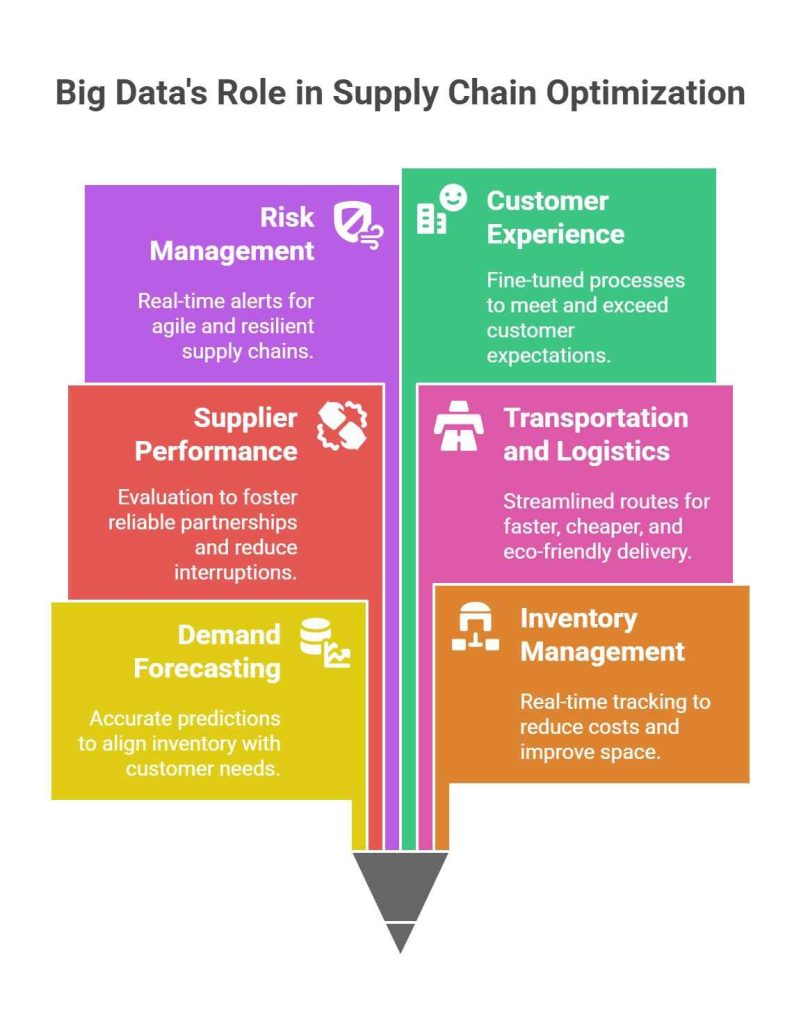
1. Demand Forecasting
Using historical sales data, social trends, weather reports, and even web searches, Big Data analytics in supply chain management can accurately forecast customer demand. This allows businesses to:
- Prevent stockouts and overstocking
- Plan production cycles more efficiently
- Align inventory with customer needs
Example: A fashion retailer can use social media trends and historical seasonal sales data to predict the popularity of specific clothing lines, ensuring they’re stocked at the right time.
2. Inventory Management
Big Data helps in real-time inventory tracking across multiple locations. It can identify slow-moving or obsolete inventory and suggest redistribution or markdown strategies.
Benefits include:
- Reduced carrying costs
- Improved warehouse space utilisation
- Automated replenishment alerts
Tip: Integrating RFID and Iot sensors provides continuous updates on stock levels, shrinkage, and expiration dates, all feeding into a central supply chain analytics platform.
3. Supplier Performance Optimisation
By analysing data from past deliveries, quality control reports, lead times, and communication logs, companies can evaluate and rank supplier performance.
Big Data tools can:
- Identify bottlenecks or delays
- Predict risks (e.g., geopolitical disruptions, financial instability)
- Foster better vendor collaboration
This leads to more reliable partnerships and fewer supply chain interruptions.
4. Transportation and Logistics
Logistics data—such as fuel consumption, traffic conditions, weather, and delivery times—can be analysed to streamline transportation.
Outcomes include:
- Route optimisation for faster and cheaper delivery
- Predictive maintenance for fleet management
- Reduced carbon emissions
Example: FedEx uses big data and supply chain analytics to track delivery operations and traffic. Data analysis helps uncover mileage, distance, and truck performance.
