In today’s hyper-competitive manufacturing landscape, having machines that work efficiently isn’t enough.
What you really need is real-time visibility, tight process control, and the ability to act quickly on the shop floor. That’s exactly where a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) steps in.

But what exactly is MES? Why are so many manufacturers – across sectors like automotive, aerospace, pharma, and electronics investing in it? And how does it differ from ERP software?
This guide breaks it all down: what MES is, how it works, how companies are using it, and why it’s quickly becoming essential for manufacturing success.
What is a Manufacturing Execution System?
At its core, a Manufacturing Execution System is software that monitors, tracks, documents, and controls the entire production process on the factory floor – in real time.
Think of it as the bridge between planning and actual production. While ERP handles planning, purchasing, and logistics, MES is focused on execution – how and when things get made.
A good MES software tells you:
- Which machines are running or idle
- How much output you’ve produced (and whether it’s within quality limits)
- If you’re on track to meet production targets
- Where bottlenecks or deviations are occurring
Now that we know what an MES is, let’s understand why it’s become such a critical tool in modern manufacturing.
Why MES Matters More Than Ever
Manufacturers today are under pressure to do more with less – less waste, less downtime, fewer defects. At the same time, customer demands are rising in terms of speed, customization, and transparency.
That’s where MES in automation plays a powerful role.
By integrating with equipment, sensors, and people on the shop floor, an MES allows for precise, data-driven control of the manufacturing environment.
For example, Bosch has integrated MES across multiple smart factories to increase traceability, minimize quality defects, and make real-time decisions using production data.
Likewise, Boeing uses MES for synchronizing its vast network of parts, processes, and suppliers for aircraft assembly – ensuring every bolt and component is accounted for.
Now that we’ve established the value of MES, let’s dig deeper into how it actually works.
Key Functions of MES Software
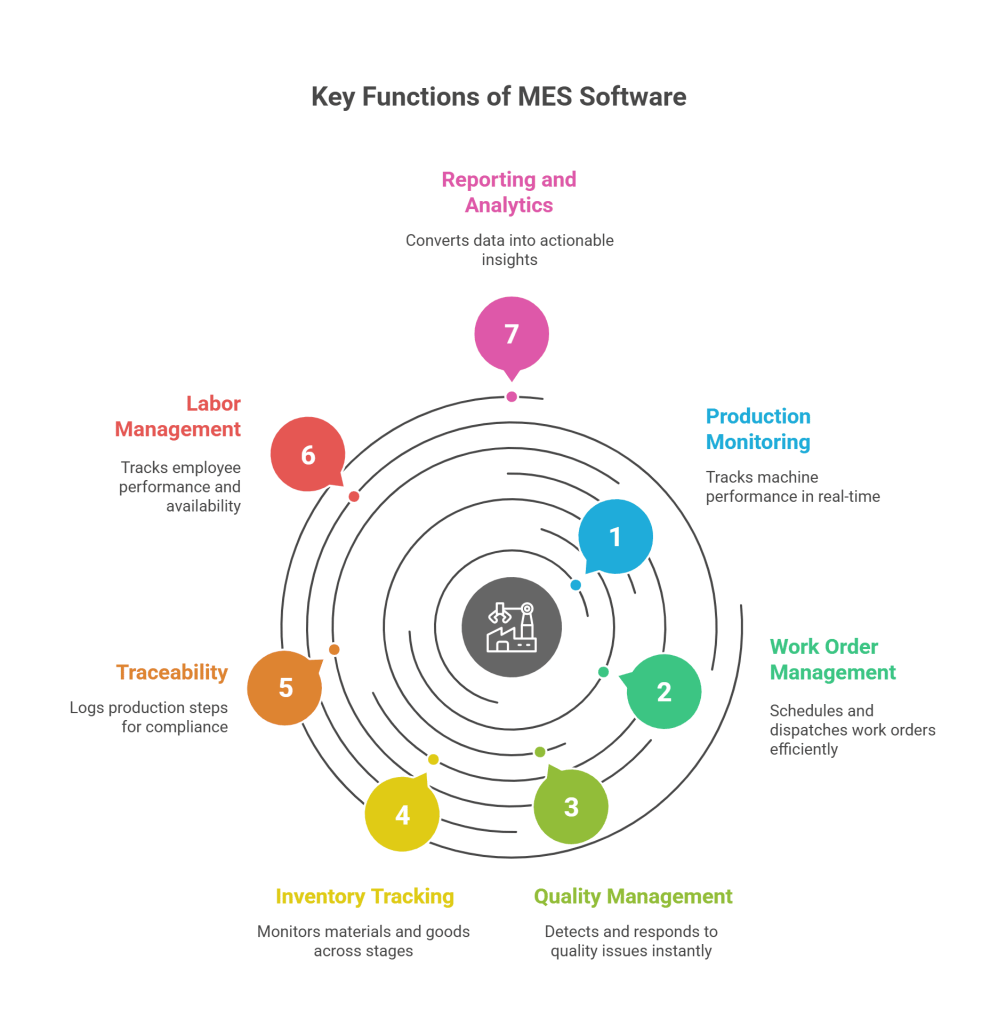
A comprehensive MES software solution usually includes the following functions:
1. Production Monitoring
Track machine uptime, downtime, speed, and production count in real-time.
