
In this rapidly developing technological world, the role of barcodes has become indispensable in identifying products, tracking inventories, and streamlining business operations. With the increase in the need for contactless transactions, barcodes have become a go-to option for businesses and consumers.
We see QR Codes almost everywhere now, but do you know what an Aztec barcode is? If not, then don’t worry. We’ve got you covered!
Aztec codes represent a highly adaptable and versatile barcode system that stands out from other technologies. They are known for their reliability, security, and ease of use, making them an excellent option for various apps.
In this blog, we will acquaint you with what an Aztec code is, its features, and the various advantages that it brings to the table.
Let’s dive in!
What Is an Aztec Barcode?
The Aztec code, developed by researchers Andrew Longacre Jr. and Robert Hussey in 1995, is a two-dimensional barcode system engineered to efficiently contain data within a compact space.
Because of its distinctive central design, the Aztec code is frequently more compact compared to other 2D barcode formats like QR codes or Data Matrix codes.
Did you know?
The finder pattern of the code has a resemblance to the aerial perspective of an Aztec pyramid, which were ancient structures constructed by the Aztecs in central Mexico, giving the barcode its name.
The Aztec code can encode a maximum of 3,832 numerical digits, 3,067 alphabetic characters, or 1,914 bytes of data.
Aztec Barcode: How Do They Work?
Now that we have a rough idea of what Aztec barcodes are, let’s understand how they actually work.
The Aztec barcode format comprises a central square featuring layers of square pixels of different dimensions, such as 9 x 9, 13 x 13, 23 x 23 pixels, and so forth. These squares contain encoded data specific to the Aztec barcode.
Additionally, Aztec barcodes include markers in their corners indicating the reading direction, eliminating the need for a “quiet zone” as required by other barcode formats. Furthermore, they possess the capability to store up to 1,914 bytes of data across their 32 layers.
Anatomy of Aztec Barcode:
Finder Pattern
Within Aztec codes, the finder pattern is a square configuration with a central bull’s-eye shape. This arrangement is composed of alternating black and white square rings, each being one module in width.
Orientation Pattern
The orientation patterns within an Aztec barcode contain details regarding the reading direction, the number of data layers present, and the number of data layers present in it. These patterns are chevron in shape and are positioned at the corners of the barcode.
Mode Message
Located in the same layer as the orientation pattern, the mode message stores information about the symbol, size, and length of the data.
Reference Grid
Made up of rows and columns of alternating black and white squares, the reference grid accurately maps the data field and maintains alignments of grids for large symbols.
Data Layers
The Aztec code comprises one or multiple data layers responsible for storing information along with check characters. These layers are scanned in a clockwise direction and start adjacent to the initial orientation pattern, having an all-black appearance.
Now let’s move on to knowing about the different types of Aztec barcode scanner.
Aztec Barcode: What Are Its Types?
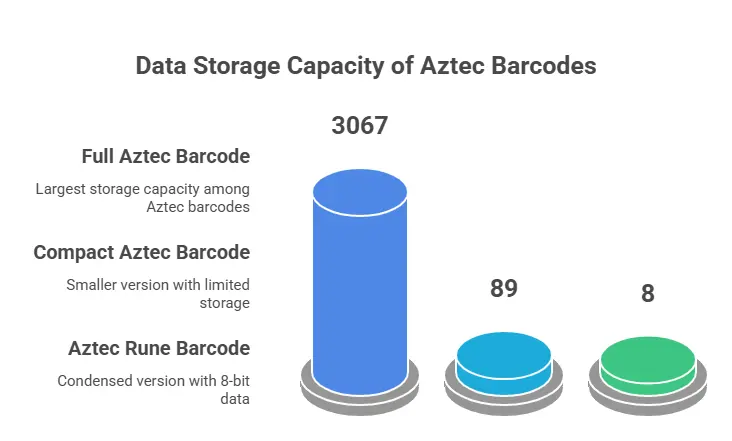
The Aztec barcode comes in three primary formats:
-Full Aztec code
-Compact Aztec code
Full Aztec Barcode
The Full Aztec barcode offers 40 symbol sizes, including modules ranging from 19 x 19 to 151 x 151. It can store up to 3067 characters of text, 3832 characters of numeric data, and 1914 characters of binary data (8-bit).