5. Risk Management and Resilience
Supply chain management in data analytics is vulnerable to disruptions from natural disasters, political instability, or supplier insolvency. Big Data provides real-time alerts and predictive insights to manage such risks.
Big Data allows companies to:
- Simulate “what-if” scenarios
- Build contingency plans
- Detect fraud and anomalies
This makes the supply chain more agile and resilient.
6. Customer Experience Enhancement
By analysing returns, reviews, purchase history, and delivery performance, companies can fine-tune supply chain analytics to meet customer expectations.
Big Data helps improve:
- On-time delivery rates
- Order accuracy
- Post-purchase support
When customers receive timely, correct, and seamless service, it directly boosts brand loyalty and retention.
Technologies Powering Big Data Supply Chains
To effectively leverage Big Data, businesses use various technologies, including:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): For pattern recognition, forecasting, and prescriptive analytics.
- Machine Learning (ML): For continuous improvement and predictive modelling.
- Iot Devices: For collecting real-time data from assets and environments.
- Cloud Computing: For scalable storage and easy access to data lakes.
- Blockchain: For secure and transparent data sharing between parties.
These technologies turn raw data into intelligent insights that drive better decisions.
Steps to Implement Big Data Supply Chain Operations
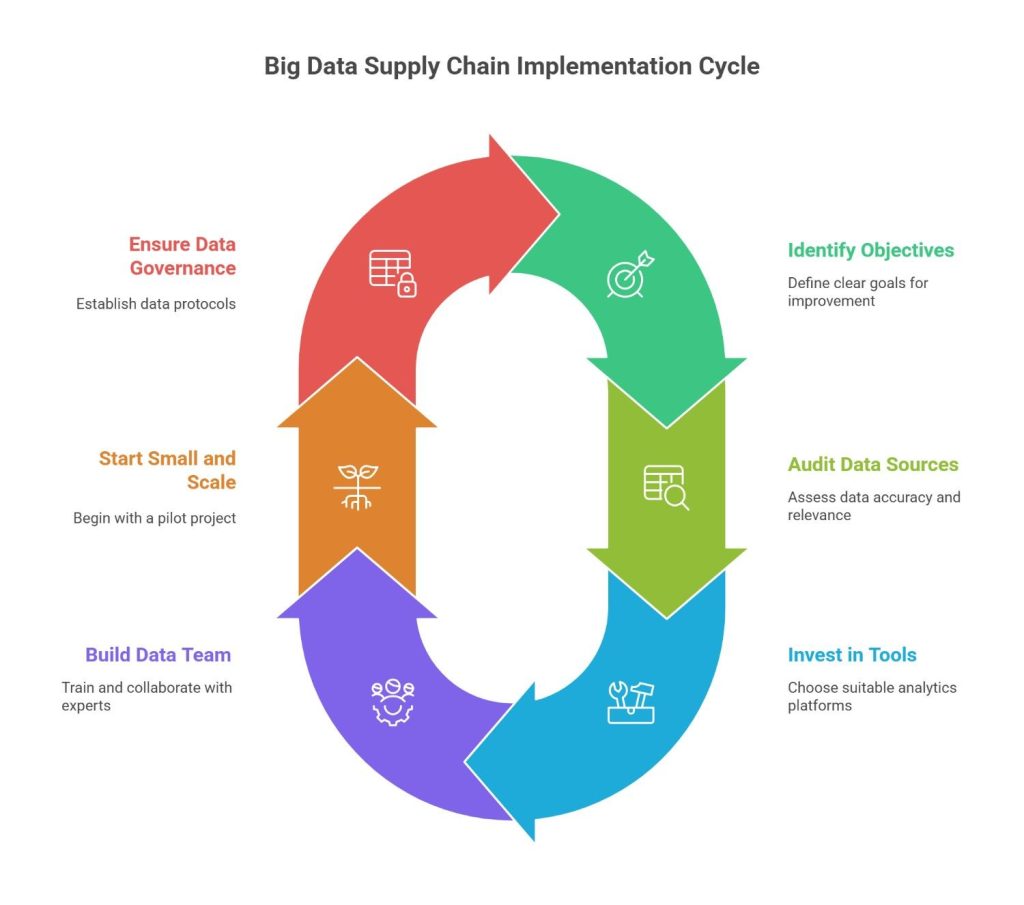
Step 1: Identify Your Objectives
Identify the deliverables, metrics, and progress you want to achieve:
- Better forecasting?
