Smart labels revolutionise how products are tracked, managed, and delivered in today’s fast-paced world. But what is a smart label? In essence, it’s an innovative tool that provides enhanced security and real-time data identification. Unlike traditional labelling techniques, smart labels deliver greater functionality, speed, and precision.
Let’s understand the technology, including how it works, benefits and more.
What is a Smart Label?
Smart labels are an advanced form of labelling that combine traditional product information with modern digital technology. These labels go beyond static printed text, integrating components such as microchips, antennas, or sensors to store, transmit, and update data. A smart label can provide real-time information about a product, including its origin, journey through the supply chain, and even its current condition.
Unlike conventional labels, which only display fixed details like price and ingredients, smart labels interact with external systems like scanners, smartphones, or IoT devices to provide dynamic, actionable insights. This fusion of physical labelling and digital communication makes smart labels a vital tool in industries like logistics, healthcare, and retail.
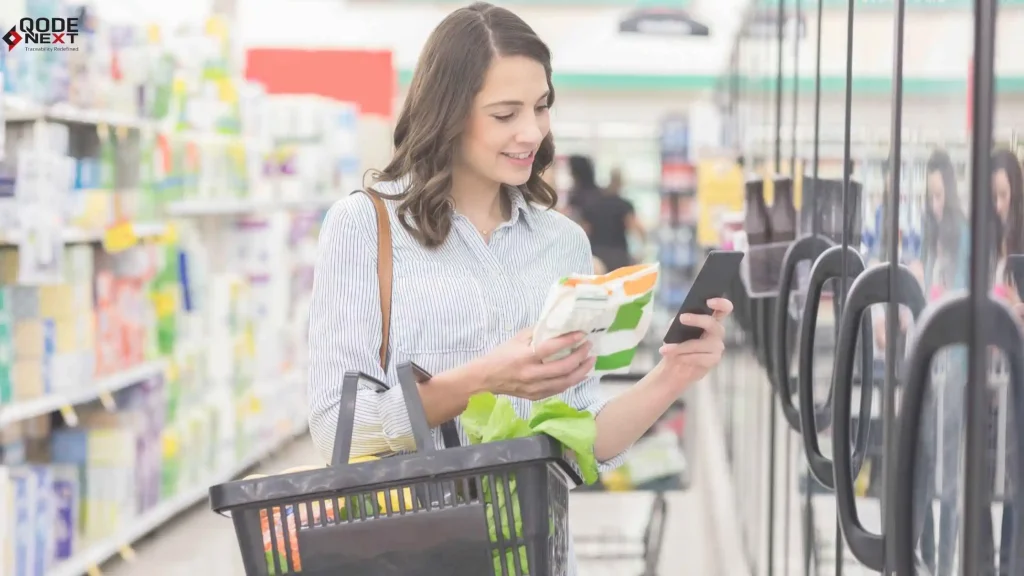

What is a Smart Label – How Does It Work?
Smart labels combine conventional labelling methods with cutting-edge technology to store and transmit data. Here’s how they work:
1) Embedded Technology
These labels are equipped with digital smart packaging, microchips, antennas, or sensors that allow them to communicate electronically. For instance, RFID-enabled smart labels use electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects.
2) Data Storage and Access
Each smart label contains specific data about the product, such as its manufacturing details, expiration date, and supply chain history. This data can be accessed using RFID scanners, QR code readers, or NFC-enabled devices.
3) Real-Time Communication
Smart label scans can transmit real-time information to tracking systems, enabling businesses to monitor the location, condition, and status of their products instantly.
4) Integration with Software
These labels are integrated with enterprise systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and WMS (Warehouse Management Systems), ensuring seamless data flow across supply chain processes.
Benefits of Smart Labels
The adoption of smart labels offers a wide range of benefits across industries. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Enhanced Inventory Management
Smart labels make inventory tracking more efficient by providing real-time updates. Businesses can reduce errors, optimize stock levels, and ensure better demand planning.