Compact Aztec Barcode
Compact Aztec barcodes are available in four symbol sizes, ranging from 15 x 15 modules to 27 x 27 modules. They can hold a maximum of 89 characters of text, 110 characters of numeric data, and 13 characters of binary data.
Aztec Rune Barcode
Aztec Runes represent compact, machine-readable marks compatible with the Aztec Code. Serving as a condensed version of the Aztec code, they convey 8 bits of data through a numerically distinct mode message. Aztec Runes consist of 256 square marks, each measuring 11 x 11 modules.
We know the types of Aztec Barcodes but do we know where these codes are used? Let’s find out.
Aztech Barcodes: Where Are They Used?
The aztec barcode reader is capable of storing extensive data and is predominantly utilized for industrial or commercial purposes rather than consumer purposes. Some common uses of aztec barcodes include the following:
- Ticketing
- Inventory management
- Payment Application
- Transportation and Logistics
- Product Labelling
- Data Storage
- Automobile Registration
You need an online aztec barcode reader or smartphone camera to read an aztec barcode.
How to Generate Aztec Barcodes
Aztec barcodes are compact, two-dimensional matrix codes that store large amounts of data efficiently. They’re ideal for inventory tracking in property management, retail, or maintenance. Follow this step-by-step guide to create Aztec barcodes tailored to your needs.
1. Select a Barcode Generation Tool
Choose a tool that supports Aztec barcodes based on your setup:
- Online platforms like Barcode Generator, Barcodes Inc, or Online Barcode Generator offer quick, no-install solutions.
- Software options like Adobe Illustrator or dedicated barcode programs provide advanced customization for professional use.
2. Enter Your Data
Determine the information to encode, such as:
- Text (e.g., product IDs, appliance serial numbers)
- URLs (e.g., maintenance logs)
- Contact details or other metadata Input this data into the tool’s designated field.
3. Configure Barcode Settings
Adjust parameters to optimize the barcode:
- Size: Balance compactness with scannability.
- Error Correction Level: Higher levels improve durability but may increase size.
- Color: Ensure sufficient contrast (e.g., black on white) for reliable scanning.
4. Create the Barcode
Click the “Generate” or “Create” button to produce the Aztec barcode based on your data and settings.
5. Save the Barcode
Download the barcode in a suitable format:
- Common formats include PNG, JPG, or SVG.
- Save it for printing or integration into your inventory system (e.g., Yardi-compatible workflows).
6. Test the Barcode
Verify functionality before deployment:
- Use a barcode scanner or mobile app to ensure the code scans correctly.
- Check readability under various conditions (e.g., lighting, print quality).
This version is polished for posting, with clear headings (H2 for the main section, H3 for steps) to improve SEO and user navigation. It’s concise, avoids fluff, and includes context relevant to inventory management (e.g., Yardi integration, property management use cases). The content is ready to be added to a blog or webpage, enhancing scannability and engagement.
Aztech Barcodes: Why Do We Need These Codes?
Aztec barcodes present prominent benefits compared to 2D barcodes such as QR codes and conventional linear barcodes like UPCs. Below are several reasons presenting the necessity of Aztec barcodes.
1. High Information Capacity
Aztec barcodes have a remarkable capacity to store substantial amounts of data when compared with linear barcodes. They exhibit a high information density, enabling the storage of extensive information, including text, numerical values, and even binary data.
2. Space-Efficient Design
Despite their capacity for storing large volumes of data, Aztec barcodes maintain a compact size. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where space is restricted, such as on product packaging or identification cards.
3. Versatility in Data Storage
Aztec barcodes possess the capability to store diverse data types, including numeric, alphanumeric, and binary data.
4. Device Compatibility
Aztec barcodes are effortlessly scannable using mobile phone cameras or dedicated barcode scanning applications. This makes them particularly well-suited for applications involving consumer-oriented technology.