2. Work Order Management
Schedule and dispatch work orders based on current machine availability and skillsets.
3. Quality Management
Detect and respond to quality issues instantly, with built-in inspection processes.
4. Inventory Tracking
Monitor raw materials, WIP (Work-in-Progress), and finished goods across stages.
5. Traceability
Log every step in the production process to meet compliance and safety standards.
6. Labor Management
Track employee performance, availability, and task completion.
7. Reporting and Analytics
Turn raw production data into actionable insights.
With these functionalities, MES becomes your central nervous system on the factory floor. With these functions in mind, let’s look at how MES compares with ERP software.
MES vs ERP: What’s the Difference?
A common misconception is that MES and ERP are interchangeable. They’re not.
While both are critical for operations, they serve very different purposes:The ideal approach? Let MES and ERP work together.
| Feature | MES | ERP |
| Focus | Shop floor execution | Business planning & resource allocation |
| Real time | Yes | Typically batch or delayed |
| Data Granularity | Machine-level, task-level | Order-level, financial-level |
| Integration | Connects with PLCs, sensors | Connects with finance, HR, CRM |
| Users | Operators, floor managers | Procurement, HR, Finance teams |
For instance, Siemens integrates MES and ERP across their factories to allow seamless decision-making from order intake to final assembly.
Now that we’ve cleared up the MES vs ERP comparison, let’s see what makes MES especially relevant today.
Benefits of Using a Manufacturing Execution System
Implementing MES delivers measurable advantages for manufacturers. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Improved production efficiency
Downtime and delays are drastically reduced thanks to real-time monitoring and faster decision-making.
2. Better product quality
Built-in inspections, alerts, and traceability ensure fewer defects and higher compliance.
3. Greater visibility
You get a clear view of your shop floor, from raw materials to finished goods.
4. Faster response to issues
MES alerts operators to machine faults or quality problems as they happen – not after.
5. Reduced waste and rework
By catching problems early, MES helps prevent defective output and overproduction.
6. Regulatory compliance
Industries like pharma, aerospace, and food use MES to meet stringent tracking and documentation standards.
Procter & Gamble, for example, uses MES to streamline batch production in their personal care product lines, enabling faster product changeovers and fewer quality incidents.
Now let’s talk about the types of MES systems companies can choose from.
Cloud-Based MES vs On-Premise MES
There’s a growing shift toward cloud-based MES solutions – especially for mid-sized manufacturers and global operations.
| Feature | On-Premise MES | Cloud Based MES |
| Cost structure | CapEx-heavy (upfront) | OpEx (subscription) |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Maintenance | Requires in-house IT | Handled by vendor |
| Updates | Manual | Automatic and frequent |
| Remote Access | Not easily available | Accessible from anywhere |
GE Healthcare has adopted cloud-based MES to support remote monitoring of its medical device assembly lines. This allows for proactive issue detection, even across different time zones.
With deployment models clear, let’s now discuss how MES is implemented on the factory floor.