2. Improved Supply Chain Visibility
With smart labels, companies gain end-to-end visibility into their supply chain. This is particularly useful for industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where traceability is crucial for compliance and quality assurance.
3. Cost and Time Efficiency
Traditional labelling processes often require manual intervention, leading to higher costs and delays. Smart label software automates data collection and sharing, reducing the need for human involvement and speeding up operations.
4. Better Customer Experience
By scanning a smart label, customers can access detailed product information, such as authenticity verification, usage instructions, and warranty details. This builds trust and enhances the shopping experience.
5. Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Smart labels contribute to sustainable practices by minimizing paper usage and optimizing supply chain efficiency, which reduces waste.
6. Temperature and Condition Monitoring
For perishable goods, some smart labels come equipped with sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions. This helps ensure product quality and safety.
Applications of Smart Labels
Smart labels are transforming various sectors by addressing specific challenges and enhancing operational efficiency. Here are some key applications:
1. Retail
Retailers use smart labels for inventory tracking, theft prevention, and enhancing the customer experience. For instance, RFID-enabled smart labels help reduce checkout times and enable automated stock replenishment.
2. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
In the healthcare sector, smart labels ensure the traceability of medicines, medical devices, and vaccines. They help monitor storage conditions and prevent counterfeit drugs.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
Smart label tracking plays a vital role in ensuring food safety and compliance. They track the entire journey of food products from farm to fork and provide transparency to consumers.
4. Logistics and Transportation
In logistics, smart labels streamline package tracking, reduce transit delays, and provide accurate delivery updates.
5. Manufacturing
Smart labels are used in manufacturing to monitor production processes, manage assets, and ensure quality control.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Labels
While smart labels offer numerous benefits, their implementation comes with challenges:
1. High Initial Costs
The technology and infrastructure required for smart labels can be expensive, especially for small businesses.
2. Data Security and Privacy
With sensitive data being transmitted, businesses must implement robust security measures to prevent breaches.
3. Integration Issues
Integrating smart labels with existing systems can be complex and may require significant customization.
4. Reliability
Environmental factors such as extreme temperatures or electromagnetic interference can affect the performance of smart labels.
FAQs – What is a Smart Label?
What is a smart label, and how is it different from a traditional label?
A smart label integrates advanced technologies like RFID, QR codes, or NFC, allowing it to store and transmit data electronically. Unlike traditional labels, which are static and require manual reading, smart labels provide dynamic, real-time information.
Are smart labels reusable?
Some smart labels, particularly those using RFID technology, can be reused depending on their design and the application. However, disposable smart label packaging are also widely used for one-time tracking purposes.
Can smart labels be used for small businesses?
Yes, while the initial investment might be higher, smart labels offer significant long-term benefits for small businesses, including enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and improved customer engagement.
What industries benefit the most from smart labels?
Industries such as retail, healthcare, food and beverages, logistics, and manufacturing benefit significantly from adopting smart labels.
What does a smart label look like?
Smart labels often take the form of QR codes on products. They are flat identification slips that vary in appearance depending on the technology used.
What technologies are commonly used in smart labels?
RFID, QR codes, and NFC are the most commonly used technologies in smart labels, each serving specific use cases and applications.
Do smart labels require specialized scanners or devices?
Yes, smart labels often require specific devices for data reading, such as RFID readers, QR code scanners, or NFC-enabled smartphones. However, these technologies are widely available and increasingly integrated into consumer and industrial devices.
Are smart labels compatible with IoT systems?
Absolutely. Smart labels are designed to work seamlessly with IoT systems, enabling real-time tracking, data sharing, and automated workflows. This compatibility makes them a cornerstone of modern smart supply chains and connected ecosystems.
Conclusion
So, what is a smart label? It’s more than just a technological upgrade—- it bridges the gap between data storage, transfer, and labelling. Smart labels can help your business stay ahead in the competitive landscape. For further assistance on logistics and supply chain management, contact Qodenext today. Start your journey towards a resilient, robust, and efficient supply chain network.