5. Scalability
Aztec barcodes show flexibility in their applicability across different surfaces and materials, ranging from paper and plastic to metal. Moreover, they can be resized to accommodate various dimensions without sacrificing their efficiency in scanning and decoding.
6. Effortless Scanning with Omnidirectional Functionality
Aztec barcodes possess the capability to be scanned from any direction or orientation, showcasing their exceptional versatility.
Aztech Barcode vs QR Code: How Are They Different?
While Aztec codes and QR Codes may seem alike at first glance, their designs and functionalities are notably distinct. Each barcode type serves a distinct purpose. Let’s find out how.
1. Design and Appearance
Upon a closer look, it becomes apparent that Aztec codes and QR Codes possess different design and visual characteristics. Aztec codes have concentric squares, whereas QR Codes utilize a square grid pattern consisting of black-and-white squares.
2. Data Capacity and Physical Dimensions
In terms of data capacity, QR Codes surpass Aztec codes. QR Codes can accommodate up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric characters, whereas Aztec codes can store a maximum of 3,832 numerical or 3,067 alphanumeric characters. However, this higher data storage capability also results in QR Codes being physically larger compared to Aztec codes.
3. Error Correction
QR Codes exhibit superior error correction capabilities compared to Aztec codes, making them more robust in real-world situations. QR Codes employ the Reed-Solomon error correction algorithm, enabling data recovery even when up to 30% of the code is damaged or obscured.
Aztec codes utilize a less complex error correction method.
4. Scanning Equipment
QR Codes are compatible with any device equipped with a camera and a QR Code scanning application. In contrast, Aztec codes require specialized equipment like laser scanners or a dedicated Aztec barcode reader to ensure accurate scanning and decoding of the pattern.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Aztec code barcode emerges as a potent 2D barcode system gaining traction across numerous industries globally. Its notable attributes, including high data storage capacity, scalability, error correction capabilities, and compact design, position it as one of the most efficient barcode solutions available.
From marketing campaigns and event management to healthcare operations and transportation logistics, the Aztec code serves as a dependable means of securely encoding diverse information.
We hope that Qodenext article has provided a comprehensive overview of Aztec barcodes, including their types and various applications.
FAQ: An Introduction To Aztec Barcode
1.What is the main advantage of Aztec barcodes over traditional barcodes?
Aztec barcodes provide higher data density and can store a larger amount of information in a smaller space compared to traditional linear barcodes, making them ideal for compact packaging and space-limited applications.
2.Are Aztec barcodes readable by smartphone cameras?
Yes, most modern smartphones with camera apps or dedicated barcode scanning apps can read Aztec barcodes, making them convenient for consumer use and practical for many industries.
3.What industries commonly use Aztec barcodes?
Aztec barcodes are widely used in transportation (such as airline ticketing), healthcare (for patient identification and medication labeling), logistics, retail inventory management, and vehicle registration.
4.How do Aztec barcodes handle damage or wear?
Aztec barcodes include error correction features that allow them to be read accurately even if partially damaged or obscured, though their error correction capability is generally less robust than QR codes.
5.Can Aztec barcodes store both text and binary data?
Yes, Aztec codes are versatile and capable of encoding numeric, alphanumeric, and binary data, allowing for a wide range of applications and data types.
6.How do Aztec codes differ visually from QR codes?
Aztec codes feature a bull’s-eye pattern at the center with concentric square rings, while QR codes consist of three large squares at the corners and a pattern of smaller squares filling the grid.
7.What is the ‘quiet zone’ in barcode scanning and why is it not needed in Aztec codes?
The quiet zone is a blank margin around a barcode that helps scanners distinguish it from other elements. Aztec codes do not require a quiet zone because their distinctive central finder pattern helps scanners identify and orient the code precisely.
8.What are Compact Aztec codes best suited for?
Compact Aztec codes are ideal for applications requiring small barcode sizes with moderate data capacity, such as ID cards, small product labels, or tickets where space conservation is important.