- Reduced costs?
- Enhanced visibility?
Clear goals will guide the tools, data sources, and technologies you need.
Step 2: Audit Your Data Sources
Collect the supply chain analytics data in a single dashboard. Use predictive analytics tools to simplify your operations.
- ERP systems
- CRM software
- Transportation systems
- Supplier databases
Assess their accuracy, relevance, and accessibility.
Step 3: Invest in the Right Tools
Choose analytics platforms that can handle large volumes of diverse data, integrate with existing systems, and provide user-friendly dashboards. Some popular platforms include:
- SAP HANA
- Microsoft Azure Synapse
- IBM Watson Supply Chain
- Tableau
Step 4: Build a Skilled Data Team
Employ or train data analysts, supply chain professionals, and IT specialists who understand both logistics and data science. Cross-functional collaboration is key.
Step 5: Start Small and Scale
Begin with a pilot project, such as demand forecasting in a specific region, then expand once results are proven.
Step 6: Ensure Data Governance
Establish protocols for:
- Data accuracy and validation
- Privacy and compliance (e.g., GDPR)
- Access control and cybersecurity
- Good governance builds trust and ensures long-term sustainability.
Challenges to Be Aware Of
While Big Data offers tremendous value, companies may face challenges such as:
- Data silos across departments
- Poor supply chain analytics data quality or outdated records
- High initial investment
- Skill gaps in data analytics
- Privacy concerns with customer and partner data
Overcoming these requires strategic planning and ongoing training.
Benefits of Using Big Data Supply Chain Operations
- Increased supply chain visibility
- Faster and more accurate decisions
- Reduced operational costs
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Proactive risk mitigation
- Sustainable and efficient logistics
In short, Big Data enables a data-driven supply chain—one that is predictive, responsive, and adaptive to change.
Conclusion
Big Data is revolutionising how supply chain analytics are managed, turning reactive systems into proactive ecosystems. Whether you’re a small manufacturer or a global retailer, integrating Big Data into your operations can unlock unparalleled efficiency, cost savings, and agility.
The key is to start strategically, focus on solving real-world problems, and build a culture that values data-driven decision-making. For robust traceability and supply chain tracking solutions, contact Qodenext today.
FAQS – Supply Chain Analytics
1. What is the role of AI in big data supply chain systems?
AI helps analyse vast datasets to identify patterns, make predictions, and suggest optimal actions. It’s used in demand forecasting, route optimisation, and automated decision-making.
2. How can small businesses benefit from Big Data supply chains?
Small businesses can use Big Data tools (even low-cost ones) to understand customer behaviour, monitor stock levels, and improve delivery efficiency, leading to better competitiveness and reduced waste.
3. Is Big Data only useful for logistics?
No. While logistics is a major area, Big Data also supports sourcing, production, demand planning, quality control, and customer service across the entire supply chain.
4. How is Big Data different from traditional supply chain analytics?
Traditional analytics rely on historical data and manual reports. Big Data involves real-time, diverse data from multiple sources, offering deeper insights and predictive capabilities.
5. What industries are using big data in supply chains?
Industries like retail, manufacturing, automotive, pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and eCommerce are actively leveraging Big Data for enhanced supply chain performance.
6. What is the role of AI in big data supply chain systems?
AI analyses large datasets to find patterns, generate predictions, and recommend optimal actions. It’s commonly used for demand forecasting, optimizing delivery routes, automating decision-making, and enhancing overall supply chain responsiveness.
7. How can small businesses benefit from Big Data supply chains?
Small businesses can leverage accessible Big Data tools to better understand customer behavior, efficiently monitor stock levels, and improve delivery processes. This boosts competitiveness, reduces waste, and helps scale operations smartly.
8. Is Big Data only useful for logistics?
No, Big Data supports various supply chain functions beyond logistics, including sourcing, production planning, demand management, quality control, and customer service, enabling end-to-end optimization.
9. How is Big Data different from traditional supply chain analytics?
Traditional supply chain analytics typically rely on historical data and manual reporting, providing limited insight. Big Data, however, uses real-time, diverse data from multiple sources, enabling deep insights and predictive, proactive decision-making.
10. What industries are using Big Data in supply chains?
Retail, manufacturing, automotive, pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, eCommerce, and many other industries actively use Big Data to enhance supply chain operations, improve efficiency, and drive innovation.