Key Steps to Implement MES Successfully
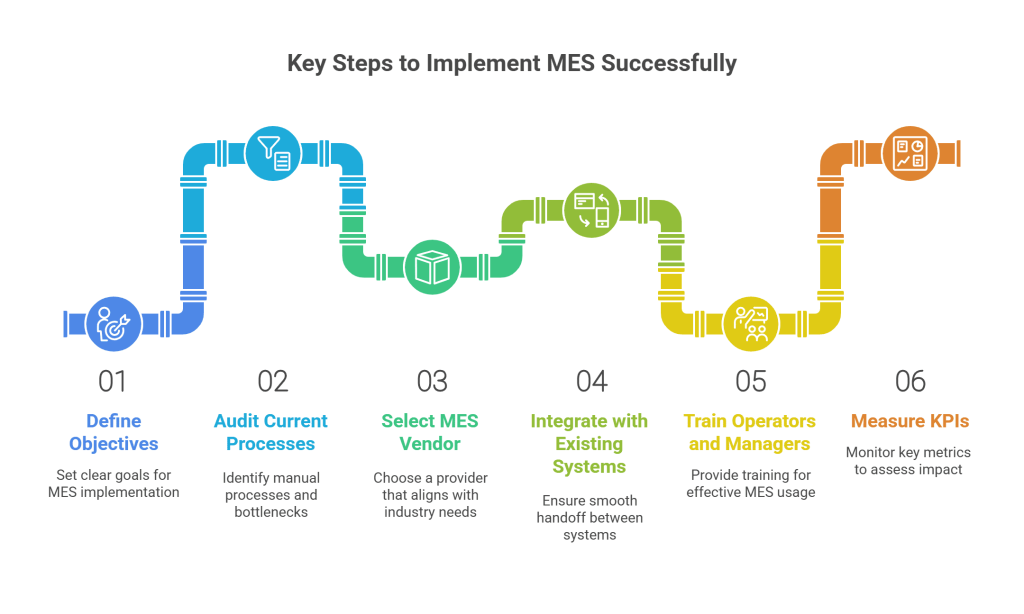
Rolling out an MES system isn’t just a software installation – it’s a transformation of how your operations run. Here are the steps that usually go into a successful MES deployment:
- Define Objectives – Set clear goals like reducing downtime, improving OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), or enhancing traceability.
- Audit Current Processes – Identify manual processes, data gaps, and production bottlenecks.
- Select the Right MES Vendor – Choose a provider that aligns with your industry needs (e.g., Pharma vs. Automotive).
- Integrate with Existing Systems – Ensure smooth handoff between MES, ERP, and machine-level controls.
- Train Operators and Managers – Your MES is only as good as the people using it.
- Measure KPIs – Monitor key metrics like cycle time, yield rate, and defect rate to assess impact.
With implementation covered, let’s move to the future of MES and how AI and IoT are changing the game.
The Future of MES
MES is no longer just about digitizing your shop floor. It’s evolving into a smart, predictive, and even autonomous control layer.
What’s driving this evolution?
- AI/ML: Predict machine failure before it happens.
- IoT Sensors: Real-time visibility into temperature, pressure, vibration, etc.
- Digital Twins: Simulate production changes without disrupting actual output.
- Edge Computing: Faster decision-making right at the machine level.
Foxconn is experimenting with AI-enabled MES software to optimize its electronics assembly lines – adjusting production flow dynamically based on sensor input and order volume.
As these technologies mature, MES will become the brain behind Industry 4.0.
FAQs: How Smart Manufacturing Is Getting Smarter With MES
1. Can small manufacturers use MES?
Yes. Scalable cloud-based MES solutions are available for small and mid-sized businesses without heavy infrastructure costs.
2. Does MES replace ERP?
No. They work best together. While ERP handles planning and finance, MES handles production and execution.
3. How long does MES implementation take?
It depends on factory size and complexity – typically 3 to 12 months.
4. Is MES industry-specific?
While core functions are similar, MES is often tailored for industries like pharma, automotive, or electronics.
5. Can MES improve sustainability?
Yes. MES helps reduce energy use, waste, and raw material consumption through smarter resource planning.
Conclusion
In a world where every second and every unit counts, a manufacturing execution system gives manufacturers the visibility, control, and agility they need to stay competitive.
Whether you’re scaling operations, improving product quality, or embracing smart manufacturing, MES isn’t just helpful – it’s essential.
The future of manufacturing is digital, connected, and intelligent. MES is how you get there.






